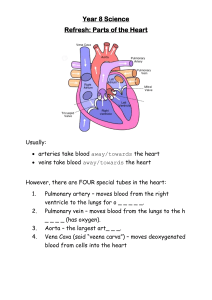
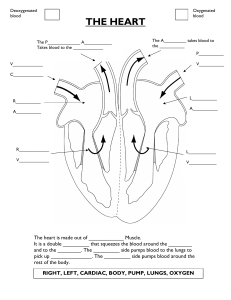
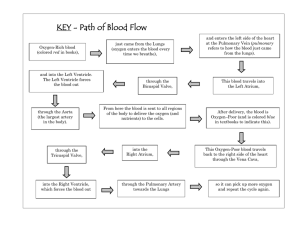
HHS O Level School Handout for Class VI (General Science – Chapter 2) Organs involved in breathing system: Sinus cavity is the area around the nose and eyes that clean the air people breathe in. Pharynx is behind the nose and mouth. Larynx is in the neck and contains the vocal cords. Trachea connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs and is responsible for the passage of air. Bronchi (singular: bronchus) are small tubes that bring air to and from the lungs. Lung is the main part of the gas exchange system and puts oxygen into the bloodstream. Diaphragm is a muscle that moves up and down to expand the lungs. This helps a person breath Intercostal muscle is attached to ribs, pulling ribs up and out during inhalation and down and in during exhalation. Thorax is the area between the neck and abdomen. Function of circulatory system: It is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and other essential substances to cells and removing waste products from the body. Double circulatory system: It consists of two circuits; the pulmonary circulation (which carries blood between the heart and the lungs) and the systemic circulation (which carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body Pulmonary artery: A blood vessel that takes deoxygenated blood away from the heart into the lungs. Pulmonary vein: A blood vessel that brings oxygenated blood towards the heart from the lungs. Aorta: Main artery that takes the blood away from the heart to all parts of the body Vena cava: Main vein that brings blood to the heart from the body Atrium: Upper chamber of heart that receives the blood from the lungs and body. Ventricle: Lower chamber of heart that are distributing chambers of blood. Pulse: The pulse is the pressure caused by each heartbeat. Path of blood: Oxygen enters your blood in your lungs. As the blood flows through the tiny capillaries in the lungs, it picks up oxygen. The blood is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood flows back to the left atrium of heart through the pulmonary vein It is then pumped out from the left ventricle to the rest of the body through aorta. By the time it gets back to the right atrium again through vena cava, it has given up most of its oxygen. It is deoxygenated. Then it flows into the lungs through pulmonary artery to get oxygenated again. Platelets: A component of blood that helps in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding. Three types of blood vessels: