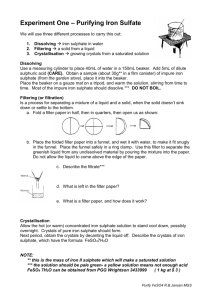
INTRODUCTION PREPARATION OF MOHR’S SALT aim: To study Mohr’s salt. THEORY: Mohr’s Salt, also referred to as ammonium ferrous(II) sulphate, is an inorganic compound that consists of two primary cations - the ammonium cation (NH4+) and the ferrous cation (Fe2+).It is categorized as a double salt of ammonium sulphate and ferrous sulphate. It is commonly used as a laboratory reagent. When dissolved in water, it yields an aqua complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+ which has an octahedral molecular structure. Mohr’s Salt is named after the German scientist Karl Friedrich Mohr who discovered it. Mohr's salt has a molar mass of 392.21 g/mol and it appears as a blue green solid. STRUCTURE OF MOHR’S SALT: Preparation: Mohr's salt is prepared by dissolving an equimolar mixture of hydrated ferrous sulphate and ammonium sulphate in water; containing a little of sulphuric acid and the crystallization from the solution. On crystallization light green crystals of ferrous ammonium; sulphate separate out. Ferrous sulphate FeSO4.7H2O Ammonium sulphate (NH4)2 SO4\ Mohr's Salt FeSO4-(NH4)2SO4.6H2O MATERIALS REQUIRED: Apparatus : Two beakers, china dish, funnel, funnel stand, glass rod, wash bottle, tripode stand, wire gauze, ferrous sulphate crystals, ammonium sulphate crystals,dilute sulphuric acid. CHEMICALS: Before coating, steel sheet or rod is passed through sulphuric acid. This treatment produces large quantities of iron(II) sulphate as a by product. A little more sulphuric acid may be added to ensure that the final solution remains slightly acidic. Since ammonia solution is moderately alkaline, the change from excess sulphuric acid to excess ammonia may be detected either with an indicator eg:- litmus paper, or by measuring the pH of the mixture with a pH meter. PROCEDURE: 1. Take a clean 250ml beaker, transfer 7g of FeSO4 and 3.5g of (NH4)2SO4 crystals to it. Add 2.3ml dilute H2SO4(to prevent hydrolysis). 2. In another beaker boil 20ml H2O for 5 minutes(to expand air). 3. Add boiling hot H2O to the content in small quantities. Stir until salts have completely dissolved. 4. Filter it and heat the filtrate in a china dish till it concentrate to crystallisation point. 5. Place the china dish over the beaker full of cold H2O, cool it and collect the crystals. Observation: Weight = Colour = Result: