Types of Acids: Strong, Weak, Concentrated, Dilute, Organic, Inorganic
advertisement

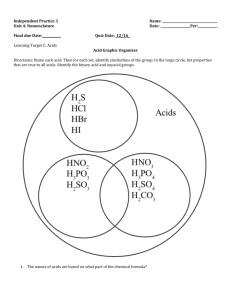
Types of acids 1. Strong and weak acids 2.Concentrated and dilute acids 3.Organic and inorganic acids 1.STRONG ACID => Those acids are called strong acids which dissolve completely in water (aqueous solution) to produce large amount of hydrogen ions+ (H+). E.g.- Hcl (hydrochloric acid), H2SO4 (sulphuric acid), HNO3 (nitric acid), HBr (hydrobromic acid). 2.Weak acid=> Those acids are called weak acids which don’t dissolve completely in water (aqueous solution) to give large amount of hydrogen ions+ (H+). E.g.-H2CO3 (carbonic acid), H3PO4 (phosphoric acid), CH3COOH (acetic acid) H3BO3 (boric acid)[ to make antiseptic] 3.Concentrated acids=> when an aqueous solution contains a large amount of acid in it, then it is called concentrated acid. 4.Dilute acids=> when an aqueous solution contains a less amount of acid in it, then it is called dilute acid. ✓ Dilution of acid :- The process of mixing concentrated acid with water to make it dilute is called dilution of acid. ✓ Note:- Dilution of acid should be done by adding C.A with water not by adding water with C.A. (because it is an exothermic reaction and produce a large amount of heat which can break the glass or splash to burn or face ) :-less than 1% concentrated HCl is present in human stomach :-approx 5% concentrated CH3COOH is present in vinegar. 5.organic acids=> Those acids which are obtained from living things(plants and animals) are called organic acid. ➢ E.g.- citric acid (lemon and orange) ➢ Lactic acid (milk and curd) ➢ tartaric acid (tamarind and grapes) ➢ Oxalic acid (tomatoes) ➢ Formic or Methanoic acid or HCOOH ant sting and nettle leaf sting) ➢ Acetic or ethanoic acid (vinegar) ➢ Malic acid (apples) ➢ Amino acid (proteins) ➢ Ascorbic acid (vitamin c). 6.Inorganic acids=> Those acids which are obtained from minerals are called inorganic acids. ➢ E.g. H2SO4 (sulphuric acid) ➢ HCl (hydrochloric acid) ➢ HNO3 (nitric acid) ➢ H2CO3 (carbonic acid). Note:- Basicity of acid=> Number of ionisable hydrogen ions (H+) present in one molecules of acid is called its basicity. ➢ H2SO4 basicity=2 (monobasic) ➢ HCL basicity=1(monobasic) ➢ HNO3 Basicity=1(monobasic) ➢ H2SO4 Basicity=2(monobasic) ➢ H2CO3 Basicity=2(monobasic) ➢ H3PO4 Basicity=3(tribasic) ➢ CH3COOH Basicity=1(monobasic) ➢ HCOOH Basicity=1(monobasic) Formation of acids ✓ Acids are formed by the:1. Reaction of non-metals with hydrogen ➢ ➢ Cl2 + H2 Br2 + H2 HCl HBr 2.Reaction of non-metal oxide with water:➢ ➢ ➢ CO2 + H2O SO3 + H2O NO2 + H2O H2CO3 H2SO4 HNO3. INDICTORS :- Indicators are those substances which change their colours when put into acid or base to show whether the given substance is base or acid. Indicator 1 litmus paper/soln[obtained from lichen plant of thallophyta group] 2 Methyl orange 3 Phenolphthalein 4 Turmeric 5 Beetroot 6 Red cabbage leaves Colour in acid Red Red Colourless Yellow Red-purple Red-purple Colour in base Blue Yellow Pink Reddish-brown Yellow Green ➢ Olfactory indicators :- Those substances which change their smell in acidic or basic solution is called olfactory indicators. E.g- onion, clove oil, vanilla essence. ➢ Universal indicator:- Universal indicator is a mixture of different indicators() which shows the strength of acids and bases with the help of a pH scale.