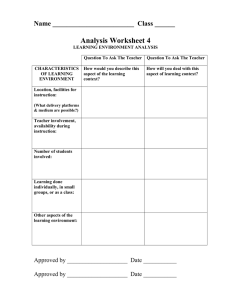
TENSE AND ASPECT While tense tells us when a situation occurs (=tense refers to the location of an action in time.), aspect tells us how it occurs, or how it is viewed by the speaker, in terms of its frequency, its duration, and whether or not it is completed. In other words, how an action relates to time. TENSE: 1. PRESENT 2. PAST 3. FUTURE* *Future is not considered as a separate tense since it does not involve any inflections of the verb. English uses the modal verb will or the present continuous tense to talk about the future. What are the aspects in English? There are four aspects in English: Simple aspect – 1. With the simple aspect there is no indication of how the event occurs or how it is viewed by the speaker. - It is used to express single actions, habits or routines. - There are no auxiliary verbs involved in the expression of this aspect. Present simple – I work – She works Past simple – I worked – She worked 2. Progressive aspect – this is used by the speaker to indicate that a situation is in progress: Present progressive – I am working Past progressive – I was working 3. Perfect aspect – this is used to indicate a complete action (or not) that begins in the past and continues upto the present, a recent past or a complete action in an earlier past. . Present perfect – I have worked Past perfect – I had worked 4. Perfect progressive aspect – this is used to describe a completed part of a continuous action. I have been working since 9 AM. We can combine these last two aspects to make the present perfect progressive (I have been working) and the past perfect progressive (I had been working). The SIMPLE PRESENT is used to refer to routines. …..to refer to an action that….