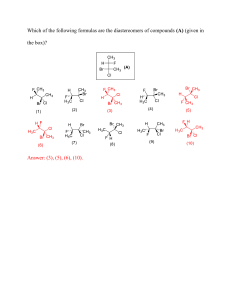
FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL SCIENCES B Eng Tech in Engineering Metallurgy / Extraction Metallurgy MODULE CAMPUS CETM1A1 DFC PAPER 2 DATE: 2022 ASSESSOR Dr. MC FOTSING INTERNAL MODERATOR DR P. F. MSOMI DURATION 180 MINUTES TOTAL MARKS: 100 NUMBER OF PAGES: 9 PAGES, INCLUDING 4 ANNEXURES INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER SECTION A ON THE MULTIPLE QUESTION ANSWER SECTION AND SECTION B IN THE PROVIDED ANSWER SCRIPT. CONSULT THE DATA SHEET AND THE PERIODIC TABLE FOR ALL SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. CALCULATORS ARE PERMITTED (ONLY ONE PER STUDENT). 2/… CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 A separation process that depends on differing abilities of substances to form gases is called __________. A) filtration B) solvation C) distillation D) chromatography E) all the above are correct 1.2 Elements in Group 6A are known as the __________. A) alkali metals B) chalcogens C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 1.3 The ground-state electron configuration of the element __________ is [Kr]5s14d5. A) Nb B) Mo C) Cr D) Mn E) Tc 1.4 In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first ionization energy __________. A) decreases, decreasingly, increases B) increases, increasingly, decreases C) increases, increasingly, increases D) decreases, increasingly, increases E) decreases, increasingly, decreases 3/… 2 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 1.5 The Lewis structure of AsH3 shows __________ nonbonding electron pair(s) on As. A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) This cannot be determined from the data given. 1.6 The total number of π bonds in the H–C≡C–C≡C–C≡N molecule is __________. A) 3 B) 4 C) 6 D) 9 E) 12 1.7 According to VSEPR theory, if there are three electron domains on a central atom, they will be arranged such that the angles between the domains are __________. A) 90° B) 180° C) 109.5° D) 360° E) 120° 1.8 The combustion of ammonia in the presence of excess oxygen yields NO2 and H2O: 4 NH3 (g) + 7 O2 (g) → 4 NO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) The combustion of 43.9 g of ammonia produces __________ g of NO2. A) 2.58 B) 178 C) 119 D) 0.954 E) 43.9 4/… 3 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 1.9 Calcium carbide (CaC2) reacts with water to produce acetylene (C2H2): CaC2 (s) + 2H2O (g) → Ca(OH)2 (s) + C2H2 (g) Production of 13g of C2H2 requires consumption of __________ g of H2O. A) 4.5 B) 9.0 C) 18 D) 4.8 × 102 E) 4.8 × 10-2 1.10 The formula weight of silver chromate (Ag2CrO4) is __________ amu. A) 159.87 B) 223.87 C) 331.73 D) 339.86 E) 175.87 1.11 Combining aqueous solutions of BaI2 and Na2SO4 affords a precipitate of BaSO4. Which ion(s) is/are spectator ions in the reaction? A) Ba2+ only B) Na+ only C) Ba2+ and SO42D) Na+ and I E) SO42- and I- 1.12 When aqueous solutions of AgNO3 and KI are mixed, AgI precipitates. The balanced net ionic equation is __________. A) Ag+ (aq) + I- (aq) → AgI (s) B) Ag+ (aq) + NO3 - (aq) → AgNO3 (s) C) Ag+ (aq) + NO3 - (aq) → AgNO3 (aq) D) AgNO3 (aq) + KI (aq) → AgI (s) + KNO3 (aq) E) AgNO3 (aq) + KI (aq) → AgI (s) + KNO3 (s) 5/… 4 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 1.13 The molarity of a solution prepared by diluting 43.72 mL of 1.005 M aqueous K2Cr2O7 to 500 mL is __________. A) 0.0879 B) 87.9 C) 0.0218 D) 0.0115 E) 0.870 1.14 A 31.5 mL aliquot of HNO3 (aq) of unknown concentration was titrated with 0.0134 M NaOH (aq). It took 23.9 mL of the base to reach the endpoint of the titration. The concentration (M) of the acid was __________. A) 0.0102 B) 0.0051 C) 0.0204 D) 0.227 E) 1.02 1.15 Identify the reducing agent in the following reaction? 14H+ + Cr2O72- + 3Ni → 3Ni2+ + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O A) Ni B) H+ C) Cr2O72D) H2O E) Ni2+ 1.16 What is the coefficient of Fe3+ when the following equation is balanced? CN- + Fe3+ → CNO- + Fe2+ (basic solution) A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 1.17 On a phase diagram, the critical pressure is __________. A) the pressure required to melt a solid B) the pressure below which a substance is a solid at all temperatures C) the pressure above which a substance is a liquid at all temperatures D) the pressure at which a liquid change to a gas E) the pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature 6/… 5 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 1.18 The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g) is Keq = 4.34 × 10-3 at 300 °C. At equilibrium, __________. A) products predominate B) reactants predominate C) roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present D) only products are present E) only reactants are present 1.19 The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.25: SO2 (g) + NO2 (g) SO3 (g) + NO (g) The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is __________. 2SO2 (g) + 2NO2 (g) 2SO3 (g) + 2NO (g) A) 0.50 B) 0.062 C) 0.12 D) 0.25 E) 16 1.20 Which of the following is an exothermic process? A) ice melting B) water evaporating C) boiling soup D) condensation of water vapor E) Ammonium thiocyanate and barium hydroxide are mixed at 25°C: the temperature drops. [20 x 2= 40] 7/… 6 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 SECTION B QUESTION 2 2.1 Identify the specific element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations and indicate the number of unpaired electrons for each 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 1s22s2 1s22s22p4 [Ar]4s13d5 (2) (2) (2) 2.2 Use Lewis symbols to represent the reaction that occurs between Ca and F atoms. (2) 2.3 Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following ions or molecules. Identify those that do not obey the octet rule, and explain why they do not: 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 SO32AlH3 SbF5 (2) (2) (2) [14] QUESTION 3 3.1 Determine the empirical formulas of the compounds with the following composition by mass: 3.1.1 3.1.2 10.4 % C, 27.8 % S, and 61.7 % Cl 21.7 % C, 9.6 % O, and 68.7 % F 3.2 Hydrofluoric acid, HF (aq), cannot be stored in glass bottles because compounds called silicates in the glass are attacked by the HF (aq). Sodium silicate (Na2SiO3), for example reacts as follows: Na2SiO3(s) + 8 HF(aq) 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 (3) (3) H2SiF6(aq) + 2 NaF(aq) + 3 H2O(l) How many moles of HF are needed to react with 0.300 mol of Na2SiO3? (2) How many grams of NaF form when 0.500 mol of HF reacts with excess Na2SiO3? (2) How many grams of Na2SiO3 can react with 0.800 g of HF? (2) [12] 8/… 7 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 QUESTION 4 4.1 Will precipitation occur when the following solutions are mixed? If so, write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 4.1.1 4.1.2 Na2CO3 and AgNO3 NaNO3 and NiSO4 4.2 Referring to figure 1 below, describe the phase changes and the temperatures at which they occur when CO2 is heated from – 80 oC to – 20 oC at 4.2.1 A constant pressure of 3 atm. (4) 4.2.2 A constant pressure of 6 atm. (4) (4) (4) Figure 1: Phase diagram of CO2. Note that a linear scale is used to represent temperature and a logarithmic scale to represent pressure. [16] 9/… 8 CETM1A1_Examination_Paper 2_2022 QUESTION 5 5.1 At 1000 K, Kp = 1.85 for the reaction SO3(g) SO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) 5.1.1 What is the value of Kp for the reaction below? SO3(g) 5.1.2 (4) SO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) What is the value of Kp for the reaction below? (4) 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) 5.1.3 What is the value of Kc for the reaction in question 5.1.2? 5.2 The following is known as the thermite reaction: 2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) 5.2.1 (5) Al2O3(s) + 2 Fe(s) This highly exothermic reaction is used for welding massive units, such as propellers for large ships. Using standard enthalpies of formation in Appendix C, calculate Ho for this reaction. (5) [18] FULL MARKS:100 TOTAL MARKS: 100 9 DATA INFORMATION x= − b b 2 − 4ac 2a Avogadro’s number: N = 6.02 x1023 0oC = 273.15 K Standard pressure = 1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 1.01325 bar R = 8.31451 L.kPa.K–1.mol–1 = 8.31451 x10–2 L.bar.K–1.mol–1 = 8.20578 x10–2 L.atm.K–1.mol–1 = 62.364 L.torr.K–1.mol–1 Equilibrium constants (Temperature = 25.0oC) Kw = 1 10–14 Table 1: Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K(25 oC) Substance Aluminium Al(s) AlCl3(s) Al2O3(s) f Gf (kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) S (J/mol.K) 0 - 705.6 - 1669.8 0 - 630.0 - 1576.5 28.32 109.3 51.00 Iron Fe(g) Fe(s) Fe2+(aq) Fe3+(aq) FeCl2(s) FeCl3(s) FeO(s) Fe2O3(s) Fe3O4(s) FeS2(s) 415.5 0 - 87.86 -47.69 -341.8 -400 -271.9 -822.16 -1117.1 -171.5 369.8 0 -84.93 -10.54 -302.3 -334 -255.2 -740.98 -1014.2 -160.1 180.5 27.15 113.4 293.3 117.9 142.3 60.75 89.96 146.4 52.92 Oxygen O(g) O2(g) O3(g) OH-(aq) H2O(g) H2O(l) H2O2(g) H2O2(l) 247.5 0 142.3 -230.0 -241.82 -285.83 -136.10 -187.8 230.1 0 163.4 -157.3 -228.57 -237.13 -105.48 -120.4 161.0 205.0 237.6 10.7 188.83 69.91 232.9 109.6 Table 2: Solubility Guidelines for Common Ionic Compounds in Water Soluble Ionic Compounds Compounds containing NO3CH3COOClBrISO42- Insoluble Ionic Compounds Compounds containing S2CO32PO43OH- Important Exceptions None None Compounds of Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Compounds of Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Compounds of Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Compounds of Sr2+, Ba2+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Important Exceptions Compounds of NH4+, the alkali metal cations, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ Compounds of NH4+ and the alkali metal cations Compounds of NH4+ and the alkali metal cations Compounds of NH4+, the alkali metal cations, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ UNIVERSITY OF JOHANNESBURG Department of Chemical Sciences 1 2 H Atomic Number He 1.0079 3 4 Li 4.0026 4.0026 5 Atomic Weight Na K Ca 39.098 37 Rb 39 56 Cs 57 88 Fr (223) 72 73 74 75 76 O F 14.007 15.999 18.998 14 77 190.2 47 15 78 P S 30.974 32.064 Pt 192.22 195.08 Cd 107.87 In 81 Hg 196.97 Sn 82 Tl 200.59 I 85 Po 207.2 208.98 (209) 226.03 68 69 70 71 (210) Ac 227.03 58 59 Ce Pr 140.12 90 60 Th 232.04 Nd 140.91 91 61 Pa 231.04 Pm 144.24 92 62 U 238.03 Sm 146.92 93 63 Np 237.05 Eu 150.36 94 64 Pu (244) Gd 151.97 95 65 Am (234) Tb 157.25 96 66 Cm (247) Dy 158.93 97 67 98 Bk 247 Ho 162.50 99 Cf (251) Er 164.93 100 Es (252) Tm 167.26 101 Fm (257) Yb 168.93 102 Md (258) Lu 173.04 174.97 103 No (259) 131.29 86 At 204.38 Xe 126.90 89 Ra 83.80 54 127.60 84 Bi Kr 79.904 Te 83 Pb Br 53 121.75 39.948 36 78.96 Sb Ar 35.453 Se 52 118.71 20.179 18 35 74.922 51 114.82 80 As Ne Cl 34 72.61 50 112.41 Au 33 Ge 49 17 28.086 69.723 48 79 Ir Ga 16 Si 32 65.39 Ag 106.42 31 Zn 63.546 Pd 102.91 Os 186.2 46 30 Cu 58.69 Rh 101.07 Re 183.85 45 29 Ni 58.933 Ru (98) W 180.95 44 28 Co 55.847 Tc 95.94 Ta 178.49 43 27 Fe 54.938 Mo 92.906 Hf 138.91 42 26 Mn 51.996 Nb 91.224 La 137.33 41 25 Cr 50.942 Zr 88.906 Ba 132.91 40 24 V 47.88 Y 87.62 23 Ti 44.956 Sr 85.47 87 Sc 40.078 38 55 N 26.982 22 10 12.011 Al 21 9 C 24.305 20 8 10.811 13 Mg 22.990 7 B 9.0122 12 19 6 Be 6.941 11 He 2 Lr (260) Rn (222)