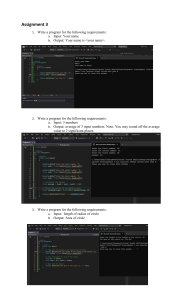
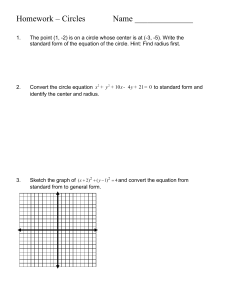
17-11-2022 What to expected in class GEOMETRICAL DRAWING • Go through your topics notes before you come to your class • NOTES • Each one of you should post class notes immediately after the google classroom • CLASS RECORDINGS • Do your assignments honestly and post on time • WORKED OUT EXAMPLES • Assignments at least 1 per each topic • ASSIGNEMENTS • EXAMINATIONS / TEST PAPERS INTRODUCTION 1 • GOOGLE CLASSROOM 4 Architectural Learning University Examinations • What is Architecture • 4 Hour Exam • CORRECTNESS • ANNOTATION • How do you learn Designing • DIMENSIONS • NOTES • 8 short note question (5 marks each) • • • • • Information • Knowledge All compulsory 2 questions each from each module 8 x 5 = 40 marks Expects sketches where necessary • CLARITY • LINE WEIGHT • NEATNESS • Wisdom • 8 Drawings • 2 each from each module. You have to answer one out of these two • 4 x 15 = 60 marks 2 5 SYLLABUS Drawing requirement 2014 Syllabus • Sample Scale Conics Spirals Helix • MODULE 2 • Points & Lines • Planes • Solids • MODULE 3 • Intersection of solids • Sections of solids • Development of surfaces • MODULE 4 • Isometric drawing • Perspective drawing 3 • • • • • • CORRECTNESS • Draw projections of line ‘AB’, where point ‘A’ is ‘da’ units in front of Vertical Plane (VP) and ‘ha’ units above Horizontal Plane (HP); while point ‘B’ is ‘db’ units in front of Vertical Plane (VP) and ‘hb’ units above Horizontal Plane. • Question No : 1 • Note: in this case, ‘da’ = ‘db’ Triangles, quadrilaterals, trapezoids, regular polygons. Tangent, curves. Conic sections, spirals, helix, Involutes, cycloids trochoids, Plain scale, diagonal scale b’ • MODULE 2 a’ • Projection of solids, sections of solid prisms, pyramids, cylinders cones, spheres • Development of surfaces of solids • Intersection of surfaces θ • ANNOTATION • DIMENSIONS • NOTES • CLARITY • LINE WEIGHT • NEATNESS VP ha • • • • 2021 Syllabus • MODULE 1 • MODULE 3 x • Isometric, axonometric and Oblique views • Perspective, one-point, two-point, and 3 point y da (db) • MODULE 1 • MODULE 4 • Sciography, Shadow of lines, planes, and simple solids due to near and distant sources. • Application of sciography on pictorial view a b HP projection of line 6 1 17-11-2022 Perpendicular Bisector Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Line bisector • Given a line segment AB ; Construct the line bisector. A perpendicular bisector can be defined as a line segment which intersects another line perpendicularly and divides it into two equal parts. • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB . 01 A B Basic geometric constructions 7 10 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Line bisector • Line bisector • Given a line segment AB ; Construct the line bisector. A • Given a line segment AB ; Construct the line bisector. B A 8 O B 11 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Line bisector • Line bisector • Given a line segment AB ; Construct the line bisector. • Given a line segment AB ; Construct the line bisector. • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB A 9 • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB • Join the arc intersection with a line • The line intersect the segment AB at O B A O 90 o B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB • Join the arc intersection with a line • The line intersect the segment AB at O • The line insect 90th with AB and hence it is a perpendicular bisector of AB 12 2 17-11-2022 Perpendicular to a given line at a given point on it Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular through a given point O on a line. • • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B 02 A B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB Basic geometric constructions 13 16 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular through a given point O on a line. • Construct a perpendicular through a given point O on a line. • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B O A 14 B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB 17 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular through a given point O on a line. • Construct a perpendicular through a given point O on a line. • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B A O • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B B A O 90 o B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB • Join the arc intersection with a line which will passing through the point O and will be perpendicular to Line AB 15 18 3 17-11-2022 Perpendicular to a given line from a given point outside of it Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular to a line and passing through a given point O outside of the line. • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B O 03 A B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB Basic geometric constructions 19 22 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular to a line and passing through a given point O outside of the line. • Construct a perpendicular to a line and passing through a given point O outside of the line. • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B O O A 20 B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB 23 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Perpendicular to a Line • Perpendicular to a Line • Construct a perpendicular to a line and passing through a given point O outside of the line. • Construct a perpendicular to a line and passing through a given point O outside of the line. • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B • Draw a circle with center O which intersects the line at two points A &B O A O B A 90 o B • Draw two arcs with center A and B; and with same radius bigger than half the length of AB • Join the arc intersection with a line which will passing through the point O and will be perpendicular to Line AB 21 24 4 17-11-2022 Angle bisector Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Angle bisector • Given a two lines creating and angle θ ; Construct the line bisecting the angle θ. A • Draw a circle with center O and intersects the lines OA & OB at C & D respectively C E θ/2 θ/2 04 • Draw two arcs with center C and D; and with same radius and intersects at point E θ O B D Basic geometric constructions 25 28 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Angle bisector • Angle bisector • Given a two lines creating and angle θ ; Construct the line bisecting the angle θ. • Given a two lines creating and angle θ ; Construct the line bisecting the angle θ. A A • Draw a circle with center O and intersects the lines OA & OB at C & D respectively C E • Draw two arcs with center C and D; and with same radius and intersects at point E θ O O B 26 B D • Draw the line connecting O and E which will be bisecting the angle θ 29 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Angle bisector • Angle bisector • Given a two lines creating and angle θ ; Construct the line bisecting the angle θ. • Given a two lines creating and angle θ ; Construct the line bisecting the angle θ. A A • Draw a circle with center O and intersects the lines OA & OB at C & D respectively C C θ/2 θ O 27 E θ/2 D O B D B 30 5 17-11-2022 60o & 30o angle Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 60 0 Angle • Construct a line 60 0 with a given line • Draw a circle with center O and with any radius “r” intersecting the lines OB at D C 30o 30o • Draw an arc with center D and with same radius “r” and intersecting circle at C 05 O B D Basic geometric constructions 31 34 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 60 0 Angle • 60 0 Angle • Construct a line 60 0 with a given line • Construct a line 60 0 with a given line A • Draw a circle with center O and with any radius “r” intersecting the lines OB at D C • Draw line OA passing through the points O and C 60o O O B 32 • <AOB = 600 B D 35 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 60 0 Angle • 30 0 Angle • Construct a line 60 0 with a given line • Construct a line 30 0 with a given line A • Draw a circle with center O and with any radius “r” intersecting the lines OB at D • Draw a circle with center O and with any radius “r” intersecting the lines OB at D C E • Draw line OA passing through the points O and C 60o O 33 D O B • ∠ AOB = 600 D B • Furthermore, to create 30o angle, create two more circles of same radius with centers C and D intersecting at point E 36 6 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 30 0 Angle • 45 0 Angle • Construct a line 30 0 with a given line • Construct a line 45 0 with a given line A • Draw a circle with center O and with any radius “r” intersecting the lines OB at D C E • Draw line OA passing through the points O and C 30o O A • ∠ AOB = 600 30o B D B • Furthermore, to create 30o angle, create two more circles of same radius with centers C and D intersecting at point E • Line OE will bisect ∠ A0B 37 40 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Equilateral triangle • 45 0 Angle • Construct a line 30 0 with a given line • Construct a line 45 0 with a given line A • Joining O, C and B will form an equilateral triangle. C • Draw a perpendicular to AB passing through a point O E A O D O 90 o B B 38 41 45o angle Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 45 0 Angle • Construct a line 45 0 with a given line 45o • Draw a perpendicular to AB passing through a point O C 06 A O 90 o • Draw an arc with radius OA and intersecting the perpendicular line at C B Basic geometric constructions 39 42 7 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • 45 0 Angle • Congruent Angles • Construct a line 45 0 with a given line • Draw a perpendicular to AB passing through a point O C A 45o • Draw an arc with center A intersecting the lines AB and AC at D and E respectively • Match the given angle C • Draw an arc with radius OA and intersecting the perpendicular line at C 90 o B O • The line AC will create an angle of 45o with AB P E A θ B D Q 43 46 Congruent Angles Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Congruent Angles θ • Draw an arc with center A intersecting the lines AB and AC at D and E respectively • Draw another angle with same radius with P as center intersecting the line PQ at S • Match the given angle Congruent angles are angles with exactly same measure. C 07 P E A θ B S D Q Basic geometric constructions 44 47 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Congruent Angles • Congruent Angles • Match the given angle • Draw an arc with center A intersecting the lines AB and AC at D and E respectively • Draw another arc with same radius with P as center intersecting the line PQ at S • Draw an arc with center S and radius DE intersect the arc at T • Match the given angle C C P A θ P E A B θ B D Q 45 T S Q 48 8 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Congruent Angles • Points and Lines • Match the given angle C E • Draw an arc with center A intersecting the lines AB and AC at D and E respectively • Draw another arc with same radius with P as center intersecting the line PQ at S • Draw an arc with center S and radius DE intersect the arc at T • Connect the points P and T to construct the matching angle θ P T • Line parallel to a given line through a given point • Draw a line passing through the given point P and intersect the given line (at A) at any angle P θ A θ B S D Q 49 B 52 Line Parallel to a given line Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Line parallel to a given line through a given point • Draw a line passing through the given point P and intersect the given line (at A) at any angle • Draw an arc with A as center and with any radius (r) , and intersecting the lines at points B and C P 08 B A C Basic geometric constructions 50 53 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Line parallel to a given line through a given point • Line parallel to a given line through a given point Q P P • Draw a line passing through the given point P and intersect the given line (at A) at any angle • Draw an arc with A as center and with any radius (r) , and intersecting the lines at points B and C • Draw a circle with the same radius r and with center point P, intersecting the line at Q as indicated in the figure. B C A B 51 54 9 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Line parallel to a given line through a given point Q R P B C • Draw a line passing through the given point P and intersect the given line (at A) at any angle • Draw an arc with A as center and with any radius (r) , and intersecting the lines at points B and C • Draw a circle with the same radius r and with center point P, intersecting the line at Q as indicated in the figure. • Draw and arc with Q as center and with a radius equal to BC, intersecting the circle at R • In fact, we created vertices of two congruent triangles PQR and ABC • Dividing a given line into N equal parts A How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts B A 55 58 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Draw a line passing through the given point P and intersect the given line (at • Line parallel to a given line through a given point A) at any angle • Draw an arc with A as center and with any radius (r) , and intersecting the lines at points B and C Q • Draw a circle with the same radius r and with center point P, intersecting the line at Q as indicated in the figure. R P • Draw and arc with Q as center and with a radius equal to BC, intersecting the circle at R B • In fact, we created vertices of two congruent triangles PQR and ABC • Join the points P and R, the line PR is A parallel to the given line. C 56 • Dividing a given line into N equal parts A How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. B 59 Dividing a line segment into equal parts Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Dividing a given line into N equal parts Basic Proportionality theorem by Thales Any two equiangular triangles, the ratio of any two corresponding sides is always the same. If two triangles are similar to each other then, i) Corresponding angles of both the triangles are equal ii) Corresponding sides of both the triangles are in proportion to each other A 09 How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) B Basic geometric constructions 57 60 10 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A B How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A B D 61 How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Draw two arcs with radius BC and AC and with A and B respectively. • Let D be the intersecting point of the arcs. Connect D with A and B. • [AC=BD & BC=AD] • Divide the line BD into 7 equal parts marking arc of ‘r’ unit radius as indicated. 64 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A B How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Draw two arcs with radius BC and AC and with A and B respectively. • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A B D 62 How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Draw two arcs with radius BC and AC and with A and B respectively. • Let D be the intersecting point of the arcs. Connect D with A and B. • [AC=BD & BC=AD] • Divide the line BD into 7 equal parts marking arc of ‘r’ unit radius as indicated. • Connect the intersection points of arc and lines as indicated 65 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Points and Lines • Points and Lines • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A B How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Draw two arcs with radius BC and AC and with A and B respectively. • Let D be the intersecting point of the arcs. Connect D with A and B. • [AC==BD & BC==AD] • Dividing a given line into N equal parts C A D D 63 66 B How to divide a given line AB into 7 equal parts • Draw a line passing through A and at any angle . Mark an arc with any radius (r) on the line with center A. • Mark six more arcs with same radius ( r) on the line as indicated. (7 equal division of ‘r’ units each) • Connect the intersection of last arc and line with the point B forming line BC as indicated • Draw two arcs with radius BC and AC and with A and B respectively. • Let D be the intersecting point of the arcs. Connect D with A and B. • [AC=BD & BC=AD] • Divide the line BD into 7 equal parts marking arc of ‘r’ unit radius as indicated. • Connect the intersection points of arc and lines as indicated • Essentially Line AB gets divided into 7 11 17-11-2022 Centre of a Circle Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Finding the Center of a given circle • Draw a chord AB connecting any two points B • Construct a perpendicular bisector of chord AB intersecting the circle at C and D C 10 A D Basic geometric constructions 67 70 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle • Finding the Center of a given circle • Finding the Center of a given circle • Draw a chord AB connecting any two points B • Construct a perpendicular bisector of chord AB intersecting the circle at C and D (Diameter) C • Construct a perpendicular bisector of CD with midpoint O A O D 68 71 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Tangents to a Circle • Circle • Finding the Center of a given circle The tangent to a circle is a straight line which touches the circle at a single point. The point where the tangent touches a circle is known as the point of tangency or the point of contact. • Draw a chord AB connecting any two points B 11 A Basic geometric constructions 69 72 12 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle • Constructing tangents to a circle from a given point • Constructing tangents to a circle from a given point • Draw a line connecting O and P • Let O be the center of the circle and P be the given point • Construct a perpendicular bisection of line OP T1 • Mark the midpoint M O O P M P • Draw an arch with Center M and radius OM • March the intersecting points of the arc with the circle as T1 and T2 T2 73 76 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle • Constructing tangents to a circle from a given point • Constructing tangents to a circle from a given point • Draw a line connecting O and P • Let O be the center of the circle and P be the given point • Draw a line connecting O and P • Construct a perpendicular bisection of line OP T1 • Mark the midpoint M O P O M P • Draw an arch with Center M and radius OM • March the intersecting points of the arc with the circle as T1 and T2 T2 74 • Lines connecting Point P with T1 and T2 are tangent to the circle. 77 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Inscribed Circles of Triangles • Circle • Constructing tangents to a circle from a given point Given a triangle, an inscribed circle is the largest circle contained within the triangle. The inscribed circle will touch each of the three sides of the triangle in exactly one point. The center of the circle inscribed in a triangle is the incenter of the triangle, the point where the angle bisectors of the triangle meet. • Draw a line connecting O and P • Construct a perpendicular bisection of line OP • Mark the midpoint M O M 12 P Basic geometric constructions 75 78 13 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle C C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B • Mark the intersection of the bisectors as O • Draw a line perpendicular to AC passing through point O O B B 79 82 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B • Mark the intersection of the bisectors as O • Draw a line perpendicular to AC passing through point O O B B 80 83 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B P C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B • Mark the intersection of the bisectors as O • Mark the intersection of the bisectors as O • Draw a line perpendicular to AC passing through point O O O • Mark the intersecting point of the perpendicular and Line AC as P B 81 B 84 14 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle A • Circle inscribed in a given triangle • Circle circumscribed on a given triangle P C • Construct angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠B • Construct perpendicular bisectors line AB A • Mark the intersection of the bisectors as O C • Draw a line perpendicular to AC passing through point O O • Mark the intersecting point of the perpendicular and Line AC as P • Construct the inscribed circle with center O and radius OP B B 85 88 Circumscribed Circles of Triangles Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle circumscribed on a given triangle Given a triangle, the circumscribed circle is the circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle. The center of the circumscribed circle is the circumcenter of the triangle, the point where the perpendicular bisectors of the sides meet. • Construct perpendicular bisectors line AB • Construct perpendicular bisectors line BC A C • Mark intersecting point of the perpendicular lines as O O 13 B Basic geometric constructions 86 89 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Circle • Circle • Circle circumscribed on a given triangle • Circle circumscribed on a given triangle A • Construct perpendicular bisectors line AB • Construct perpendicular bisectors line BC C • Mark intersecting point of the perpendicular lines as O A C O • Draw the circle with center O and radius OA. The circle will be passing through other vertices ( B and C ) of the triangle as well B 87 B 90 15 17-11-2022 Regular pentagon inscribed in a circle Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center O A 14 • Draw the perpendicular bisector of AF passing through O and mark the point G intersecting the circle. O G Basic geometric constructions 91 • Draw a line passing through the center and mark intersecting point A and F F 94 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Pentagon • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center O • Inscribe a pentagon in a given circle with center O A O • Draw a line passing through the center and mark intersecting point A and F • Draw the perpendicular bisector of AF passing through O and mark the point G intersecting the circle. O H G • Draw the perpendicular bisector of OG and mark midpoint H. F 92 95 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Pentagon • Inscribe a pentagon in a given circle with center O A • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center O • Draw a line passing through the center and mark intersecting point A and F A O • Draw a line passing through the center and mark intersecting point A and F • Draw the perpendicular bisector of AF passing through O and mark the point G intersecting the circle. O H F 93 G • Draw the perpendicular bisector of OG and mark midpoint H. Draw a circle with H as center and HO as radius F 96 16 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Pentagon • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center O A • Draw O a line connecting F and H. • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center • Draw a line passing through the center and mark intersecting point A and F • Draw the perpendicular bisector of AF passing through O and mark the point G intersecting the circle. J O H G • Construct an arc with center F and radius FJ intersecting the given circle at B and E. E J • Draw the perpendicular bisector of OG and mark midpoint H. Draw a circle with H as center and HO as radius 97 B O H • Draw a line connecting F and H. Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J F Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J A G • Construct an arc with center E and radius EA intersecting the given circle at D D F 100 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Pentagon • Draw O a line connecting F and H. • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J A • Draw O a line connecting F and H. • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center • Construct an arc with center F and radius FJ intersecting the given circle at B and E. E J Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J A • Construct an arc with center F and radius FJ intersecting the given circle at B and E. E B J O B O H H G G • Construct an arc with center E and radius EA intersecting the given circle at D • Construct an arc with center B and radius BA intersecting the given circle at C D F C F 98 101 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Pentagon • Draw O a line connecting F and H. • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J A • Draw O a line connecting F and H. • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center • Construct an arc with center F and radius FJ intersecting the given circle at B and E. E J Extend the line to intersect the circle (with center H) at J A • Construct an arc with center F and radius FJ intersecting the given circle at B and E. E B J O B O H H G G • Construct an arc with center E and radius EA intersecting the given circle at D • Construct an arc with center B and radius BA intersecting the given circle at C D F 99 C F • Join points ABCDE to form the regular pentagon 102 17 17-11-2022 Prerequisites – understanding basic geometric Constructions • Pentagon • Inscribe a regular pentagon in a given circle with center O A E J B O H D G C F 103 George Jacob P 104 18