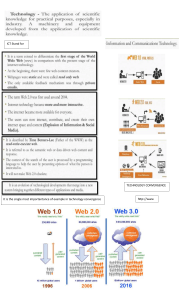
LESSON 1: INTRODUCTION TO MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY MEDIA - Communication tools - Plural form of medium - describes any channel of communication - Include anything from printed paper to digital data, and encompasses art, news, educational content and numerous other forms of information INFORMATION - Data, knowledge derived from study, experience, or instruction, signals or symbols - Knowledge of specific events or situations - broad term that can cover data knowledge derived from study, experience, or instruction, signals or symbols (UNESCO Media and Information Literacy Curriculum for Teachers) - Refers to the knowledge of specific events or situations that has been gathered or received by communication, intelligence, or news reports MEDIA AND INFORMATION - Two distinct elements that are intrinsically connected with the concept of communication - They are so intertwined that INFORMATION is one of the reasons why communication can be shared through MEDIA CATEGORIES OF MEDIA Media Modality Text, audio, video, graphics, animation Media Format Digital or analog Way of Transmitting Electromagnetic or radio waves, light waves Mass Media Form TV, radio print internet, telephone, or mobile LITERACY - equivalent to a SKILL - refers to the ability to identify, understand, interpret, create, communicate, and compute using printed and written materials associated with varying contexts (UNESCO Media and Information Literacy (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, or UNESCO) TERMINOLOGIES: MEDIA - read, analyze, evaluate and produce communication in a variety of media forms. INFORMATION LITERACY - recognize when information is needed and to locate, evaluate, effectively use and communicate information in its various formats. TECHNOLOGY (DIGITAL) LITERACY - use digital technology, communication tools or networks to locate, evaluate, use, and create information. UNESCO’S FRAMEWORK, MIL IS ESSENTIAL TO: 1. Make informed Judgement - To avoid making biased and sweeping statement, one needs to know how to evaluate information from various sources 2. Learn about the world around them - Not everything you find on the net is accurate and reliable 3. Build a sense of community - Connecting people to promote pluralism or a belief that each person is unique that promotes diversity 4. Maintain public discourse - Take an active role for self-expression and exercising freedom of expression as stated in Universal Declaration of Human Rights. 5. Engage in lifelong learning - Current workplace demands more complex skills like how to identify relevant information and how to communicate ideas using ICT (Information Communication Technology). LESSON 2: THE EVOLUTION OF TRADITIONAL TO NEW MEDIA PRE-INDUSTRIAL AGE (PRE-1700’S) Prehistoric cave paintings - earliest example of media discovered in this era - around since 35,000 B.C. Papyrus Paper - used in ancient Egypt in 2,500 B.C - clay tablets found in Mesopotamia in 2,400 B.C. Acta Diurna - considered as the world’s first newspaper - appeared in 131 B.C. - informed citizens of social and political happenings in Rome - information inscribes in a metal or stone Dibao - “reports from the official residences” - type of publications issued by central and local governments in imperial China - closest in form and function to gazettes in the western world - also called “palace reports” or “imperial bulletins” > seen as evidence that the earliest civilizations had already honed the skills to convey information, through writing and drawing on whichever material was available during that time using their primitive languages. INDUSTRIAL AGE (1700S-1930S) - period described as the product of harnessing the power of machines - responsible for the widespread dissemination of information. Typewriter (1800’s) - allowed a more uniform method of recording text without the confusion of understanding the handwriting of every person. Printing Press (19th Century) - most notable invention of this era - allowed the mass production of books, newspapers, and other printed materials. Telegraph and the Telephone (1870s) - allowed real-time communication across a great distance - allowed people to convey messages and information in a faster and more efficient manner. Motion Pictures - this era introduced this and continued to evolve from 1890’s to 1926 ELECTRONIC AGE (1930S-1980S) - started the invention of the transistor (ELECTRONIC COMPUTING) - semi-conductor device used to amplify electrical signals and power, attributed to John Bardeen, William Shockley, and Walter Brattain at Bell Labs, 1948. Transistor radio and the Television - earliest electronic devices - (transistors) paved way to the first generations of large electronic computers and mainframes, and the earliest forms of personal computers. Mass Media - thanks to this, wherein a vast number of recipients would be able to receive data transmitted from a single source in real time. INFORMATION AGE (1900S-2000S) - modern age characterized by the massive influence of the Internet. - (internet) allowed communication and information to be accessible real-time and ondemand anywhere across the globe. Personal computers, smartphones, tablets and wearable devices - harness the power and capabilities of the Internet. Social Media Websites - most notable trend of this era - application to reach out to people World Wide Web - where new media can be found - online platforms such as Facebook, YouTube and Wikis allow unlimited sharing of information among individuals around the globe. EVOLUTION OF TRADITIONAL TO NEW MEDIA - need for continuous improvement - Being able to transfer information and knowledge in a manner that is more efficient and effective is still the goal, evident in the evolution of traditional to new media. HOT MEDIA - forms requiring little involvement from the audience. - cannot be “TOUCHED” and thus the experience is relatively PASSIVE and STATIC. - television and film COLD MEDIA - high-level user interactivity - more DYNAMIC and audience is more INVOLVED - video games, online media platforms TRADITIONAL MEDIA - media experience is limited - one-directional - sense receptors used are very specific (print media- sense of sight) NEW MEDIA - more interactive - audiences are more involved and can send feedback simultaneously - integrates all the aspects of old media FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNICATION AND MEDIA 1. Inform citizens of what is happening (monitoring function) 2. Educate the audience (meaning and significance of facts) 3. Provide a platform for public discourse (public opinion and expression of dissent) 4. Give publicity to political and governmental institutions “watchdog” role of journalism 5. Channel for advocacy for political viewpoints NORMATIVE THEORIES OF THE PRESS Authoritarian - Government has full control - All forms of communications are under the control of the governing elite, authorities, or influential bureaucrats. - Controlling the media is necessary to protect and prevent the people from national threats through any form of communication (information or news). - The government has all the rights to restrict/censor any sensitive issue from press to maintain peace and security in the nation. - Different types of censors include political censor, moral censor, military censor, and corporate censor. Soviet Media - 50/50 - The government undertakes or controls the total media and communication to serve (and educate) working classes and their interests. - The state has the absolute power to control any media for the benefits of the people. - The state puts an end to private ownership of the press and other media. - Government media provides positive thoughts to create a strong socialized society as well as providing information, education, entertainment, motivation, and mobilization. - The public is encouraged to give feedback which would be able to create interests toward the media. Libertarian - Public has freedom to share without authorities - Liberalism means information is knowledge and knowledge is power. - Libertarianism is free from any authority or any control or censorship and is an idea of individualism and limited government which is not harmful to another. - The people are more than enough to find and judge good ideas from bad (because) people are rational. - The press should not give knowledge and can help make better decision during worst situations.’ Social Responsibility - Social responsibility should be reached by selfcontrol, not government intervention. - View media ownership as a form of public trust or stewardship, rather than as an unlimited private franchise. - Media has obligations to society, and media ownership is a public trust. - Media should follow agreed code of ethics and professional conduct. - The government must not merely allow freedom; it must actively promote it when necessary; therefore, the government should act to protect the freedom of its citizens. - Under some circumstances, the government may need to intervene to safeguard public interest. LESSON 3: TYPES OF MEDIA PRINT MEDIA - oldest type, use in the earliest days of written language itself. - evolved considerably, and is driven by humanity’s insatiable hunger for information. - Since the invention of the Gutenberg's printing press (1440), print media evolved to include books, newspapers, and magazines. These are prevalent in most parts of the world today despite the increasing popularity of Internet-based media. - also known as PRESS, materials that are written and are physically distributed. Books - very first mass media in history - Baran (2010) considers books as very personal because they contain records of past experiences and human knowledge that are passed on to later generations. - They provide opportunities for escape and personal reflection as experienced by one who reads a novel. - They are very specialized in that they offer more ideas about a topic. Magazines and newspapers - advertisementbased - may be targeted for the general audience or may address the interests of a particular group of readers. - Magazines typically contain features or human interests articles - Newspapers contain news stories and occasionally have other types of articles. BROADCAST MEDIA - evolved in leaps and bounds in the 20th century - do not rely on the production and distribution of physical copies as much as print media does because they distribute their messages “over the air”. - because their programming can be viewed by multitudes at once, broadcast media like radio and television have been traditionally accepted as the most efficient way to transmit messages. - One of the most distinctive characteristics of the broadcast media is their UBIQUITY. - considered “household” media because they can be found in practically any corner of a home. - Broacast media come in two forms - RADIO and TELEVISION Radio - first electronic mass medium and the precursor of television. - “Young people's media” - This is evident in the proliferation of FM radio stations catering the musical taste of younger generations, also known as format radio. - In the Philippines, it is customarily expected FM programming to be format radio, whereas AM programming is dominated by a news format. Television - the second most important invention. - “least common denominator” which means that television programs avoid burdening the audience of complex and complicated messages. FILM/CINEMA - considered impressionable and has a cathartic effect to its audience. - has evolved, from black-and-white “moving pictures” with no sound to highly sophisticated color movies, especially with the advent of digital cinema. - form of media originally recorded images onto the celluloid strips that give it its name. - generally used for storytelling purposes, although shorter instructional videos are also common. - some time after their run in theaters, films may also be re-shown on television. VIDEO GAMES (DIGITAL GAMES) - continue to grow popular to both young and old because of their increased interactivity and interconnectivity. - relatively young type, first coming into vogue in the 1970s. - most notable examples incorporate extended visualized storytelling, and feature a wide range of topics and themes. - its output and design limits are further tested every few years due to the brisk development of the technology that drives it. - Mobile games, playable on smartphones, are currently as popular as their older console-based cousins. NEW MEDIA - another young, growing type of media that has come into being with the advent of modern technology. - usually digital and Internet-based. - interactive, with two-way communication (in the form of comments, Likes, tweets, among others) usually being central to its design. - Social media is also a part of new media Digital media that are interactive, incorporate two-way communication and involve some form of computing Social Media - form of electronic communication which people create online communities to share information, ideas, personal messages, etc. SYNERGY - interaction of two or more agents or forces so that their combined effect is greater than the sum of their individual effects. CONVERGENCE - combination of various elements to create a new whole. - literally means an intersection, or a meeting of distinct forces. > Henry Jenkins (2006) “convergence is a word that manages to describe technological, industrial, cultural and social changes.” > 3 C’s of COMPUTING, COMMUNICATION AND CONTENT - interconnection brought by media convergence JENKIN’S FIVE TYPES OF CONVERGENCE 1. Technological Convergence - most common way to point out convergence in action - lines of traditional media types blur as technology makes it possible for media content to be supported on media types and platforms Radio Television Video Game Internet and Wide Web the World Digital radio Internet-based radio and podcasting Radio on Television (and vice versa) Video cassette recorders (VCR) Digital video disc (DVD) Digital video recorder (DVR) Digital television or high definition television Internet-based television Video on the internet Interactive television Phone-over-cable Mobile video Television recording Online interactive gaming Internet-capable handheld game devices Advergaming Advocacy gaming Functionalities of the traditional medimoving to the Web platform Internet technology incorporated top mobile technology 2. Cultural Convergence - includes a number of key aspects: “flow” of stories from one format to another seen in adaptations participatory culture - allows media consumers to add some input on the media they consume, as well as create their own examples of that media. 3. Organic Convergence - natural outcome of a world filled with diverse media types - also called “social convergence” or “media stacking” - Not so much a “planned” convergence as a type that “simply happens” by nature - be seen in cases where a person is using their smartphone to send messages or browse the Internet while watching television, or reading a newspaper while a radio program plays in the background. 4. Global Convergence - inevitable effect of media bridging the gap between geographically distant cultures and peoples having these cultures influence each other. 5. Economic Convergence - linking of companies and businesses to media. - Prominent examples of this type of convergence arose in the late 1990s and 2000s. MASS MEDIA - channels of communication that involve transmitting information in some way, shape or form to large numbers of people. MEDIA EFFECTS - intended or unintended consequences of what the mass media does (Denis McQuail, 2010) Third - party theory - people think they are immune to media influence than others Reciprocal effect - When a person or event gets media attention, it influences the way the person acts or the way the event functions. - Media coverage often increases self-consciousness, which affects our actions. Boomerang effect - media-induced change that is counter to the desired change. Cultivation theory (George Gerbner) - media exposure, specifically to television, shapes our social reality by giving us a distorted view on the amount of violence and risk in the world. MTRCB