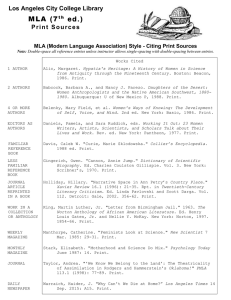
1. summary - think something big slow it down 2. Paraphrase - take the summary small and change the words but still with the same meaning. - Paraphrasing is simply the re-wording of an author's ideas into our own word - Steps: 1. Read the source. 2. Re-read actively, highlighting or underlining main points, circling key words, or making notes. 3. Put away your source and your notes! 4. Write down what you remember. Without the original in front of you you will be more likely to use your own words. 5. Double-check against the original for accuracy and to ensure you haven't borrowed any wording. 6. Cite your source! Even paraphrases need to be cited to avoid plagiarism. 3. Quotation - copy paste of the actual word - person's exact words not the ideas behind them. - this is the only last resort In citing: a. Not quotation: author and date b. Quotation: author, date and page or par. No. Resources WHO The first part of the reference citation is the who, or the author. The author could be an organization, or it could be an individual, or a group of people. When writing people’s names in your reference, you will provide the authors last name and initials. For organizations, include the full name of the organization. WHEN The second part to include is the date when the source was written or created. Usually, it is enough to just provide the year of publication. If your source is something like a newspaper, which provides a more specific date, you can also include the month and the day. WHAT The third part of the citation covers what the source is called, or in other words, the source's title. If you’re working with an item such as a book which has an edition, you can include this information as well. WHERE The last part of the reference citation gives information for where the item is published. This is the section of the reference where you will find the most variety, depending on whether the source you are using is a physical item such as a book or DVD, or if the source is located online, such as with an online journal article or streaming video. If you have a physical item, you will provide the name of the publishing company. If you have an online item such as a website, you will provide the name of the website and a URL (web address). You might also find that scholarly journal articles often have a DOI number. DOI is short for digital object identifier, and this is a special number assigned to some journal articles that is similar to a URL. It can be used to help find the article online. If there is no author In text Narrative style - Include the names of the authors in the sentence - Ex: Patterson and sing (2011) argue that cake is delicious or Patterson and singh (2011) argue that cake “increase the enjoyment of studying for students” (p.71) Parenthetical - In some cases, mentioning the authors in your sentence doesn’t make sense, so that’s why parenthetical citations exist. They look like this: o This support the concept that cake is delicious and good for studying ( Patterson & Singh, 2011) or Cake was found to “ increase the enjoyment of studying for students” ( Patterson & Singh, 2011, p. 71) Essay Components has 2 components: 1. Structure 2. Content Structure - 1-inch margin spacing, a running head, font size and style, paragraph spacing, and page numbers.’’ Close Reading: instructions • select a short section (ie: a key word, phrase, or passage) from the text and note the details that seem significant to your reading or interpretation • choose the literary device that best fits the chosen quotation, examine the textual details of the passage following the instructions below (note that the list below is not exhaustive) • why do you think these details are included in the text? what do they contribute to the content? • consider the implications or effects of these details and connect them to a larger reading or interpretation of the text: why do you think they’re important? • what do they support / contradict / illuminate / explain / demonstrate about the text?