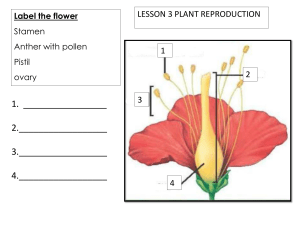
EVERWIN GROUP OF CBSE SCHOOLS (Kolathur-Maduravoyal-Mathur-Perambur-Surapet-Madurantakam-Rajamangalam) CLASS: XII UNIT TEST (ONLINE) MARKS-40 30.04.2024 BIOLOGY TIME: 1½ Hrs. SECTION – A I. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS : (8x1=8) 1. Which of the given statements are correct with respect to pollination in Vallisneria? (i) Pollen grains are light and non-sticky. (ii) Female flowers reach the surface of water by long stalks. (iii) Pollen grains are carried passively by water currents. (iv) Female flowers remain submerged in water. Choose the correct option. (a) (i) and (iv) (b) (ii) and (iv) (c) (i) and (ii) (d) (ii) and (iii) 2. Which one of the following events takes place after double fertilisation? (a) The pollen grain germinates on the stigma (b) The pollen tubes enter the embryo sac (c) Two male gametes are discharged into the embryo sac (d) The PEN (Primary Endosperm Nucleus) develops into endosperm 3. Which one of the following is not found in a female gametophyte of an angiosperm? (a) Germ pore (b) Synergids (c) Filiform apparatus (d) Central cell 4. Select the plant species, where emasculation is not required for artificial hybridisation experiment. (a) Castor (b) Maize (c) Papaya (d) Wheat Question No. 5 to 8 consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. B. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. C. A is true but R is false. D. Both A and R are false. 5. Assertion : Ex-albuminous seeds do not possess any residual endosperm, as it is completely consumed during embryonic development. Reason : Wheat, castor, pea and groundnut all are examples of Ex-albuminous seeds. 6. Assertion : Chasmogamous flowers require pollinating agents. Reason : Cleistogamous flowers do not expose their sex organs. 7. Assertion: Hydrophily is a major mode of pollination in most of the aquatic plants in angiosperms. Reason: Almost all the aquatic dicot and monocot plants require water for the transport of male gametes and for fertilisation. 8. Assertion: In a microsporangium, the tapetal cells possess little cytoplasm and generally have a single prominent nucleus. Reason: During microsporogenesis, the microspore mother cells (MMCs) undergo mitotic divisions to produce haploid microspore tetrads. SECTION B II. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN BRIEF: (4x2=8) 9. What is 'bagging'? State its importance in artificial hybridisation of flowering plants. 10. Write the difference between the tender coconut water and the thick white kernel of a mature coconut and their ploidy. 11. a) An anther with malfunctioning tapetum often fails to produce viable male gametophytes. Give one reason. b) Gynoecium of a flower may be apocarpous or syncarpous. Explain with the help of an example each. 12. Identify and label the parts in the given anatropous ovule. b) State the function of E. SECTION C III. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN BRIEF: (2x3=6) 13. In angiosperms, zygote is diploid, while primary endosperm cell is triploid. Explain. 14. a) Identify the figure given below and also identify the parts B, C, D and E. SECTION D 15. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below: 2×4=8 Cross pollination is the transfer-of pollen grains from the anther of a one flower to the stigma of a genetically different flower. It is performed with the help of an external agency which may be abiotic (e.g., wind, water) or biotic (e.g., insects, birds, bats, snails). The diagram shows the carpel of an insect pollinated flower. i. What is the most likely reason for non germination of pollen grain Z? (a) Pollen grains X and Y were brought to the stigma earlier, ii. iii. iv. therefore, their germination inhibited the germination of pollen grain Z. (b) Pollen grain Z was brought to the flower by wind, while pollen grains X and Y were brought to the flower by insect (c) Pollen grain Z lacks protrusions that allow it to adhere properly onto the stigma surface (d) Pollen grain Z comes from a flower of an incompatible species Which of the following best describes the function of the pollen tube? (a) It acts as a conduit to transport male gametes from the anther to the ovule (b) It acts as a conduit to transport male gametes from the stigma to the ovule. (c) It contains key nutrients that serve to nourish the newlyformed zygote (d) It digests the tissues of the stigma, style and ovary. Pollination of a flower in which the pollen is carried by an insect is called a) anemophily b) ornithophily c) entomophily d) malacophily Refer to the given characteristics of some flowers: A. The stamens hang out of the flower, exposing the anthers to the wind. B. The pollen grains are tiny and light C. The flower has a sweet scent. D. The flower petals are brightly coloured . How many of the above characteristics are of insect-pollinated flower? a) One b) Two c) Three d) Four 16. A flower of tomato plant following the process of sexual reproduction produces 200 viable seeds. Answer the following questions giving reasons. (a) What would have been the minimum number of ovules present in per pollinated pistil? (b) How many microspore mother cells would minimally be required to produce requisite number of pollen grains? (c) How many pollen grains must have minimally pollinated the carpel? (d) How many male gametes would have used to produce these 200 viable seeds? SECTION E IV. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN DETAIL: (2x5=10) 17. (a) How is apomixis different from parthenocarpy? (b) Describe any two modes by which apomictic seeds can be produced. (c) Suggest the advantage to a farmer for using apomictic seeds of hybrid varieties. 18. Study the figures given below of the development of megaspore in an angiosperm and answer the questions that follow: (i) Describe the developmental events in the nucellus of the ovule. What is this type of development of megaspore referred to as? (ii) How many free nuclear mitotic divisions will the functional megaspore undergo to form a mature embryo sac? (iii) Describe the structure of a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant.