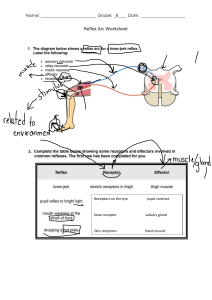
Salivary gland stones (Sialolithiasis) Sahil Bhimrao Boeni Salem Mostafael Salima Hamed Amor Al Habsi Samiya Bint Saleh Abood Basalam Sandas Mohammedal-Rashdi Sandas Saleh Al-Marhubia NU210716 NU210068 NU220237 NU220607 NU210156 NU210149 Learning Objectives Salivary gland stones (sialolithiasis) are a condition in which calculi form in a salivary gland. These stones obstruct the flow of saliva and It made of calcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite. It can cause facial pain, swelling and inflammation of glands. The majority of stones affect the submandibular glands and less commonly, the stones affect the parotid glands. This project will focus on four main points which are diagnosis, etiology and treatments. There are several diagnostic methods including physical examination by palpation of the affected area to feel for swelling or tenderness. Imaging tests can help visualize the size, location and presence of salivary gland stones for example, X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans and MRI scans. Also, sialography involves injecting a contrast dye into the salivary gland ducts, followed by X-rays to detect any blockages caused by stones. What causes the exact pathogenesis of sialolithiasis not fully understood but the relative stagnation of salivary flow and calcium concentration may be important ,but several factors are associated with salivary stone formation: Dehydration, due to inadequate fluid intake, illness, or medications such as diuretics (water pills) and anticholinergic drugs. Trauma to the inside of the mouth. Sialolithiasis treatment depends on the size and location of the stones. The treatment has the highest success rate when small stones are located in the duct. Treatments include home medications by applying moist heat and gentle massage to the salivary gland. Also, If the doctor notices evidence of infection, an antibiotic may be prescribed. For instance, Ibuprofen or (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and swelling. In addition, If patients suffer from large salivary gland stones, a surgeon inserts an endoscope into the salivary duct and removes the stones. Patients can reduce the risk by staying hydrated, avoiding smoking and practising oral hygiene. If they feel any pain around the salivary gland, try sucking sour candies to secrete more saliva, thus it can encourage stones to pass naturally. Summary Sialolithiasis is a condition in which the patient loses the ability to secrete saliva to the mouth which in order causes digestion difficulties. This condition hasn’t any known causes but the treatment has a high success percentage. References 1. American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation. (2019). Salivary Stones. [https://www.entnet.org/content/salivarystones](https://www.entnet.org/content/salivary-stones) 2. Escudier, M. P., McGurk, M., & Symons, N. (2003). "The complications of sialolithiasis." International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 32(3), 273-277. [https://doi.org/10.1054/ijom.2002.0358](https://doi.org/10.1054/ijom.20 02.0358) 3. "Salivary gland stones (sialolithiasis)." Mayo Clinic. [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/salivary-glandstones/symptoms-causes/syc20350901](https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/salivarygland-stones/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901) 4. "Sialolithiasis."StatPearls. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499852/](https://www.ncbi.nl m.nih.gov/books/NBK499852/) 5. Marmary, Y., et al. (2019). Sialolithiasis - Modern non-invasive diagnostic and treatment options. Imaging in Medicine, 11(3), 31-39. [https://doi.org/10.2217/iim-2019-0003](https://doi.org/10.2217/iim2019-0003)