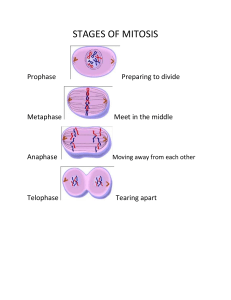
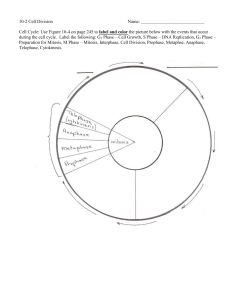
June 22 – Define/Explain: • Homologous chromosomes • Diploid • Haploid • Meiosis • Gamete • How do gametes differ from other cells ? Review – Are the two chromosomes composing a pair – Have the same characteristics – May also be called autosomes Review • A diploid cell – Has two sets of each of its chromosomes – This cell has 4 chromosomes (2n=4) Review • Unlike somatic cells – Gametes, sperm and egg cells, are haploid cells, containing only one set of chromosomes – Gametes in human cells have 23 chromosomes (n=23) Review • During fertilization – These gametes, sperm and ovum, fuse, forming a diploid zygote • The zygote – Develops into an adult organism Objectives 1. Review Cell Cycle and Mitosis 2. Explain how Meiosis is a special type of cell division where the number of chromosomes is split in half 3. Compare Mitosis and Meiosis Review of Cell Cycle • Series of events cells go through as they grow and divide • 4 Phases: – Interphase G1 – Interphase S – Interphase G2 – Mitosis Review of Cell Cycle • Mitosis: Division of Cell Nucleus • 4 stages – Prophase – Metaphase – Anaphase – Telophase Review of Mitosis: Prophase • First, longest phase • Chromosomes become visible • Nuclear membrane breaks down Review of Mitosis: Metaphase • Chromosomes line up across center of cell Review of Mitosis- Anaphase • Centromeres that join chromatids separate. • Sister chromatids separate • Chromosomes moves to opposite poles Review of Mitosis- Telophase • Condensed chromosome begin to disperse • Nuclear envelope re-forms around cluster of chromosomes • Nuclear envelope re-forms around cluster of chromosomes Cytokinesis • Division of cytoplasm following mitosis • Animal vs. Plant Cells • Animal- cytoplasm pinches inward • Plant- cell plate forms Cell Division Concept Map Development, growth, repair Genetically identical daughter cells Mitosis Binary Fission Cell Cycle Mitotic phase Interphase G1, S, G2 Prophase Multicellular organisms Metaphase Anaphase Unicellular organisms Reproduction Telophase Summary of Mitosis Genetically identical daughter cells Development, growth, repair Reproduction Unicellular Multicellular organisms organisms Prophase Binary Fission Mitosis Cell Cycle Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitotic phase G1, S, G2 Interphase Cell Growth & Division 1. When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible? a. only during interphase b. only when they are being replicated c. only during cell division d. only during the G1 phase When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible? a. only during interphase b. only when they are being replicated c. only during cell division d. only during the G1 phase 2. When during the cell cycle is a cell's DNA replicated? a. G1 phase b. G2 phase c. S phase d. M phase When during the cell cycle is a cell's DNA replicated? a. G1 phase b. G2 phase c. S phase d. M phase 3. Which event occurs during interphase? a. The cell grows. b. Centrioles appear. c. Spindle fibers begin to form. d. Centromeres divide. Which event occurs during interphase? a. The cell grows. b. Centrioles appear. c. Spindle fibers begin to form. d. Centromeres divide. 4. The cell cycle is the a. series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. b. period of time between the birth and the death of a cell. c. time from prophase until cytokinesis. d. time it takes for one cell to undergo mitosis. The cell cycle is the a. series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. b. period of time between the birth and the death of a cell. c. time from prophase until cytokinesis. d. time it takes for one cell to undergo mitosis. 5. The first phase of mitosis is called a. prophase. b. anaphase. c. metaphase. d. interphase. The first phase of mitosis is called a. prophase. b. anaphase. c. metaphase. d. interphase. 6. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell? a. prophase b. telophase c. metaphase d. anaphase During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell? a. prophase b. telophase c. metaphase d. anaphase 7. Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence? a. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase b. interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase c. interphase, prophase, metaphase, telophase d. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence? a. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase b. interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase c. interphase, prophase, metaphase, telophase d. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis 8. What is the role of the spindle during mitosis? a. It helps separate the chromosomes. b. It breaks down the nuclear membrane. c. It duplicates the DNA. d. It divides the cell in half. What is the role of the spindle during mitosis? a. It helps separate the chromosomes. b. It breaks down the nuclear membrane. c. It duplicates the DNA. d. It divides the cell in half. 9. One difference between cell division in plant cells and in animal cells is that plant cells have a. centrioles. b. centromeres. c. a cell plate. d. chromatin. One difference between cell division in plant cells and in animal cells is that plant cells have a. centrioles. b. centromeres. c. a cell plate. d. chromatin. 10. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing a. two chromosomes. b. four chromosomes. c. eight chromosomes. d. sixteen chromosomes. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing a. two chromosomes. b. four chromosomes. c. eight chromosomes. d. sixteen chromosomes. 11. Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their a. size. b. spindle fibers. c. growth rate. d. surface area. Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their a. size. b. spindle fibers. c. growth rate. d. surface area. (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 12. What phase is represented by letter (a)? Interphase (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 13. What phase is represented by letter (j)? anaphase (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 14. What are structures (c) called? Spindle fibers (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 15. What phase is represented by letter (d) metaphase (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 16. What phase is represented by letter (g) telophase (a) (b) (d) (c) (f) (e) (g) (i) (h) (j) 17. What phase is represented by letter (b)? Prophase Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Part II • Objective 2: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid • Meiosis – Takes place in two sets of divisions: Meiosis I Meiosis II Meiosis • Video • Notes – Graphic Organizer Meiosis has 2 Nuclear Divisions • Meiosis I – Reduces the number of chromosomes from diploid to haploid • Meiosis II – Produces four haploid daughter cells • Interphase and meiosis I MEIOSIS I: Separates homologous chromosomes INTERPHASE PROPHASE I Centrosomes (with centriole pairs) Sister chromatids Nuclear envelope METAPHASE I Chiasmata ANAPHASE I Sister chromatids remain attached Centromere (with kinetochore) Spindle Metaphase plate Homologous Microtubule chromosomes Tetrad attached to Chromatin separate kinetochore Pairs of homologous Chromosomes duplicate Tertads line up chromosomes split up Homologous chromosomes (red and blue) pair and exchange Figure 13.8 segments; 2n = 6 in this example • Telophase I, cytokinesis, and meiosis II MEIOSIS II: Separates sister chromatids TELOPHASE I AND CYTOKINESIS PROPHASE II Cleavage furrow Two haploid cells form; chromosomes Figure 13.8 are still double METAPHASE II ANAPHASE II Sister chromatids separate TELOPHASE II AND CYTOKINESIS Haploid daughter cells forming During another round of cell division, the sister chromatids finally separate; four haploid daughter cells result, containing single chromosomes Objectives 1. Review Cell Cycle and Mitosis 2. Explain how Meiosis is a special type of cell division where the number of chromosomes is split in half 3. Compare Mitosis and Meiosis A Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis • Meiosis can be distinguished from mitosis – By three events in Meiosis l • Synapsis and crossing over – Homologous chromosomes physically connect and exchange genetic information – This happens during Prophase I • Tetrads on the metaphase plate – At metaphase I of meiosis, paired homologous chromosomes (tetrads) are positioned on the metaphase plates Anaphase I vs. Anaphase II • Separation of homologues – At anaphase I of meiosis, homologous pairs move toward opposite poles of the cell – In anaphase II of meiosis, sister chromatids separate 1 2 2 4 Yes No Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Somatic Cells Sperm, Egg Cells Body Cell Formation Gamete Formation Cell growth, replacement Gamete Formation Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 1. In what cellular processes is mitosis involved? In what cellular processes is meiosis involved? Mitosis: development, growth, repair, asexual reproduction. Meiosis: formation of gametes or spores. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 2. In what type of cells does mitosis occur? In what type of cells does meiosis occur? Mitosis: somatic. Meiosis: sex cells or ovaries/ testes. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 3. How many times does DNA replicate in mitosis? How many times does DNA replicate in meiosis? Mitosis: one. Meiosis: one. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 4. How many cellular divisions occur in mitosis? How many cellular divisions occur in meiosis? Mitosis: one. Meiosis: two. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 5. How many daughter cells are formed by mitosis? How many daughter cells are formed by meiosis? Mitosis: two. Meiosis: four. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 6. What is the chromosome number in daughter cells formed by mitosis from diploid parent cells? What is the chromosome number in daughter cells formed by meiosis from diploid parent cells? Mitosis: 2n (diploid). Meiosis: n (haploid). Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 7. In mitosis, are daughter cells identical to or different from parent cells? In meiosis, are daughter cells identical or different from parent cells? Mitosis: identical. Meiosis: different. Review Questions: Mitosis vs. Meiosis • 8. In mitosis, when do synapsis and crossing over occur? In meiosis, when do synapsis and crossing over occur? Mitosis: never. Meiosis: prophase I.