ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING (2) - Copy
advertisement

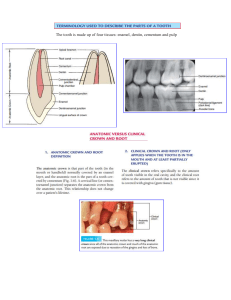
ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING BY: DR. FAMIA FOZAN LEARNING OBJECTIVES • At the end of this presentation, the audience will be able to : • Understand the importance of thorough history , clinical examination and investigations in leading the clinician towards accurate diagnosis • Develop knowledge about different pulpal and periapical pathosis • Able to identify adjuctive conditions that can coexist with pulpal and periapical diagnosis • Able to implement their gained knowledge during practise and formulate an effective treatment plan INTRODUCTION ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS True Emergency or an Urgency TREATMENT PLAN THE 1ST STEP IN DIAGNOSIS MAKING : THE SUBJECTIVE EXAMINATION • Chief Complaint : The primary reason(s) for which patient is seeking dental care. Dental history: the history of present illness past dental history • Medical history: Active and/or communicable disease Drugs , radiotherapy Allergies OBJECTIVE EXAMINATION • Extra oral examination and Vital signs: BP ,RR ,pulse ,facial swelling, discoloration ,lymphadenopathy,erythema, sinus tract etc • Intra oral examination : Soft and hard tissue examination : inspection, palpation, percussion • Clinical tests : Periodontal inflammation tests: inspection, palpation, percussion, bite test CONTD… • Pulp Sensitivity Tests 1. Cold test : Ice sticks, dry ice , ethyl chloride spray 2. Heat Test: Heated gp, frictional heat from rubber Prophy cup 3. Electric Pulp Testing • Selective Anesthesia : Used to narrow the focus of pain when patient can’t identify offending tooth • Caries Removal : Used to assess the depth of cavity • Radiographic Examination TYPES OF PULPAL PATHOSIS AND DIAGNOSIS • Reversible Pulpitis • Irreversible Pulpitis Symptomatic Asymptomatic • Hyperplastic Pulpitis • Pulp Calcification • Pulp Necrosis TYPES OF PERIAPICAL PATHOSIS AND DIAGNOSIS • Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis • Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis • Acute Apical Abscess • Chronic Apical Abscess • Condensing Osteitis ADJUNCTS TO ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS • Longitudinal fractures • Trauma • Resorption • Endodontic – periodontic pathosis LONGITUDINAL FRACTURES • Further diagnostic aids for longitudinal fractures: 1. Transillumination: craze lines vs cracked tooth 2. Wedging forces and bite test : cracked tooth vs split tooth 3. Restoration removal 4. Staining with methylene blue 5. Surgical assessment : in case of VRF BITE TEST TRANSILLUMINATION STAINING SURGICAL EXPOSURE CLASSIFICATION OF LONGITUDINAL FRACTURES • Craze lines: CRAZE LINES Common in posterior teeth FRACTURED CUSP • Fractured cusp : usually in teeth with Extensive caries or restoration CRACKED TOOTH • Cracked Tooth: an incomplete fracture More centered than fractured cusp • Split tooth: a complete fracture usually an extension and end result of cracked tooth SPLIT TOOTH • Vertical root fracture: Initiate and confined to root tooth usually has history of rct and post deep narrow periodontal defect and J-shaped radiolucency TYPES OF RESORPTION • Internal root resorption: perforating nonperforating • External Root Resorption: Apical EIRR Lateral EIRR Pressure Resorption • Invasive Cervical Root Resorption BALLOON SHAPED RADIOLUCENCY ENDODONTIC – PERIODONTIC LESIONS • Connection between pulp tissue and periodontium: Apical foramen , lateral canals, dentinal tubules CLASSIFICATION • Primary periodontal defects of Endodontic Origin: a coronally extended periapical lesion • Primary Periodontal defects: Of periodontal origin • Primary periodontal defects of Endodontic – Periodontic origin: True Combined Lesions TREATMENT PLANNING: PHASING TREATMENT • Emergency Treatment: patient presenting with pain and/or swelling, trauma r • Definitive Treatment : Involve the referral to specialised dental professionals Endodontist, Periodontist, Orthodontist, Oral surgeon, Prosthodontist, or Paediatric dentist The Comprehensive treatment plan: Treatment options along with their expected outcomes , merits and demerits Followups , further precautions and care and adjunctive procedures SUMMARY ? MCQS During a review of the patient’s medical history, it is noted that the patient is on intravenous bisphosphonates. What significance does it hold for patient and treatment plan? a) Possible side effect of bleeding disorder b) Possible side effect of osteonecrosis of jaw c) Inability to obtain adequate anesthesia d) Lowered pain threshold How does electrical pulp testing determine the degree of pulpal inflammation? a) A shorter response indicates healthier pulp b) A midrange response indicates pulp inflammation c) A midrange response indicates partial necrosis d) It can only be used to determine the presence or absence of vital tissue Which is one of the 4 characteristics of a periapical lesion of endodontic origin? a) The lamina dura of tooth socket is intact b) The radiolucency remains at the apex in radiographs at different cone angles c) The radiolucency tends to resemble a round circle d) It is usually associated with an irreversible pulpitis In which situation is caries removal necessary to obtain a definitive pulpal diagnosis? a) Deep caries with no symptoms and negative pulp testing b) Deep caries with no symptoms and positive pulp testing c) Shallow caries with mild symptoms and positive pulp testing d) Shallow caries with mild symptoms and negative pulp testing Which of the following conditions is most likely to be interpreted as tooth ache by a patient? a) TMJ dysfunction b) Inflammation of parotid gland c) Acute angina pectoris d) Maxillary sinusitis