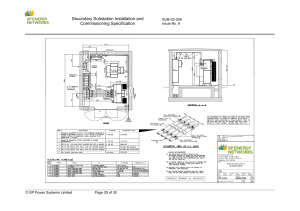
Power Substation Report Date: [Date of the report] Prepared by: [Your Name or Team Name] 1. Introduction Purpose of the report Overview of the power substation 2. Executive Summary Summary of key findings Highlights of significant issues or improvements 3. Substation Overview Location and capacity of the substation Configuration and layout 4. Equipment and Components Description of major equipment (transformers, switchgear, etc.) Condition assessment Maintenance history 5. Operational Performance Performance metrics (voltage levels, load characteristics, etc.) Analysis of recent performance trends 6. Reliability and Maintenance Reliability metrics (MTBF, MTTR, etc.) Maintenance practices and schedules 7. Safety and Environmental Considerations Safety protocols and incidents Environmental compliance 8. Challenges and Issues Current challenges and issues faced Impact on operations or reliability 9. Recommendations Proposed improvements or upgrades Mitigation strategies for identified issues 10. Conclusion Summary of the overall condition and performance Future outlook 11. Appendix Supporting documentation (diagrams, test reports, etc.) Notes: Ensure the report is concise yet comprehensive, focusing on key aspects relevant to the substation's operation and management. Use clear headings and subheadings to enhance readability. Tailor the sections based on specific requirements or additional details relevant to your particular substation. Introduction to Ethiopian Electric Power Substation in Bahir Dar The Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP) substation in Bahir Dar serves as a critical node in the region's electricity infrastructure, facilitating the transmission and distribution of electrical power to Bahir Dar city and its surrounding areas in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia. This introduction provides an overview of the substation's role, significance, and impact on the local community and economy. Key Points to Include: 1. Location and Context: Situated strategically within or near Bahir Dar, the EEP substation forms part of a broader network designed to ensure reliable and efficient electricity supply across the region. Its location plays a pivotal role in supporting urban and rural electrification efforts. 2. Infrastructure and Capacity: Equipped with transformers, switchgear, and other critical components, the substation steps down high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to levels suitable for local distribution. This infrastructure is essential for managing and balancing electricity demand and supply. 3. Operational Significance: The substation not only enhances the reliability of electricity supply but also supports economic activities by powering industries, businesses, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and residential areas in Bahir Dar and neighboring communities. 4. Challenges and Opportunities: Despite its crucial role, the substation may face challenges such as aging infrastructure, capacity constraints, and technical issues. However, these challenges present opportunities for EEP to invest in modernization, maintenance, and expansion initiatives to meet growing energy demands sustainably. 5. Community Impact: Beyond its technical function, the substation impacts the local community by contributing to socio-economic development through enhanced access to electricity, which is fundamental for improving living standards, promoting economic growth, and supporting infrastructure development. 6. Future Outlook: Looking ahead, the substation's future may involve upgrades, integration of renewable energy sources, and adoption of advanced technologies to improve efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability. These initiatives align with EEP's commitment to advancing Ethiopia's energy sector and meeting national development goals. The purpose of a report on the Ethiopian Electric Power substation in Bahir Dar is multifaceted and generally aims to provide a comprehensive overview and analysis of various aspects related to the substation's operations, management, and impact. Here are the primary purposes such a report might serve: 1. Performance Evaluation: Assessing the operational performance of the substation, including reliability metrics, efficiency of electricity distribution, and adherence to safety standards. 2. Infrastructure Assessment: Evaluating the condition of the substation's infrastructure, including transformers, switchgear, and other equipment, to identify maintenance needs, potential upgrades, or replacement requirements. 3. Capacity and Demand Analysis: Analyzing the substation's capacity to meet current and projected electricity demand in Bahir Dar and nearby areas, considering factors like peak load periods and future growth projections. 4. Financial and Economic Impact: Examining the economic impact of the substation on local communities and businesses, including its role in supporting industrial activities, job creation, and overall economic development. 5. Environmental Considerations: Assessing the substation's environmental footprint, including energy efficiency measures, emissions management, and potential impacts on the surrounding ecosystem. 6. Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with the substation's operations, such as technical failures, cybersecurity threats, or natural disasters, and proposing mitigation strategies. 7. Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with national and international regulations and standards governing electricity infrastructure, safety protocols, and environmental sustainability. 8. Strategic Planning: Providing insights and recommendations for strategic investments, upgrades, or expansions to enhance the substation's reliability, efficiency, and capacity to meet future energy needs. 9. Stakeholder Communication: Serving as a communication tool for stakeholders, including government entities, local communities, investors, and the public, to increase awareness and transparency regarding the substation's role and impact. #Overview An overview of a power substation typically includes several key aspects that outline its purpose, components, and operational functions within the broader electricity infrastructure. Here's a structured overview: 1. Purpose and Role: A power substation acts as a crucial link between electricity generation and distribution systems. It steps down high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for local distribution. Substations also provide switching, protection, and control functions to ensure safe and reliable electricity supply to consumers. 2. Components: Transformers: Step up or step down voltage levels as needed for transmission or distribution. Switchgear: Controls the flow of electricity, enabling isolation of faulty equipment and maintenance without disrupting service. Busbars and Conductors: Carry electricity within the substation and connect to transmission lines or distribution networks. Protection Equipment: Includes relays, circuit breakers, and fuses to safeguard equipment and manage faults. 3. Layout and Configuration: Substations are typically organized into high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) sections. HV side connects to transmission lines, while LV side distributes electricity to consumers. Layouts vary based on substation size, voltage levels, and specific operational requirements. 4. Operational Functions: Voltage Regulation: Maintains stable voltage levels suitable for consumer use. Load Management: Balances electricity demand and supply to prevent overloads and blackouts. Monitoring and Control: Uses SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems to monitor equipment performance and manage operations remotely. Maintenance: Regular inspections, testing, and maintenance ensure equipment reliability and longevity. 5. Types of Substations: Distribution Substations: Serve local areas, distributing electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers. Transmission Substations: Connect different transmission lines and convert voltages for longdistance electricity transport. Step-up and Step-down Substations: Adjust voltage levels between generation, transmission, and distribution stages. 6. Safety and Environmental Considerations: Safety protocols ensure protection for personnel and equipment from electrical hazards. Environmental measures manage noise, emissions, and visual impacts to minimize ecological footprint. 7. Technological Advances and Future Trends: Integration of smart grid technologies for real-time monitoring, demand response, and energy efficiency. Adoption of renewable energy sources and energy storage solutions to enhance sustainability and grid resilience. #Mission The mission of Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP) is to effectively manage and develop Ethiopia's electric power resources to ensure reliable, affordable, and sustainable electricity supply across the country. Key components of EEP's mission include: 1. Power Generation: EEP aims to develop and operate diverse sources of power generation, including hydroelectric, thermal, wind, and potentially other renewable energy sources. This includes expanding capacity through new projects and optimizing existing facilities. 2. Transmission and Distribution: EEP is responsible for maintaining and expanding the transmission and distribution network to efficiently deliver electricity from generation plants to consumers nationwide. This involves ensuring grid reliability, reducing transmission losses, and improving accessibility in both urban and rural areas. 3. Sustainability and Efficiency: EEP focuses on promoting sustainable practices in power generation and distribution, including the integration of renewable energy sources to reduce environmental impact. Enhancing energy efficiency and promoting energy conservation are also priorities. 4. Economic Development: By providing reliable electricity supply, EEP supports economic growth and development in Ethiopia. This includes fostering industrialization, supporting commercial activities, and improving living standards through increased access to electricity. 5. Operational Excellence: EEP strives for operational excellence through effective management practices, including rigorous maintenance of infrastructure, implementation of modern technologies, and adherence to international standards of safety and reliability. 6. Community Engagement: EEP aims to engage with local communities and stakeholders to ensure transparency, promote public awareness about energy issues, and address socioeconomic impacts related to electricity access and development. Vision of Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP): "To be a leading regional and global player in the sustainable generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity, powering Ethiopia's socio-economic development and enhancing the quality of life for its people." Key elements of EEP's vision may include: 1. Leadership in Energy Sector: EEP aims to establish itself as a prominent entity in the regional energy sector, leveraging Ethiopia's abundant renewable energy resources, such as hydroelectric power, for sustainable development. 2. Sustainable Electricity Generation: EEP seeks to lead in the development and operation of environmentally sustainable power generation projects, including hydroelectric, wind, solar, and potentially other renewable energy sources. 3. Reliable Transmission and Distribution: EEP envisions a robust and efficient transmission and distribution network that ensures reliable and affordable electricity supply across Ethiopia, supporting industrial growth, urbanization, and rural development. 4. Innovation and Technology: EEP aims to adopt cutting-edge technologies and best practices in power generation, transmission, and distribution to enhance operational efficiency, reduce losses, and improve service delivery. 5. Community and Stakeholder Engagement: EEP is committed to engaging with communities, stakeholders, and international partners to foster transparency, accountability, and sustainable development in the energy sector. 6. National Development: EEP's vision aligns with Ethiopia's broader development goals, contributing to economic growth, job creation, and improved living standards through increased access to reliable electricity. Background on Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP): 1. Overview: EEP plays a crucial role in Ethiopia's energy sector, overseeing the development and management of electric power resources nationwide. It operates under the Ministry of Water, Irrigation, and Energy. 2. Generation Capacity: EEP manages various hydroelectric, thermal, and wind power generation projects throughout the country. Hydroelectric power, particularly from dams like the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) on the Blue Nile, constitutes a significant portion of Ethiopia's electricity production. 3. Transmission and Distribution: EEP maintains an extensive transmission network to transport electricity from power generation facilities to distribution centers and consumers across Ethiopia. This network is critical for ensuring reliable electricity supply to urban centers like Bahir Dar and rural communities alike. 4. Projects and Initiatives: EEP is involved in ongoing projects to expand Ethiopia's power generation capacity and improve infrastructure resilience. This includes efforts to harness renewable energy sources and enhance transmission efficiency. Bahir Dar: 1. Location and Significance: Bahir Dar is situated on the southern shore of Lake Tana, near the Blue Nile River. It serves as the capital of the Amhara Region and is a key economic and cultural hub in northern Ethiopia. 2. Electricity Supply: Bahir Dar benefits from EEP's transmission and distribution network, receiving electricity from various sources including nearby hydroelectric power plants. The reliability and availability of electricity are crucial for the city's industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. 3. Development and Growth: Like other urban areas in Ethiopia, Bahir Dar has seen significant development in recent years, driven in part by improved access to electricity. Reliable power supply supports economic growth, infrastructure development, and improves living standards for residents. #Problems Identifying potential problems or challenges related to the Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP) substation in Bahir Dar could include several factors: 1. Infrastructure Aging: Substations require ongoing maintenance and occasional upgrades to ensure reliability. Aging infrastructure may lead to increased maintenance costs and potential reliability issues. 2. Capacity Constraints: As demand for electricity grows in Bahir Dar and surrounding areas, the substation may face challenges in meeting peak demand periods without sufficient capacity upgrades. 3. Technical Failures: Electrical equipment within the substation, such as transformers or switchgear, could experience technical failures due to various factors like overloading, weather conditions, or aging components. 4. Operational Efficiency: Ensuring the efficient operation of the substation, including monitoring systems, minimizing transmission losses, and optimizing voltage regulation, is crucial for effective electricity distribution. 5. Safety Concerns: Substations are high-voltage environments, and safety protocols must be strictly followed to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of workers and the public. 6. Environmental Impact: While EEP strives to use renewable energy sources, the environmental impact of electricity generation and distribution, including potential issues related to emissions or land use, is a consideration. 7. Community Relations: Engaging with the local community and addressing concerns related to land use, visual impact, or noise from the substation can be important for maintaining positive relationships.