Uploaded by
William Romero
Duloxetine (Cymbalta) Medication Template | Pharmacology

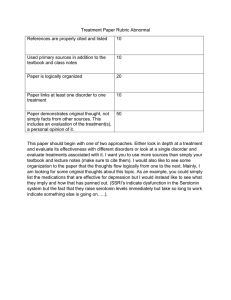
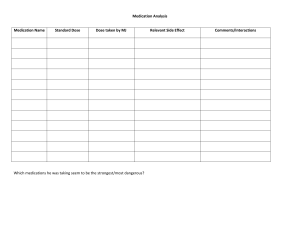
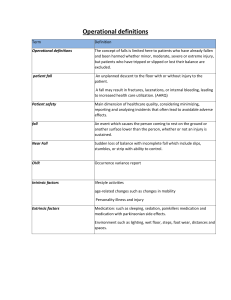
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication William Romero STUDENT NAME______________________________________ Duloxetine (Cymbalta) MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________ CATEGORY CLASS_Serotonin-norepinephrine ______________________________________________________________________ PURPOSE OF MEDICATION Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use Action SNRIs block reuptake of norepinephrine as well as serotonin with effects similar to the SSRIs. Major depression, Generalized anxiety disorder, Social anxiety disorder, Panic disorder, Pain due to fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, low-back pain, diabetic neuropathy (duloxetine; unlabeled use for venlafaxine) Complications Nausea, anorexia, weight loss - Headache, insomnia, anxiety Hypertension, tachycardia - Dizziness, blurred vision - Withdrawal syndrome - Risk for suicide in children and adolescents - Sexual dysfunction - Serotonin syndrome - Bronchitis, dyspnea Medication Administration PO Contraindications/Precautions Contraindications/Precautions - These medications are pregnancy category risk C. Avoid during the third trimester and avoid breastfeeding while taking an SNRI. - SNRIs are contraindicated in clients taking SSRIs, MAOIs, or TCAs. SNRIs need to be discontinued at least 2 weeks before initiating an MAOI. - Precautions are needed for older adults, and clients who have bipolar disorder, mania, seizure disorder, recent MI, or interstitial lung disease Interactions Concurrent use with MAO inhibitors may result in serious potentiallyfatal reactions, may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, risk of hepatotoxicity with alcohol use disorder Nursing Interventions Monitor closely for notable changes in behavior that could indicate emergence or worsening of suicidal thoughts or behavior or depression Assess for serotonin syndrome Assess for rash periodically during therapy Concurrent use with MAO inhibitors may result in serious potentially fatal reactions, may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, risk of hepatotoxicity with alcohol use disorderIncreased sense of well-being, renewed interest in surroundings, Client Education Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness Verbalizing improvement in mood - Increased hopefulness and will to live Ability to perform ADLs - Improved sleeping and eating habits - Increased interaction with peers ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Instruct clients to continue therapy after achieving therapeutic effects. Sudden discontinuation of medication can result in relapse. - Advise clients to take medication in the morning to minimize sleep disturbances. - Advise clients to take medications with food to minimize GI disturbances. - Advise clients about potential sexual side effects. - Avoid use of MAOIs. Therapeutic Procedure A7