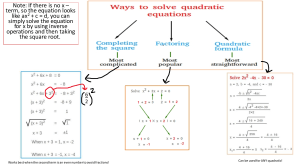
1 Arjuna JEE 2.0 (2023) Quadratic Equation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. If α and β are the roots of the equation, 7x2 – 3x – 2 = 0, then the value of is + 2 1− 1 − 2 equal to (1) 3/8 (2) 1/24 (3) 27/16 (4) 27/32 If the roots of the equation x2 – 8x + (a2 – 6a) = 0 are real, then (1) –2 < a < 8 (2) 2 < a < 8 (3) –2 a 8 (4) 2 a 8 The number of integral values of m for which the equation (1 + m2) x2 – 2(1 + 3m)x + (1 + 8m) = 0 has no real roots is : (1) 2 (2) Infinitely many (3) 1 (4) 3 8. Find p and q such that px2 + 5x + 2 = 0 and 3x2 + 10x + q = 0 have both roots in common. 9. If the quadratic equations x2 + ax + b = 0 and x2 + bx + a = 0 (a 0) have a common root, then the numerical value of (a + b) is (1) 0 (2) 1 (3) −1 (4) 2 10. Find the value of m for which the quadratic equations x2 – 11x + m = 0 and x2 – 14x + 2m = 0 may have common root. 11. If the equations x2 + 2x + 3 = 0 and ax2 + bx + c = 0, a, b, c R, have a common root, then a : b : c is: (1) 1 : 2 : 3 (2) 3 : 2 : 1 (3) 1 : 3 : 2 (4) 3 : 1 : 2 12. If both the root of k (6x2 + 3) + rx + 2x2 – 1 = 0 and 6k (2x2 + 1) + px + 4x2 – 2 = 0 are common, then 2r – p is equal to (1) –1 (2) 0 (3) 1 (4) 2 13. If the equation x2 + px + q = 0 and x2 + qx + p = 0, have a common root, then p + q + 1 = (1) 0 (2) 1 (3) 2 (4) –1 14. If the roots of the equation 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0 are reciprocals of the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + 2 = 0, then (1) a = 2 and b = 3 (2) a = 2 and b = –3 (3) a = 5 and b = –3 (4) a = 5 and b = 3 15. If the quadratic equation 3x2 + ax + 1 = 0 and 2x2 + bx + 1 = 0, have a common real root, then the value of the expression 5ab – 2a2 – 3b2 is (1) 0 (2) 1 (3) –1 (4) none of these If the equation (k2 – 3k + 2)x2 + (k2 – 5k + 4)x + (k2 – 6k + 5) = 0 is an identity then the value of k is (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 4 If a + b + c = 0 and a, b, c are rational, then the roots of the equation (b + c – a)x2 + (c + a – b)x + (a + b – c) = 0 are (1) Rational (2) Irrational (3) Imaginary (4) Equal The quadratic equation whose roots are reciprocal of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is (1) cx2 + bx + a = 0 (2) bx2 + cx + a = 0 (3) cx2 + ax + b = 0 (4) bx2 + ax + c = 0 2 2 If the equations ax + bx + c = 0 and x + x + 1 = 0 has one common root then a : b : c is equal to (1) 1 : 1 : 1 (2) 1 : 2 : 3 (3) 2 : 3 : 1 (4) 3 : 2 : 1 DPP-03 2 Note: Kindly find the Video Solution of DPPs Questions in the Quiz Section. Answer Key 1. (3) 9. (3) 2. (3) 10. (24 or 0) 3. (2) 11. (1) 4. (1) 12. (2) 5. (1) 13. (1) 6. (1) 14. (3) 7. (1) 15. (2) 8. (p= 3 ,q = 4 ) 2 For more questions, kindly visit the library section: Link for app: https://links.physicswallah.live/vyJw For more questions, kindly visit the library section: Link for web: https://physicswallah.live/tabs/tabs/library-tab PW Mobile APP: https://physicswala.page.link/?type=contact-us&data=open For PW Website: https://www.physicswallah.live/contact-us