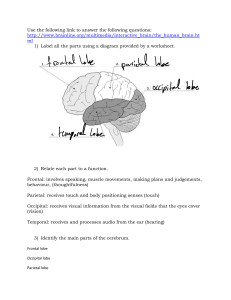
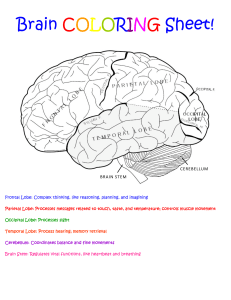
3 00 Project I summary 3 2 page minimum of 3 Highlights to 4 optional video sources share in link to discussion in impairment 9 30 stare of Apraxia affects Lecture left class sample of speech lang cognitive swallowing Apraxia frontal Lobe Dysarthria muscle weakness 17 00 can cause dysarthria Damage to these areas Basal ganglia cerebellum precentral gyrus 19 57 Frontal lobe Prefrontal memory and lobe attention frontal working lobe syndrome of Disinhibition speech and other behaviors Prefrontal Orbitofrontal cortex span lesion and memory with changed personality intelligence shorttemper irritability poor impulse control antisocial and to a act Normal one tendency 24 20 Right Hemisphere 37155 shethrowing shade cause I'm dozing off inclass Parietal Lobe 21 30 parietal lobe symptoms Right Left side neglect spatial dysfunction confusion finding way around inability to draw read or information in speech Affected emotionalmap deficit 35 05 Pragmatic or Grasp of sarcasm humor idioms and jokes parietal Right inferiororientation spatial lobe with 42 0 temporal Lobe Lesion RightAcute confessional state spatial disorder Temporal Lobe Impaired appreciation environmental sounds memory Bilateral medial lesions of rhythm and musical properties and in nonverbal with subsequent deficits BI medal eral Lasting loss Bilateral cortical es of new learning and memory wont lesions deafness auditory agnosia Laecotenderstanding 99 most in dominance left hemisphere for language with left dominance handed right left handed with Right hemishere visuospatial and musical TEST Tim boiler knockout 4255Disorders of Cortex Cerebral dominance bear left forme other dominance constructional tasks emotional appreciation processing and Back to Ceti hemisphere Aphasia and Aphasiatype An acquired disorder of language 53105 58555 Broca aphasia frontal region Left verbal Non fluent and ungrammatical retention of nouns and verbs deficit tip of tongue Naming Largely unaffected Impaired writing output my comprehension for spoken Lang and written into 1 04 50 left superior temporal gyrus Posterior Fluent semantic verbal output with overuse of phrases multiple verbal paraphasic errors and neologisms primary deficit in auditory comprehension Impaired naming repetition reading and writing Wernicke's Aphasia verbal neologisms paraphasia Examples I verbal semantic error bae but mean red Neologistic nonsense word in place of another word Paraphasia tat for cat Break 1 10 00 we're watching a video icon 1 18 30 Global Aphasia of Broca and Wernicke aphasias Inclusion functions naming writing Profound impairment of all language speaking and understanding 126 05 Conduction Aphasia fibers of arcuate fasciatus Repetition most affected Fluent verbal wept with paraphasieemers variable impairments of naming 31 04 Cognition Become During an aware of or obtains knowledge of event the following ocares perception Judgement problem solving recognition Reasoning Attention and into processing Attention capacity to focus on manipulate the information particular stimuli Attentional that time capacity amount of into Attention controls guiding Types of Attention Focused to sustainedability ability period of object an to time selective ability presence of attentional focus attention attend to Same time be attended to capacity where it on a stimulus a stimulus or to attend to specific stimulus other distracting stimuli Alternating ability to change focus stimuli Divided ability to can attend diff attention stimuli and overtime is any needed 1 40 00 over long activity or in actively between or at to a attention the or more at the 149 0 Systems of Attention reticular system RAS In charge of sustained attention activating sub cortical nerve cells frontal lobe thalamus and basal ganglia one Cal nerve s frontal lobe thalamus and basal ganglia In charge of focused Attention and stimuli Posterior Attentional system PAs selective Attention of visual cortex Posterior parietal Anterior Attentional in of charge Attention Prefrontal and basal ganglia 3 system that helps Cognition Memory Memory retention and mid brain Execution system this system is Attention sustained Attention and divided System Acts selective thalamus or orbitofrontal manage the 5 cortex premotor cortex types of attention 200145 2 05 40 of experience dependent changes overtime sensory storage visual auditory tactile etc encoded based on experiences associations perception requires a STM short term mem MClong term mem and temporary in nature permanent storage limited unlimited capacity capacity to be