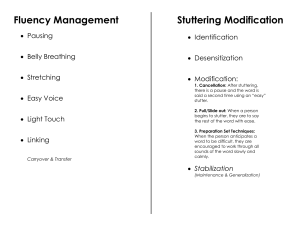
How Can Speech and Language Therapy Help With Stuttering? Stuttering is a speech disorder that affects the flow of speech, often characterized by repetitions of sounds, syllables, or words, prolongations of sounds, and interruptions in speech, known as blocks. It can have a significant impact on an individual's communication and emotional well-being. However, speech and language therapy has been proven to be highly effective in helping individuals manage and often reduce Stuttering. In this post, we will discuss the prominent signs and causes of Stuttering, plus how these therapies can help people with this problem. What is Stuttering? Before diving into therapeutic techniques, it's important to understand that Stuttering affects not just speech patterns but also self-esteem and daily interactions. A Speech pathologist (SLP) starts by assessing the individual's speech patterns, emotional responses to Stuttering, and the impact of Stuttering on their life. This holistic approach helps in creating a more personalized therapy plan. What are the Common Symptoms of Stuttering? Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder characterized by disruptions in the normal flow and timing of speech. These disruptions, referred to as disfluencies, can manifest in several ways. Before going for speech and language therapy, have a look at the common signs of Stuttering: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Repetitions: This is the most recognizable sign of Stuttering. It involves the repetition of sounds, syllables, or words. For example, someone might say "b-b-b-ball" or "can-can-can I go?" Prolongations: Prolongations occur when a sound is elongated significantly. For example, "sssssssun" instead of "sun". Blocks: A block is when the mouth is positioned to say a word, but no sound comes out for several seconds. It may be accompanied by a tense struggle to produce the sound. Interjections: The use of interjections like "um" or "uh" more frequently than typical in an attempt to delay the initiation of a word the speaker anticipates difficulty with. Revisions: Changing a word or phrase mid-sentence due to difficulty in speaking it smoothly. This can be a way of avoiding stuttered speech. Physical Tics: Some individuals might exhibit physical signs of struggle while stuttering, such as blinking rapidly, twitching of the lips or face, or jerking of the head. Avoidance behaviors: Often, people who stutter might develop avoidance behaviors to prevent Stuttering. They might avoid certain words or social situations where they have to speak. Anxiety about speaking: Due to past experiences of Stuttering, an individual might feel anxiety or fear about speaking, which can sometimes exacerbate the Stuttering. What Causes Stuttering in People? The causes of Stuttering are complex and not completely understood, but research suggests that several factors contribute to the development of this speech disorder. These factors can be broadly categorized into genetic, neurological, developmental, and environmental influences: ● Genetic Factors: There is strong evidence that Stuttering has a genetic component. Many individuals who stutter have a family member who also suffers from stuttering. Studies involving twins and families have shown that genetic factors with Autism signs can contribute significantly to the disorder. In such cases, speech therapy's role in autism treatment is beneficial. ● Neurological Factors: Neuroimaging studies have shown that people who stutter may have differences in the way their brains process language and speech. These differences are often seen in the areas of the brain responsible for speech production. There might be anomalies in the way speech-related brain circuits are activated and how these areas communicate with each other. ● Developmental Factors: Stuttering often begins in early childhood during the developmental period of intense speech and language learning. Rapid language development phases can sometimes trigger stuttering in children who are predisposed to the disorder. Additionally, motor speech coordination issues during early childhood can also play a role. ● Environmental Factors: Elements such as family dynamics, communication styles, and high parental expectations can sometimes influence the onset or continuation of Stuttering, particularly in individuals who are already genetically predisposed. Stressful social or familial situations might exacerbate Stuttering. ● Psychological Factors: Although psychological factors like anxiety, stress, and temperament are not direct causes of Stuttering, they can influence its severity. These factors can also impact how individuals cope with the disorder. Discussing Speech and Language Therapy for Treating Stuttering In this section, we will discuss different techniques of speech and language therapy to understand their role in treating Stuttering: ● ● ● ● ● Fluency Shaping: This technique aims to teach the individual how to speak more fluently by modifying their speaking patterns. This includes training in breath control, gradual and smooth speech initiation, and reduced speaking rate. Fluency shaping helps individuals gain better control over their speech muscles, thus reducing Stuttering. Stuttering Modification: Unlike fluency shaping, stuttering modification does not aim to eliminate Stuttering but rather to modify it so it becomes less severe. It teaches individuals to stutter more easily, with less struggle and avoidance. Techniques such as 'easy onsets' and 'light contacts' encourage smoother transitions between words and sounds. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Often used in conjunction with other techniques, CBT helps address the psychological aspects of Stuttering. It involves strategies to reduce anxiety, decrease avoidance behaviors, and improve self-esteem, thereby indirectly improving fluency. Desensitization: The goal of desensitization is to reduce the individual's negative reactions to Stuttering. This involves practicing Stuttering deliberately to reduce fear of stuttering episodes and increase acceptance. Technology-Assisted Practices: Various technological tools like delayed auditory feedback and frequency-altered feedback can be used to improve speech fluency by altering the perception of one's own voice, which can help modify speaking patterns and reduce stuttering. What's Speech Therapy's Role in Autism Treatment? Speech Therapy's Role in Autism Treatment is a crucial role to support individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Since communication challenges are a key feature of autism, a speech pathologist is often integral to the development and implementation of an effective therapy plan. Here's how speech therapy can help individuals with autism and its developing signs like Stuttering: Enhancing Communication Skills ● ● Many individuals with autism may struggle with verbal communication. Speech therapists work to develop these skills, focusing on articulation, the formation of complete sentences, and the use of language in social contexts. Techniques may include modeling, repetition, and the use of visual aids. Speech therapy's role in Autism treatment is effective, as SLPs with the treatment can help individuals understand the language used around them, which involves improving listening skills, following instructions, and understanding questions. Improving Social Communication ● ● Communication isn't just about words; it's also about understanding social cues and rules. A speech pathologist often helps individuals with autism learn how to interpret gestures, maintain eye contact, take turns in conversation, and understand and use appropriate facial expressions and tone of voice. This aspect of speech therapy focuses on the use of language in social contexts, helping individuals learn to make requests, greet others, or make comments appropriate to the situation. Supporting Educational and Behavioral Goals ● ● Speech and language therapists often contribute as part of a multidisciplinary team that may involve teachers, healthcare professionals, occupational therapists, and behavioral therapists. This collaboration helps integrate speech therapy goals with educational and behavioral objectives, providing a cohesive approach to therapy. Since communication frustrations can often lead to behavioral challenges, improving communication skills can help reduce behavior issues. Speech and language therapy helps provide the tools and skills needed to express needs, desires, and emotions more effectively. Contact Reflect Within and Book a Session! Speech and language therapy offers a comprehensive approach to managing Stuttering. By employing a variety of techniques tailored to each individual's needs, SLPs not only help improve fluency but also empower individuals to communicate more effectively and confidently. If you or someone you know is struggling with Stuttering, consider consulting Reflect Within. You can contact us at +91 8928467288 and book a session for professional therapy treatment.