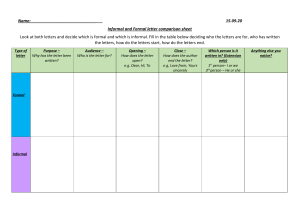
Types of Businesses Businesses can be divided into three main categories: trading, manufacturing, and service. Each type of business plays a unique role in the economy, offering a diverse range of products and services to consumers and other businesses. Trading Businesses Formal Trading Informal Trading Examples Formal trading businesses, also Informal trading businesses can Examples of trading businesses known as retailers, sell products sell from market stalls, home- include CNA, Fruit & Veg City, made by other companies based setups, or other temporary Toys-R-Us, furniture stores, and directly to consumers. They buy goods from suppliers at a certain locations. They follow a similar model of buying and reselling spaza shops. price and sell them at a higher products, but often operate on a price to make a profit. These businesses typically operate from smaller scale or in more flexible, mobile environments. dedicated shop premises. Manufacturing Businesses Raw Materials Distribution Manufacturing businesses take raw materials or semi-finished products and transform them into finished goods that people or other businesses Manufacturers can sell their products directly to the public or in large quantities to retail or trading need or want. businesses, who then sell the goods to customers. 1 2 Production Formal manufacturing businesses typically operate from well-equipped factories, while informal manufacturers may work from home or smaller facilities. The production process involves turning the raw materials into the final product. 3 Service Businesses 1 3 Formal Services 2 Informal Services Formal service businesses often operate Informal service businesses may from dedicated business premises, but can also work from home. They provide operate from home, temporary structures, or mobile setups, offering a a service and charge a fee for their range of personal and professional expertise and time. services. Examples Examples of service businesses include hairdressers, doctors, mechanics, plumbers, airlines, banks, architects, and travel agents. Formal vs. Informal Businesses Formal Businesses Informal Businesses Formal businesses typically operate from Informal businesses may operate from dedicated, well-equipped premises and follow established regulations and temporary or home-based setups, with a more flexible and adaptable approach. procedures. They often have a larger scale They often have a smaller scale of of operations and a more structured approach to their activities. operations and may not adhere to the same level of regulations as formal businesses. Coexistence Both formal and informal businesses play important roles in the economy, catering to different needs and serving diverse communities. The two types of businesses can often coexist and complement each other. Service Businesses Formal Services Operate from dedicated business premises or can work from home, providing a service and charging a fee for their expertise and time. Informal Services May operate from home, temporary structures, or mobile setups, offering a range of personal and professional services. Examples Hairdressers, doctors, mechanics, plumbers, airlines, banks, architects, and travel agents.