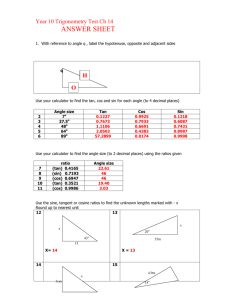
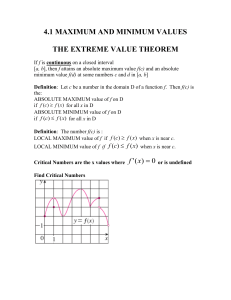
ACA
DEM
Y
FO
RE IN W E R E
O
M
U
FOR
N YO
SCAN N E E D E D WE RH E
D. M
BE W
HO Y
OU
ATH
YOU
NG
D. MATH ACADEMY
A* REVISION GUIDE
FOR IGCSE MATH
Achieve your desired grade with keyword
identification method, examples question.
D .
M A T H
A C A D E M Y
PREFACE
Welcome to our world of assisted learning in 'O'
Level Mathematics. Purchasing this GUIDE is your
FIRST STEP to achieve your desired mathematics
results.
Content included:
* TOPIC BY TOPIC example notes
**Graph drawing chapter was explained through
video format. Kindly click on the link attached to
learn more about it.
*** Variety of work examples per topic to help
student understand the KEY CONCEPTS.
Hope you will find this note USEFUL & ENRICHING
This note should be used in conjunction with:
* Regular school classes on Mathematics
*Doing practice on IGCSE Past Year Papers
W W W . D M A T H A C A D E M Y . C O M
D .
M A T H
A C A D E M Y
CONTENTS
RULES OF FRACTION
PERCENTAGE & INVESTMENT
(SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTEREST)
RATIO
STANDARD FORM
DIRECT & INVERSE PROPORTIONAL
SPEED, DISTANCE & TIME GRAPH
RECURRINGS DECIMALS
UPPER & LOWER BOUND
D .
M A T H
INDICES
A C A D E M Y
CONTENTS
SEQUENCES
SUBSTITUTION, FACTORISE & SIMPLIFY,
INEQUALITIES
LINEAR EQUATION
FUNCTION
SETS & VENN DIAGRAM
ANGLE & SHAPES PROPERTIES
D .
M A T H
A C A D E M Y
CONTENTS
INTERIOR & EXTERIOR ANGLE
SIN COS TAN & SIN + COS RULE
AREA & VOLUME
CIRCLE THEOREM
DRAWING & BEARING
MATHEMATICALLY SIMILAR
MATRIX & VECTOR
MEAN MODE MEDIAN
D .
M A T H
A C A D E M Y
CONTENTS
CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY & FREQUENCY
DENSITY GRAPH
CORRELATION & LINE OF BEST FIT
PROBABILITY
GRAPH DRAWING
SIN, COS, TAN GRAPH
COMPLETING THE SQUARE
2020
FUNCTION GRAPH IDENTIFICATION
GRADIENT FUNCTION & TURNING POINT
CHAPTERS WITH THIS FOLLOWING BATCH
MEAN IT'S SLIGHTLY HARDER & USUALLY
STUDENT WILL FALL INTO THE TRAP SET BY
EXAMINER
D. MATH ACADEMY
RULES OF
FRACTION
4
5
Numerator
Denominator
Rules on solving fraction with
different denominator
Improper
Fraction
L
L
A
16
1
D
E
=3
V
R
5
5 E
S
G
I
R
E
R
S
T
H
4 7 4 ×EM
3Y7×5
+ =AD +
5 3
C 5×3 3×5
A
H
T
A
12
+
35
47
2
M
.
=
=
=3
D
15
15
15
©
Mixed
Number
Rules on solving fraction with
different denominator
.
D
©
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
G
I
4𝑥
7
4𝑥 L×R
(3𝑥) 7 × (5𝑦)
+
= AL
+
Y
5𝑦 3𝑥
5𝑦
×
(3𝑥)
3𝑥
×
(5𝑦)
M
E
D
2
A
12𝑥
+
35𝑦
C
A
=
H
T
A
M
15𝑥𝑦
D
E
V
D. MATH ACADEMY
PERCENTAGE &
INVESTMENT
SIMPLE
&
COMPOUND
INTEREST
1. The current price of $ 5243 is an increased of 40% from the
previous year pricing.
ED
Original Price
V
R
E
S
E
R
New Price
S
T
Changes in % = (100+40)%
H
𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 = 5243 ÷ 140%
G
I
R
L
𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 = $3745
L
A
Y
M
E
2. The membership D
price of $ 3684 is expected to lowered by
A
C
15% next month
due to decrease in demand.
A
H
T
Original
Price
3684 × 85% = 𝑁𝑒𝑤 𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑛𝑔
A
M
.
Changes in % = (100-15)%
D
𝑁𝑒𝑤 𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑛𝑔 = $3131.40
©
𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 × 140% = 5243
John invested his savings that amount to $10,000 into a mutual fund. The rate of return
is 4% per annum. Find the return of this investment deal if he were to invest 5 years.
Solution guide:
• List down key information:
[Capital=10000, Rate=4%, Year=5, Return = ?]
• Fill up the value and identify the return.
10000 × 5 × 4% = $2000
D
E
V
R
E
Formula for Simple Interest
𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 × 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 × 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛
= 𝑅𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
L
L
A
Dixon investment generated $900 from his
capital of $8000 within 4 years. Find the
Y
rate of return of this investment per
annum.
M
E
D
Solution guide:
A
C
• List down key information:
A
900
H
?% =
× 100
[Capital=8000,
Rate=? %, Year=4]
T
8000 × 4
A
Mthe value and identify rate of return.
• Fill. up
D
? % = 2.81%
©8000 × 4 ×? % = 900
John invested his savings of $10,000 into a growth fund. The fund provide a 4%
compounded interest per annum. Find return of this deal after he invested for 5 years.
Solution guide:
• List down key information:
[Capital=10000, Rate=4%*, Year=5, Return = ?]
• Fill up the value and identify the return.
Y
M
E
D
CA
R
E
Formula for Compound Interest
𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 × (100 ± 𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒)𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒
= 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 + 𝑅𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛
S
T
H
G
I
R
10000 × 100% + 4% 5 = 12166.52902 ≈ 12166.53
** Return = 12166.53 − 10000 = $2166.53
L
L
A
D
E
V
S
E
R
Sam high risk growth fund is not performing and his investment fund suffer a 4%
exponential decrease. Find the loss from his $10,000 investment after 2 year.
A
• List down key
Hinformation:
T
A
[Capital=10000,
Rate=- 4 %*, Year=2]
M
.
D
• Fill up the value and identify his loss.
©
Solution guide:
10000 × 100% − 4% 2 = 9216
** Loss = 10000 − 9216 = $784
Jason purchased $10,000 worth of IBM stock. The return of the stock grew
exponentially and he received $3,000 worth of return in 4 year. Find the compound
interest earned by Jason.
Solution guide:
S
T
H
• List down key information:
[Capital=10000, Rate=?%*, Year=4, Return + Capital=13000]
L
L
A
• Fill up the value and identify the return.
10000 × 100%+? % 4 = 13000
©
D.
A
H
T
A
M
Y
M
E
D
CA
13000
4
100%+? % =
10000
4 13
100%+? % =
10
?% =
4
13
−1
10
? % ≈ 6.78%
× 100
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
Formula for Compound Interest
𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 × (100 ± 𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒)𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒
= 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 + 𝑅𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛
D. MATH ACADEMY
RATIO
1. The total price pool of $5000 is being distributed to Sam &
John with the ratio of 10:15. Find the amount John receive. ED
Total price pool
15
5000 ×
= 𝐽𝑜ℎ𝑛
25
𝐽𝑜ℎ𝑛 = $3000
John’s ratio
V
R
E
S
E
R
S
T
Total
ratio = 10 + 15
H
G
I
R
L
L
2. A to B ratio is 5:7 & B to C ratio
is 4:7. Find ratio of A to C.
A
Y
M∶ 𝐶
𝐴 ∶E𝐵
C’s 7 is required
D
A
5 ∶ 7
to multiply by 7
C
A’s 5 is required A
4 ∶ 7
H
to multiply
by
4
T
A
20 ∶ 28 ∶ 49
M
.
D
©
Ratio A: C will be 20:49
L.C.M of B will be 28
3. The map of Country is drawn under the following ratio
D
1: 1,000,000. Find the actual area in 𝑘𝑚2 of the township
E
V
2
R
with 3.2𝑐𝑚 on the map.
E
Unit conversion
Step 1
1: 1,000,000 = 1𝑐𝑚: 1,000,000𝑐𝑚
Step 2
1𝑐𝑚2 : 10 × 10 𝑘𝑚2
.
D
©
E
D
CA
A
H
1𝑐𝑚2 : 100𝑘𝑚2
T
A
M
1
1
1𝑐𝑚 =
𝑚=
𝑘𝑚
100
100000
Y
M
= 1𝑐𝑚: 10𝑘𝑚
S
T
H
S
E
R
L
L
A
÷ 100
G
I
R
÷ 1000
Final answer
3.2𝑐𝑚2 = 3.2 × 100𝑘𝑚2
= 320𝑘𝑚2
4. The map of Country is drawn under the following ratio
D
1: 5,000. Find the actual area in 𝑚2 of the township with
E
V
2
R
5.7𝑐𝑚 on the map.
E
Unit conversion
Step 1
1: 5,000 = 1𝑐𝑚: 5,000𝑐𝑚
Y
M
= 1𝑐𝑚: 50𝑚
Step 2
1𝑐𝑚2 : 50 × 50 𝑚2
1𝑐𝑚2 : 2500𝑚2
.
D
©
E
D
CA
T
A
M
A
H
S
T
H
1
1𝑐𝑚 =
𝑚
100
L
L
A
G
I
R
÷ 100
Final answer
5.7𝑐𝑚2 = 5.7 × 2500𝑚2
= 14,250𝑚2
S
E
R
D. MATH ACADEMY
STANDARD
FORM
Transform the following numbers into standard form:
Solution guide:
i) 1590000000
= 1.59 × 109
ii) 0.0000000923
= 9.23 × 10−8
.
D
©
Y
Mhow many times you need to
1. Count
E
D
shift the number to the RIGHT & make
A
C
A
H
T
A
M
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
1. Count how many times you need to
shift the number to the LEFT & make it
1.59
2. I shifted 9 times hence the 10 will have
a power of POSITIVE 9.
Solution guide:
it 9.23
2. I shifted 8 times hence the 10 will have
a power of NEGATIVE 8.
D
E
V
D. MATH ACADEMY
PROPORTIONAL
DIRECTLY &
INVERSE
𝑒 variable is directly proportional to 𝑥 + 1 2 . 𝑒 variable will be
D
E
equivalent to 20 when 𝑥 value is 4. Find the value of 𝑒 whenV
𝑥 is 9.
S
T
H
Solution guide:
• Adjust the formula according to variable given by the question.
𝑒 =𝑘 𝑥+1 2
L
L
A
• Fill up the value and identify value of k.
20 = 𝑘 4 + 1 2
20
4
𝑘= =
25
5
Y
M
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
• Fill up the value of e based on value of k & x.
4
𝑒 = 𝑥+1 2
.
D
©
5
4
= 9 + 1 2 = 80
5
G
I
R
R
E
S
E
R FORMULA
Direct
𝑦 = 𝑘𝑥
Indirect
𝑘
𝑦=
𝑥
𝑤 variable is inversely proportional to 𝑧 2 . 𝑤 variable will be
E9.D
equivalent to 8 when 𝑧 value is 4. Find the value of 𝑤 when 𝑧Vis
R
E
S
FORMULA
E
• Adjust the formula according to variable given by the question. R Direct
S
T
𝑦 = 𝑘𝑥
H
𝑤=
G
Indirect
I
R
𝑦=
• Fill up the value and identify value of k. LL
A
8=
Y
M
E
𝑘 = 16 × 8 = 128
D
A
C
• Fill up the value ofA
e based on value of k & x.
H
T
𝑤=
A
M
.
=D = 1 ≈ 1.58
©
Solution guide:
𝑘
𝑧2
𝑘
𝑥
𝑘
42
128
92
128
81
47
81
D. MATH ACADEMY
GRAPH
SPEED,
DISTANCE &
TIME
Distance (km)
D
E
V
1. Find how long the subject stop for a rest.
NOT TO
SCALE
30
R
E
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡 ℎ𝑎𝑑 𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑢𝑡 3 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟 𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒.
𝐼𝑡 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑏𝑒 𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑦 𝑡ℎ𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑔ℎ 𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑐𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑎 ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑧𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙
𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 − 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ.
S
T
H
G
I
R
S
E
R
2. Find what time the subject reaches his/her desired
destination. Show the answer in am/pm format.
0
12:00
14:00
17:00
21:00
Y
M
E
D
3. Find total distance travelled.
A
C
A
H
T
A
M Speed.
4. Find. Average
D
©
Time (24-hour format)
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 = 30 + 30 = 60𝑘𝑚
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 =
L
L
A
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠 ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑜𝑟 ℎ𝑒𝑟 𝑑𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑎𝑡 9𝑝𝑚.
5. Find the speed of the first 2 hour of his/her journey.
(30−0 )𝑘𝑚
30 𝑘𝑚
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = (14:00 −12:00)ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟 = 2 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟 = 15 𝑘𝑚/ℎ
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒
60𝑘𝑚
=
= 6.67 𝑘𝑚/ℎ
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒
9ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟
Speed (km/h)
1. Find the deacceleration of the last 30 minutes.
𝐷𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
= (90−120) or 50 ÷
NOT TO
SCALE
50
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑
𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒
50
60
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
= −100𝑘𝑚/ℎ2
D
E
V
(90−120)
60
2. Find the acceleration of the first 70 minutes.
0
70
90
Y
M
120
E
D
3. Find total distance travelled.
A
C
A
H
T
A
M
.
D
©
Time (minutes)
L
L
A
G
I
R
*Alternatively, you can calculate using trapezium formula
1 70
×
× 50
2 60
1 120 − 90
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 = ×
× 50
2
60
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 =
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 =
90 − 70
× 50
60
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 = 58.33𝑘𝑚
Convert the minutes
into hour format
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑
𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = 𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒
50
70
= 70 or 50 ÷ 60
60
= 42.86𝑘𝑚/ℎ2
4. Convert the speed 50km/h into m/s.
50 × 1000
𝑚/𝑠
1 × 60 × 60
125
50𝑘𝑚/ℎ =
𝑚/𝑠
9
50𝑘𝑚/ℎ ≈ 13.89𝑚/𝑠
50𝑘𝑚/ℎ =
D. MATH ACADEMY
RECURRING
DECIMALS
D
E
V
Type 1 of recurring decimals
Solve 𝟎. 𝟑ሶ 𝟐ሶ
0. 3ሶ 2ሶ = 0.323232 …
𝑆𝑒𝑡 𝑥 = 0.323232 …
100𝑥 = 32.323232 …
*Minus to cancel off the part that’s recurring
99𝑥 = 32
.
D
©
A
H
T
A
M
32
𝑥=
99
Y
M
E
D
CA
100𝑥 − 𝑥 = 32
R
E
Type 2 of recurring decimals
S
E
Solve 𝟎. 𝟐ሶ 𝟐ሶ
R
S …
0. 2ሶ 2ሶ = T0.222222
H
G
I
𝑆𝑒𝑡
𝑥 = 0.222222 …
R
L 10𝑥 = 2.222222 …
L
A
10𝑥 − 𝑥 = 2
*Minus to cancel off the part that’s recurring
9𝑥 = 2
2
𝑥=
9
D. MATH ACADEMY
UPPER &
LOWER
BOUND
Common term used to describe Upper Bound & Lower Bound:
Upper Bound:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Highest possible value
Greatest possible value
Maximum
The most
Lower Bound:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Lowest possible value
Smallest possible value
Minimum
The least
A
H
E
D
CA
Y
M
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
T
A
StudentM
is advise to map out the equation of the question. By doing so you can
. rounding the wrong value & fulfil the requirement of the respective question.
eliminate
D
©
1. The perimeter of a square is 60cm and it’s rounded to the nearest 5cm. Find
the Upper & Lower bound of it’s area. 𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 = 𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 = 5 = 2.5𝑐𝑚
2
2
Upper
Lower
60
𝑆𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 = = 15𝑐𝑚
4
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
𝑆𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 = 15𝑐𝑚
D
E
V
𝑈𝐵 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 = (15 + 2.5) × (15 + 2.5) 𝐿𝐵 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 = (15 − 2.5) × (15 − 2.5)
= 306.25𝑐𝑚2
= 156.25𝑐𝑚2
L
L
A
G
I
R
2. A rectangle has a side which is 5cm and 8cm. The sides of the rectangle is
rounded to the nearest millimeter. Find it’s perimeter Upper & Lower bound.
Y
M 1cm= 10mm
E
D
𝑈𝐵 = 2 5 + 0.05 + 2(8A
+ 0.05)
C
= 26.2𝑐𝑚 H A
T
Lower
A
M
.
𝐿𝐵
= 2 5 − 0.05 + 2(8 − 0.05)
D
© = 25.8𝑐𝑚
Upper
Hence,1mm=0.1cm
𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 =
2
0.1
= 0.05𝑐𝑚
2
3. Jamie bought a piece of cloth that’s 50m long and it’s rounded to the nearest
1200cm. She uses 10m to create a dress, and it’s rounded to the nearest 2 meter.
Find the maximum & least dress she can make with the cloth.
R
E
𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 =
2
Cloth rounding value
100cm = 1m Hence, 1200cm=12m
12
= 6𝑚
2
Y
M
E
D
(50 + 6)
A
C
𝑈𝐵 =
= 6.22
≈ 6 𝑑𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠
A
10 − 1
H
T
Lower
A
M
.
(50 − 6)
D
© 𝐿𝐵 = 10 + 1 = 4.88 ≈ 4 𝑑𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠
Upper
D
E
V
S
E
Dress rounding value R
S
T
H
= 1𝑚
G
I
R
LFor student to obtain upper bound in fraction question.
L
A
2
1
The numerator is required to adjust to upper bound and
denominator is required to adjust to lower bound. By
doing so, student is able to get the maximum value
For student to obtain lower bound in fraction question.
The numerator is required to adjust to lower bound and
denominator is required to adjust to upper bound. By
doing so, student is able to get the least value
D. MATH ACADEMY
INDICES
𝑥
𝑦
✓Represent number that was raised to a power.
✓Commonly known as power or index
(Shows how many times the number multiply by itself)
Core concept:
✓𝑎1 = 𝑎
✓𝑎0 = 1
✓𝑎 × 𝑎 × 𝑎 = 𝑎1 × 𝑎1 × 𝑎1 = 𝑎1+1+1 = 𝑎3
Y
M
.
D
©
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
L
L
A
G
I
R
D
E
V
𝑎 𝑥 × 𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥+𝑦
𝑥 2 × 𝑥 5 = 𝑥 2+5 = 𝑥 7
𝑎 𝑥 ÷ 𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥−𝑦
𝑦 4 ÷ 𝑦 3 = 𝑦 4−3 = 𝑦1 = 𝑦
(𝑎 𝑥 ) 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥𝑦
(𝑥 4 )3 = 𝑥 4×3 = 𝑥 12
𝑎−𝑛 =
1
𝑎𝑛
Y
M
E
D
A
C
𝑎 =A𝑎 = ( 𝑎 )
H
1
𝑎𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑎
𝑦
𝑥
.
D
©
𝑥
𝑦
G
I
R
1
1
=
=
= 𝑦 −(−15) = 𝑦15
−5
3
−5×3
−15
(𝑦 )
𝑦
𝑦
1
g3 = 3 g
𝑥
𝑦
2
3
g 3 = 𝑔2 = ( 3 𝑔)2
𝑦
𝑦
( 𝑥 × y)2 = 𝑥 2 × 𝑦 2
T 𝑎×𝑏 = 𝑎 ×𝑏
A
M
𝑦
L
L
A
1
S
T
H
𝑎 3
𝑎3
= 3
𝑏
𝑏
S
E
R
𝑥
𝑦𝑧
3
𝑥3
= 3 3
𝑦 𝑧
R
E
D
E
V
D. MATH ACADEMY
SEQUENCES
Type 1: Arithmetic Sequence (also known as Linear Sequence)
0th
Term
-1
3
7
1st
Term
.
D
©
•
Y
M
E
•
D
A
C
A
•
H
T
A
•
M
?
L
L
A
15
G
I
R
S
T
H
19
S
E
R
R
E
D
E
V
Type 2: Geometric Sequence (also known as Quadratic Sequence)
4
Question
1st
9
5
2
©
7
2
2nd
D.
16 25
9
2
E
D
5
CA
A
H
T
A
M
Y
M
2
𝑎𝑛 + 𝑏𝑛 + 𝑐
?
L
L
A
4
•
S
T
• H
G
I
R
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
2
𝑛 + 2𝑛 + 1
2
(𝑛 + 1)
Special Type: Sequences with POWER
4
8
▪
Y
M
▪
.
D
©
E
D
CA
R
E
S
E
16 32 64 R
S
T
H
G
I
R
L
L
A
A
H
T
A
M
▪
D
E
V
(𝑛−1)
×2
Special Type: Sequences with CUBE
84
Question
24 64 140 264
5 40 76 124
16
1st
2nd
T
A
M
.
D
©
•
G
I
R
S
T
H
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
2 36 48 ALL
24
Y
M
3
2
E
𝑎𝑛 + 𝑏𝑛 + 𝑐𝑛 + 𝑑
2 AD12
12
C
A
H
3rd
12
•
16
24
8
3
2𝑛 + 2𝑛 + 4
D. MATH ACADEMY
SUBSTITUTION
FACTORISE &
SIMPLIFY
Solve the following simultaneous equation:
Solution guide [Method 1]:
From 1
1
𝑥 − 8𝑦 = 1
2
1
𝑥 + 2𝑦 = 6
2
Substitute 3 into 2
12+1
2 + 16𝑦 + 2𝑦 =
2
1
𝑥
2
− 2(8𝑦) = 2(1)
E
D
CA4 + 32𝑦 + 4𝑦 = 13
𝑥 − 16𝑦 = 2
𝑥 = 2 + 16𝑦
©
D.
T
A
M
A
H
3
Y
M
L
L
A
1
S
T
H
2
G
I
R
2
R
E
S
E
R
1
Substitute 𝑦 = into 3
4
1
𝑥 = 2 + 16
4
2 2 + 16𝑦 + 2(2𝑦) = 13
𝑥 =2+4=6
36𝑦 = 9
Final answer
𝑥=6
𝑦=
9
1
=
36
4
D
E
V
𝑦=
1
4
Solve the following simultaneous equation:
Solution guide [Method 2]:
Multiply 2 by 4
4 𝑥 + 4(2𝑦) = 4
1
6
2
4𝑥 + 8𝑦 = 26
3
©
D.
T
A
M
1
1
𝑥 − 8𝑦 = 1
2
1
2
𝑥 + 2𝑦 = 6
2
Substitute 𝑥 = 6 into 3
3 minus 1
1
4 6 + 8𝑦 = 26
𝑥 − 8𝑦 + 4𝑥 + 8𝑦 = 1 + 26
2
8𝑦 = 26 − 24
1
𝑥 − 8𝑦 + 4𝑥 + 8𝑦 = 27
2
1
2
𝑦= =
8
4
1
4 𝑥 = 27
Final answer
Y
M
E
D
CA
A
H
R
E
D
E
V
L
L
A
S
T
H
G
I
R
S
E
R
2
𝑥=
27
4
1 = 6
2
𝑥=6
𝑦=
1
4
Solve the following question:
TYPE 1
10
35 − 4 3𝑥 + 4 = 22 − 3𝑥
−12𝑥 + 3𝑥 = 22 − 35 + 10
−9𝑥 = −3
1
𝑥 = −9 = 3
6𝑥−3
4𝑥+5
=
5
2
A
H
2(6𝑥 − 3) = 5(4𝑥 + 5)
T
A
M
12𝑥 − 6 = 20𝑥 + 25
.
D
−8𝑥 = 31
©
12𝑥 − 20𝑥 = 25 + 6
31
7
𝑥 = 8 = 38
Y
M
E
D
CA
TYPE 2
L
L
A
S
T
H
G
I
R
2(5 − 2𝑥)
TYPE 3
2 5 − 2𝑥 = 8 − 3𝑥
10 − 4𝑥 = 8 − 3𝑥
−4𝑥 + 3𝑥 = 8 − 10
−𝑥 = −2
𝑥=2
R
E
S
E
R
This is a rectangle shape.
Find the value of x & the longer
side’s value of this shape.
35 − 12𝑥 − 10 = 22 − 3𝑥
−3
D
E
V
8 − 3𝑥
D
E
V
Rearrange & make “x” the subject of all following equation:
•
2𝑚−𝑥
𝑘=
𝑥
𝑘 2𝑚 − 𝑥
=
1
𝑥
𝑘𝑥 = 2𝑚 − 𝑥
•
3𝑥 3 𝑦
= 𝑡2
5
3𝑥 3 𝑦
5
𝑘𝑥 + 𝑥 = 2𝑚
2𝑚
𝑥=
𝑘+1
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
S
T
H
G
I
R
=
(𝑡
)
L
AL
1
2
Y
M 3𝑥 𝑦
E
D
CA
𝑥 𝑘 + 1 = 2𝑚
•
3
5
2
2 2
4
𝑡
=
1
4
5𝑡
𝑥3 =
3𝑦
𝑥=
3
5𝑡 4
3𝑦
R
E
S
E
R
𝑥2𝑦
= 𝑘𝑡
3𝑘
𝑥2𝑦
𝑘𝑡
=
3𝑘
1
𝑥 2 𝑦 = 3𝑘 2 𝑡
2𝑡
3𝑘
𝑥2 =
𝑦
3𝑘 2 𝑡
𝑥=±
𝑦
If 𝑎 = −4, 𝑏 = 2 & 𝑐 = −3. Find the value of these expressions.
Solution guide:
•
𝑎𝑐 2
8−
𝑏
•
3𝑎
4𝑐
+
𝑏
𝑎
=8−
−4 −3 2
2
3 −4
=
2
=8−
−4 (9)
2
=−
= 8 + 18
= 26
.
D
©
4 −3
+
−4
12
−12
+
2
−4
E
D
= −3
A
C
Y
M
= −6 + 3
−36
=8−
2
T
A
M
A
H
•
L
L
A
𝑎2 +𝑏2 +𝑐 2
𝑎+𝑏+𝑐
S
T
=H
G
I
R
S
E
R
−4 2 + 2 2 + −3 2
−4+2+(−3)
16+4+9
=
−5
=
29
−5
= −5.8
R
E
D
E
V
A theatre is running a special show this month. The adult ticket is
D
$10 more expensive than the children ticket. They collected $1700
E
V
R
for this Saturday’s show for 50 adult guest and 30 children.
Find
E
S
E
the price of adults and children ticket respectively.
R
Solution guide:
G
I
R
S
T
Result
H
L
L
𝐴𝑑𝑢𝑙𝑡 𝑡𝑖𝑥
= 10 + 𝑥
A
Y
EM
• Construct equation based on info given. Set children price as x.
𝐶ℎ𝑖𝑙𝑑𝑟𝑒𝑛 𝑡𝑖𝑥 = 𝑥
&
D
500 + 50𝑥 + 30𝑥 = 1700 A
C
A
80𝑥H= 1700 − 500
T
A
80𝑥 = 1200
M
.
D
©
𝑥=
= 15
50 10 + 𝑥 + 30𝑥 = 1700
1200
80
Children ticket
𝑥 = 15
Adult ticket
10 + 𝑥 = 25
Simplify the following equation:
• 2𝑚𝑛 + 𝑚2 − 6𝑛 − 3𝑚
• 2𝑛 + 4𝑚2 − 𝑛2 − 2𝑛𝑚2
= 2𝑚𝑛 − 6𝑛 + 𝑚2 − 3𝑚
= (2𝑛 + 𝑚)(𝑚 − 3)
2
2
• 4𝑦 − 81
= 2𝑦
2
−9
Y
M
E
D
CA
2
= (2𝑦 − 3)(2𝑦 + 3)
.
D
©
− 𝑛(𝑛 + 2𝑚2 )
2
= 2𝑛 𝑚 − 3 + 𝑚 𝑚 − 3
T
A
M
A
H
R
E
S
E
= (2 − 𝑛) 𝑛 + 2𝑚 R
S
T
H
G
I
R
•
7𝑦
L − 28
L
A
= 2 𝑛 + 2𝑚2
= 7(𝑦 2 −4)
= 7 𝑦 2 − 22
= 7[ 𝑦 − 2 𝑦 + 2 ]
D
E
V
Factorize the following equation:
•
3𝑡 2 −18𝑡+24
•
3𝑡+15
3(𝑡 2 −6𝑡+8)
=
3(𝑡−5)
3(𝑡−2)(𝑡−4)
=
3(𝑡−5)
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
9𝑥 − 17𝑥 + 4 ; 𝑎 =
9 , 𝑏 = −17, 𝑐 = 4
S
T
H
𝑥 = IG
R
L
L
A 𝑥=
𝑜𝑟
2𝑎
2
𝑡 2 − 6𝑡 + 8
−
𝑡
4
−
𝑡
2
−4𝑡
− 2𝑡
(𝑡−2)(𝑡−4)
=
(𝑡−5)
−𝑏±
2
𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 ≈
𝑏2 −4𝑎𝑐
Y
M
−4 × −2 = + 8
−4𝑡 − 2𝑡 = −6𝑡
E
D
CA
−(−17)±
−17 2 −4 9 (4)
2(9)
17+ 145
18
17− 145
18
𝑥 = 1.61 𝑜𝑟 0.275
This type of question
couldn’t be solve using
method 1, as no
combination could get -17x
A
H to solve this type of equation:
There’s two method
T
A
1. Method
1
is shown in the question on the left. [BASIC method]
M
. 2 is using the quadratic equation formula as shown at the righthand side.
2. D
Method
©
[ ADVANCE method]
Expand & Simplify the following question:
•
• 2 3𝑥 + 1 2 − 3 2𝑥 + 5 2
3(5𝑥 − 3)(2𝑥 + 1)
R
E
D
E
V
S
E
= 30𝑥 + 15𝑥 − 18𝑥 − 9
= 2 9𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 1 − 3 4𝑥 R
+ 10𝑥 + 10𝑥 + 25
S
T
= 30𝑥 − 3𝑥 − 9
= 2 9𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 1 − 3(4𝑥
+ 20𝑥 + 25)
H
G
I
= 18𝑥 + 12𝑥L+R
1 − 12𝑥 − 60𝑥 − 75
L
A
• 8 − 3𝑦
= 6𝑥 − 48𝑥 − 74
Y
M
= (8 − 3𝑦)(8 − 3𝑦)
E
D
A
C
= 64 − 24𝑦 − 24𝑦 +A
9𝑦
H
T
= 9𝑦 − 48𝑦
+ 64
A
M
.
D
©
= 15𝑥 − 9 2𝑥 + 1
= 2 3𝑥 + 1 3𝑥 + 1 − 3[ 2𝑥 + 5 2𝑥 + 5 ]
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
D. MATH ACADEMY
INEQUALITIES
Common term used to describe inequalities:
>
1. More than…
<
1. Less than…
≥
1. More than equal to…
2. Not less than…
3. At least…
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
≤
1. Less than equal to…
2. Not greater or More than…
3. At most…
.
D
©
Y
M
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
D
E
V
Expand & Simplify the following inequalities:
D
E
V
• −12 − 3𝑦 > 3 + 2𝑦
• −10 + 3𝑦 > 3 + 2𝑦
• 4 + 5𝑦 > 3 + 4𝑦
−3𝑦 − 2𝑦 > 3 + 12
3𝑦 − 2𝑦 > 3 + 10
5𝑦 − 4𝑦 > 3 − 4
−5𝑦 > 15
𝑦 > 13
5𝑦 < −15
𝑦<−
15
5
𝑦 < −3
Example 1:
Trickiest among all inequalities question.
Things to take note:
When you convert the -5y back into 5y,
the inequalities sign changed it’s
direction. The value at the opposite side
is changed into -15.
.
D
©
Y
M
≤ : Less than equal to
< : Less than
E
D
CA
A
H
T
A
M
Signage:
≥ : More than equal to
> : More than
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R𝑦 > −1
E.g. y ? 5
if y ≥ 5, the possible integer results could be 5, 6,7, …
if y > 5, Value of 5 will be exclude. The possible integer
result will be 6, 7, 8, …
if y ≤ 5, the possible integer result could be 5, 4, 3, …
if y < 5, Value of 5 will be excluded. The possible integer
result will be 4, 3, 2, …
L
L
A
Example 2:
Simplest among all inequalities
question.
No changes required.
Example 3:
Type of inequalities question that
might causes confusion on student.
No changes required.
The negative sign at the right-hand
side you can leave it as it is.
D. MATH ACADEMY
LINEAR
EQUATION
Core Formula
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐
( 1, 8)
𝑦 −𝑦
𝑚= 2 1
𝑥2 −𝑥1
𝑚𝑂𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 × 𝑚𝑛𝑒𝑤 = −1
𝑚𝑖𝑑𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡:
( 7, 5)
𝑥1 +𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2
,
2
2
( 2, 5)
𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒:
.
D
©
L
L
A
𝑥2 − 𝑥1 2 + 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 2
S
T
H
G
I
R
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
Y
MFind L. A’s gradient
Step 1:
E
D
𝑚=
=
=−
A
C
A
H
T
A
M
Question 1
Line A passed through two
point (1, 8) and (7, 5).Line
B is parallel to Line A and
passed through (2, 5). Form
the equation of line B.
𝑦2 −𝑦1
𝑥2 −𝑥1
5−8
7−1
1
2
Step 2: Substitute m into L. B’s formula
1
𝑦 =− 𝑥+𝑐
2
5=−
1
2
2 +𝑐
𝑐 =5+1=6
1
Equation for B: 𝑦 = − 2 𝑥 + 6
Core Formula
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐
(1, 6)
𝑦 −𝑦
𝑚= 2 1
𝑥2 −𝑥1
𝑚𝑂𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 × 𝑚𝑛𝑒𝑤 = −1
𝑚𝑖𝑑𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡:
𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒:
𝑥2 − 𝑥1 2 + 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 2
(3, 4)
A
Step 2: Find L. A’sH
gradient
T
A
𝑚
×M
𝑚
= −1
.
D
©× 𝑚 = −1
𝑂𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙
1
2
𝐴
𝑚𝐴 = −2
𝑁𝑒𝑤
L
L
A
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
Y
M Step 3: Substitute m of L. A into the formula
E
D
CA
Step 1: Find L. B’s gradient
𝑦 −𝑦
5−3
1
𝑚= 2 1=
=
𝑥2 −𝑥1
7−3
2
S
T
H
(7, 5)
𝑥1 +𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2
,
2
2
Question 2
Line B passed through two
point (3, 4) and (7, 5).Line A
is perpendicular to Line B
and passed through (1, 6).
Form the equation of line A.
𝑚𝐴 = −2
𝑦 = −2𝑥 + 𝑐
Step 4: Form the equation after identifying C
6 = −2(1) + 𝑐
𝑐 =6+2=8
Equation:
𝑦 = −2𝑥 + 8
Find the inequalities equation that defines Region R
•
𝑦2−𝑦1
𝑚 = 𝑥2−𝑥1
5−0
1
= 10 − 0 = 2
L
L
A
x1, y1
( 0, 0)
G
I
R
( 10, 5)
Y
𝑐E
=M
𝑦 − 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡 = 0,
D
because (0,0)
A
C
A
H
T
A
• 𝐹𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 M
𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
• 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑟𝑑 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
𝑥 ≥D
2. ≈ 𝑥 𝑚𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑛 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜 2 y > 𝑥
©• 𝑆𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
1
2
y≤5
S
T
H
x2, y2
≈ 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑙𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑛 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜 5
D
E
V
Steps to identify the
answer:
1. Always focus on
the horizontal &
vertical line first as
they’re the easiest
R
E
S
E
R
2. Find 2 coordinate
of the slanted lines
to calculate it’s
gradient & identify
it’s Y – intercept
3. Inequalities
question with
graph will always
involve the
following formula:
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐
1
2
≈ 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑚𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑛 𝑥 *Because the line is dotted
Solve the following question:
D
E
V
A 4500 Box need to be packed into storage unit. There are two sizes of storage unit available. The large unit can hold up to 500
box and the small one can fit 300 box only. No more than 11 storage unit can be used and at least 2 unit storage must be small.
Lets x be the largest unit used and y be the small unit used. Label the region they lapse with each other as R.
Equation:
1. 500𝑥 + 300𝑦 ≤ 4500
5𝑥 + 3𝑦 ≤ 45
3𝑦 ≤ 45 − 5𝑥
45 − 5𝑥
𝑦≤
3
When x=0, y=15
When y=0, x=9
2. 𝑥 + 𝑦 ≤ 11
𝑦 ≤ 11 − 𝑥
When x=0, y=11
When y=0, x=11
.
D
©
3. 𝑦 ≥ 2
L
L
A
G
I
R
11
Y
M
E
D
CA
A
H
T
A
M
S
T
H
15
𝑅
2
9 11
S
E
R
R
E
SHADE
Dixon bought some fruits for his family.
He wanted to get x amount of Watermelon & y box of Kiwi
5𝑥 + 15𝑦 ≤ 105
15𝑦 ≤ 105 − 5𝑥
105 5
𝑦≤
− 𝑥
15 15
1
𝑦 ≤ 21 − 𝑥
3
X
0
21
y
7
0
1. He bought more Watermelon than Kiwi
2. He wanted to buy less than 10 Watermelon
3. He also want to get at least 2 box of Kiwi
SHADE
SHADE
SHADE
R
SHADE
SHADE
SHADE
SHADE
A
H
T
A
M
Y
M
E
D
CA
SHADE
Q4.
Find the maximum amount of each fruit Dixon can
buy.
Dixon can at most buy 9 Watermelon and 4 box of
Kiwi.
.
D
©
*Because the line is doted instead of solid when x = 10 & y =5
S
T
H
Q1. Write down the inequalities
• 𝐹𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
𝑥>𝑦
• 𝑆𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
𝑥 < 10
• 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑟𝑑 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
y≥2
L
L
A
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
Q2. The price of Watermelon on promotion is $5 each & each box
of Kiwi is price at $15. Dixon don’t want to spend more than $105
on buying fruits. Form an inequalities for the statement above:
• 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒:
5𝑥 + 15𝑦 ≤ 105
Q3. Draw out the inequalities line at the graph on the left & shade
the unwanted region.
D. MATH ACADEMY
FUNCTION
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2 + 1 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑥, 𝑥 > 0
ℎ 𝑥 = 2𝑥 − 3
• Find 𝑥 when ℎ 𝑥 = 7
ℎ 𝑥 =7
• Find 𝑓𝑓 2
= 𝑓(22 + 1)
L
L
A
10
𝑥= =5
2
−1
= 26
• Find 𝑓 𝑥 + 2 , Give your
• Find ℎ (𝑥)
ℎ 𝑥 = 2𝑥 − 3
answer in the simplest form
𝑓 𝑥 + 2 = (𝑥 + 2)2 +1
𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 3
= 𝑥+2 𝑥+2 +1
𝑥 = 2𝑦 + 3
= 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 4 + 1
2𝑦 = 𝑥 − 3
= 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 5
𝑥−3
ℎ−1 𝑥 = 𝑦 =
Y
M
.
D
©
S
T
H Hence, 𝑥 = 4
G
I
R
2𝑥 = 7 + 3
= 52 + 1
E
D
CA
T
A
M
A
H
2
R
E
S
E
R𝑥 = 4 = 256
𝑥
2𝑥 − 3 = 7
= 𝑓(5)
D
E
V
• Find 𝑥 when g 𝑥 = 256
𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑥 = 256
4
• Find 𝑓𝑓 −1 2
=2
• Find ℎ ℎ−1 𝑥 + 2
=𝑥+2
D. MATH ACADEMY
SETS & VENN
DIAGRAM
Sets & Venn diagram
•A collection of numbers or objects
Example: D = {m, a, t, h,}
What’s Set?
The alphabet m, a, t, & h is the ELEMENT OR MEMBERS of the D Set.
L
L
A
Symbol that usually being use in this chapter:
Y
M
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
D
E
V
Example:
1. When D = {M, A, T, H} & G = { } & B = { M, A, T, H} & Z = {A, T}
A ∈ of set D
X ∉ DD
A element is an element
X element is not an element of set D
G=Ø
B⊆D
Y
M
E
D
CA
G is an empty set
L
L
A
S
T
H
G
I
R
T
A
M
A
H
Set B is a subset of set D, as set B has some or all element of set D
.
D
©
Z⊂D
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
A∪B
A∩B
B’
Z is a proper subset of D, as set Z has some element of set D
A∩(B ∪ C)’
D. MATH ACADEMY
ANGLES &
SHAPE
PROPERTIES
Angle properties example:
𝐼𝑠𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑇𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
L
L
A
𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑙 𝑇𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
Y
M
•
•
•
•
-
𝑨𝑪𝑼𝑻𝑬 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
Between 0 to 90 degree
𝑹𝑰𝑮𝑯𝑻 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
90 degree
𝑶𝑩𝑻𝑼𝑺𝑬 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
Between 90 to 180 degree
𝑹𝑬𝑭𝑳𝑬𝑿 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
More than 180 degree
S
T
H
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
• 𝐼𝑠𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑇𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
- Two side of it has the same length
- Two side that has the same length has the same angle value
E
D
CA
A
H
• 𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑙T𝑇𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
Aof it has the same length
- ThreeM
side
. side that has the same length has the same angle value
- All
three
D
©
- Each side is 60 degree as the interior angle of any triangular shape is 180 degree
Angle properties example:
𝑏
𝑎
𝑎
𝑏
S
T
H
E
D
CA
𝑏
T
A
M
A
H
𝑐
Y
M
𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 180
𝑰𝒏𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒓 𝑨𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒂 𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆
𝑎
L
L
A
G
I
R
𝑐
𝑎+𝑏 =𝑐
𝑬𝒙𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒓 𝑨𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒂 𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆
R
E
S
E
R
𝑐
𝑑
𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 360
𝑨𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆 𝒂𝒕 𝒂 𝒑𝒐𝒊𝒏𝒕
𝑏
.
D
©
𝑎
𝑐
𝑎 + 𝑏 = 180
𝑨𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆 𝒐𝒏 𝒂 𝒔𝒕𝒓𝒂𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒕 𝒍𝒊𝒏𝒆
𝑎
𝑏
𝑎=𝑐 & 𝑏=𝑑
𝑽𝒆𝒓𝒕𝒊𝒄𝒂𝒍𝒍𝒚 𝒐𝒑𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒊𝒕𝒆 𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆𝒔
𝑏
𝑐
𝑎
D
E
V
𝑑
𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 + 𝑑 = 360
𝑨𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆 𝒊𝒏 𝒂 𝒒𝒖𝒂𝒅𝒓𝒊𝒍𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒍
Angle properties example:
40
𝑎
S
T
H
25
G
I
R
𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑎:
T
A
M
A
H
𝑎=𝑏
𝑪𝒐𝒓𝒓𝒆𝒔𝒑𝒐𝒏𝒅𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆
.
D
©
Y
M
E
D
CA
𝑏
𝑎
L
L
A
𝑷𝒆𝒓𝒑𝒆𝒏𝒅𝒊𝒄𝒖𝒍𝒂𝒓 𝒍𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒔
𝑷𝒂𝒓𝒂𝒍𝒍𝒆𝒍 𝒍𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒔
𝑏
𝑎
𝑎=𝑏
𝑨𝒍𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒏𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
𝑻𝒊𝒎𝒆 𝒕𝒐 𝒕𝒊𝒎𝒆 𝒔𝒕𝒖𝒅𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝒊𝒔 𝒓𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒊𝒓𝒆𝒅 𝒕𝒐 𝒂𝒅𝒅 𝒍𝒊𝒏𝒆 𝒊𝒏𝒕𝒐
𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒈𝒓𝒂𝒑𝒉 𝒕𝒐 𝒇𝒊𝒏𝒅 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒄𝒐𝒓𝒓𝒆𝒄𝒕 𝒂𝒏𝒔𝒘𝒆𝒓:
40
40
25
25
𝑎 = 25 + 40 = 65
Shapes & detailed information:
Popular Triangle Shapes
- Equilateral
- Isosceles
- Right, Obtuse & Acute
Y
M
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
S
T
H
G
I
R
S
E
R
Popular Quadrilateral Shapes
- Parallelogram
- Rectangle
- Trapezium
L
L
A
R
E
Popular Polygon Shapes
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Octagon
Keyword:
Regular: Means that all side is
the same length & Interior angle
will be the same as well
D
E
V
Line of Symmetry & Rotational Symmetry:
Shape
Line of Symmetry
Rotational Symmetry
Scalene Triangle
0
1
Isosceles Triangle
1
1
Equilateral Triangle
3
3
Kite
1
Trapezium
0
L
L
A
Parallelogram
Rectangle
2
A
H 4
T
A
M
Square
.
D
© Regular Octagon
Regular Pentagon
Regular Hexagon
Y
M
E
D
C2A
0
Rhombus
1
1
2
2
2
4
5
5
6
6
8
8
G
I
R
S
T
H
ISOSCELES TRIANGLE
It has 1 line of
symmetry
&
Rotational symmetry of
order 1
(Choose one point, turn
it 360 degree & identify
how may times it maps
on to itself
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
PARALLELOGRAM
It has NO line of
symmetry
&
Rotational symmetry of
order 2
(Choose one point, turn
it 360 degree & identify
how may times it maps
on to itself
Plane of Symmetry:
Y
M
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
E
D
A
C
A rectangle has 3A
plane of symmetry.
H the plane you drew is a valid plane of symmetry by
Determine whether
T
A
making
Msure that each part of it is mirror image to the other.
.
D
©
D. MATH ACADEMY
INTERIOR &
EXTERIOR
ANGLE
Polygon, Sides & Angle formula :
Interior angle formula
𝑛 − 2 × 180
Formula to identify value of
each side of a regular shaped
polygon
(𝑛−2)×180
𝑛
E
D
Exterior angle of a polygon
A
C
A
360
= 𝐸𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟
𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
H
T
𝑛
A
360
M =𝑛
.
D
𝐸𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟
𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
©
Y
M
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
The side of this polygon: 6
Red dot represent numbers of side
Interior Angle:
6 − 2 × 180 = 720
D
E
V
The is a regular Hexagon:
Red dot represent numbers of side
Interior Angle of one side :
6−2 ×180
= 120
6
The graph show incomplete shape &
requested you to find the number of side of
6𝑥
this polygon
1. Find value of x:
39𝑥
6𝑥 + 39𝑥 = 180
180
𝑥=
=4
45
2. Number of side :
360
= 15
6(4)
D. MATH ACADEMY
SIN COS TAN
+ SIN & COS
RULE
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
𝑥
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
sin 𝑥 =
cos 𝑥 =
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
L
L
A
E
D
CA=
A
H
sin 35
12
sin 𝐵
15
15×sin 35
12
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
G
I
R 𝐶𝑜𝑠 𝑅𝑢𝑙𝑒:
= B ≈ 45.8o
𝐶
𝑎
𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 − 2 𝑏 𝑐 cos(A)
cos A
b2 +c2 −a2
=
2 b c
b2 +c2 −a2
−1
cos
2 b c
15×sin 35
sin 𝐵 =
12
sin−1
𝑏
𝐵
𝐶
Y
M
T
A
M
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
=𝑥
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑐
sin 𝐴 sin 𝐵 sin 𝑐
𝑆𝑖𝑛 𝑅𝑢𝑙𝑒:
=
=
𝑎
𝑏
𝑐
For example:
𝐴 = 35𝑜 , 𝑎 = 12, 𝑏 = 15
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
=𝑥
𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
.
D
©
𝑏
𝑎
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
cos −1
=𝑥
𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
tan−1
𝑐
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
D
E
V
𝐴
𝐵
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
tan 𝑥 =
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
sin−1
𝐴
=𝐴
Student need to be able to
determine which rule to use based
on condition or information given
by the respective question.
Calculate the angle of ADE
𝐴𝐷 = 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
E𝐷 = 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝐸
6𝐶𝑀
COS ADE
𝐷
𝐴
12𝐶𝑀
©
6𝐶𝑀
6
12
S
T
H
= 𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝐴𝐷𝐸 = 60
G
I
R
Calculate the length of AB
𝐵𝐶 2 + 𝐴𝐶 2 = 𝐴𝐵2
Pythagoras Theorem
𝐴𝐵 = 62 + 122 = 6 5 ≈ 13.42
Calculate the angle of ADC
Y
M
E
D
𝐶
A
C
A
H
AT
M𝐵
.
D
COS −1
R
E
S
E
R
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
6
=
=
𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
12
D
E
V
L
L
A
180
𝐴𝐷𝐶 =
= 60
3
Interior angle of any triangle is 180 degree and
attached is a equilateral triangle.
𝐴
𝐵
𝐶
𝐷
5𝐶𝑀
𝐸
𝐹
Y
M
8𝐶𝑀
©
D.
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
Calculate the angle between FB
and the plane EFGH
Step 1: Calculate FG
𝐹𝐻 2 + 𝐻𝐺 2 = 𝐹𝐺 2
G
I
R
S
E
R
𝐵
5𝐶𝑀
4𝐶𝑀
𝐻
R
E
𝐹𝐺 = 82 + 42 = 4 5 ≈ 8.94
L
L
A
𝐺
S
T
H
D
E
V
𝐹
8.94𝐶𝑀
𝐺
Step 2: Calculate the angle
TAN 𝐵𝐹𝐺
TAN −1
𝐵𝐺
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
= 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝐹𝐺
5
8.94
= 𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝐵𝐹𝐺 ≈ 29.2
D. MATH ACADEMY
AREA &
VOLUME
𝑑
𝑥
𝑟
𝑟 = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠
d = 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟
Area ∶ π𝑟 2
Circumference ∶ 2π𝑟
©
M
.
D
AT
A
H
L
L
A
S
T
H
G
I
R
𝑥
Area ∶
π𝑟 2
360
Y
M
E
D
CA
𝑟
𝑥
Circumference ∶
2π𝑟
360
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
4
Volume ∶ π𝑟 3
3
Surface area ∶ 4π𝑟 2
1
4
Volume ∶ × π𝑟 3
2
3
Surface area ∶ π𝑟
2
+
1
× 4π𝑟 2
2
𝑟 = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠
d = 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟
ℎ = ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
Volume ∶ π𝑟 2 × ℎ
Surface Area: 2 π𝑟 2 + 2π𝑟ℎ
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
G
I
R
S
T
H
L
L
A
S
E
R
1
Volume ∶ π𝑟 2 × ℎ
3
Surface Area: π𝑟 2 + π𝑟𝑙
D
E
V
R
E
𝑟 = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠
ℎ = ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
𝑙 = 𝑠𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑡 ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
*Pythagoras Theorem is required*
Y
M
E
D
CA
Other shape such as
triangle, square,
rectangle & pyramid
etc. concept is
required as well in
this topic
Find the capacity of this cone shape water tank, it has a
radius of 15cm & slant height of 35cm. *Capacity = Volume
𝑟
ℎ
Y
M
.
D
©
S
E
R
Pythagoras Theorem to identify the height
𝑟 2 + ℎ2 = 𝑙 2
ℎ2 = 𝑙 2 − 𝑟 2
ℎ = 352 − 152 = 10 10 = 31.62𝑐𝑚
𝑙
E
D
CA
1
Volume ∶ π𝑟 2 × ℎ
3
1
π152 × 31.62
3
4743
=
π
2
A
H
T
A
M
L
L
A
= 7450.29
≈ 7450𝑐𝑚3
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
D
E
V
A metal sphere was added into the full water tank & It has
a radius of 10. Find litres of water remaining in the tank.
𝑟
ℎ
ℎ = 31.62
𝑟 = 15
𝑙 = 35
𝑙
𝑟: 10
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
4
Volume of the metal ball ∶ π𝑟 3
3
4
= π × 103
3
4000
=
π 𝑐𝑚3
3
D
E
V
Y
DifferenceEinM
volume = Litres of water remaining:
4743 D 4000
= CAπ −
π
2
3
Key
conversion:
A
6229
Volume of the H
3
=
π
1,000𝑐𝑚
= 1 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠
water tankA
∶T
6
M 3 = 3261.496773
4743
.
= D π 𝑐𝑚
3
Amount of water leaks is 3.26 litres
2
≈
3261.5𝑐𝑚
©
≈ 3.26 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠
Water flows through a cylindrical pipe at a speed of
12cm/s. The radius of the pipe is 1.5cm and it’s
always completely full of water.
Calculate the amount of water that flows through
the pipe in 2 hour.
Give your answer in litres.
S
T
H
Area: π𝑟 2
= π × 1.52
= 2.25π
Time conversion:
′
A
H
E
D
CA
T
A
2hour M
.
=D
2 × 60 × 60
©= 7200 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠
Y
M
G
I
R
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
L
L
A Litres of water that flows through:
Each hour there s 60 minutes & each minutes got 60 seconds
2.25π × 7200 × 12 ÷ 1000
= 610.725611858
≈ 610.73
D. MATH ACADEMY
CIRCLE
THEOREM
Calculate the area of shaded region
𝐶
Area of Triangle A0C
D.
©
Y
M
E
D
CA
𝐴
Angle of A0C
S
T
H
𝐵
𝑜
T
A
M
A
H
5 × 15 ×
1
= 37.5𝑐𝑚2
2
𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 15
TAN A𝑂𝐶 =
=
𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
5
15
TA𝑁 −1
= 𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝐴𝑂𝐶 = 71.6 𝑑𝑒𝑔𝑟𝑒𝑒
5
L
L
A
G
I
R
R
E
D
E
V
S
E
R
𝑜
Area of Sector AOB
71.6
× 52 × 𝜋 = 15.6𝑐𝑚2
360
Area of Shaded Region
37.5 − 15.6 = 21.9𝑐𝑚2
Y
M
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
D
E
V
Theorem 2
Example:
𝐵
90𝑜
90𝑜
𝐴
𝐴
Y
M
E
D
CA
A
H
T
A
An angle
in the semiM
.is already right
circle
D
©
angle.
S
T
H
𝑜
𝐶
𝑜
D
E
V
𝐵
𝐶
L
L
A
𝐴
G
I
R
R
E
S
E
R
𝑜
90𝑜
𝐴
𝐵
𝑜
𝐶
90𝑜
𝐵
𝐶
Y
M
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
R
E
D
E
V
Theorem 4
Example:
D
E
V
𝐷
𝐵
𝐶
𝐷
R
E
𝐸
𝑥
𝑦
𝐶
𝑥
∠𝐴𝐷𝐶 = ∠𝐴𝐵𝐶
𝑥=𝑦
𝐴
𝐴
Y
M
A
H
E
D
CA
T
A
Angle from
the same
M
arcD
in .the same
©
segment are equal
L
L
A
G
I
R
∠𝐷𝐴𝐶 = ∠𝐷𝐵𝐶
𝑥=𝑦
S
E
R
S
T
H
𝑦
𝐷
𝑧
𝑥
𝑦
𝐵
𝐶
𝐴
𝐵
∠𝐸𝐴𝐷 = ∠𝐸𝐵𝐷 = ∠𝐸𝐶𝐷
𝑥=𝑦=𝑧
D. MATH ACADEMY
DRAWING
&
BEARING
𝑥
𝑥
D
E
V
𝑦
R
E
S
E
R
5𝑐𝑚
S
T
H
The graph G
above
show locus of point that
The graph above show locus of point
I
R
are 5cm
away from line xy.
that are 5cm away from point x.
L
L
A
The graph at M
theY
left
The graph at the left
E
shows the
way you
shows the way you
𝑦
D
A
construct
a
construct a
C
𝑥
𝑦 A
perpendicular
perpendicular
H
T bisector of the line XY
bisector of the angle
A
M
YXZ.
.
D
©
𝑥
𝑧
𝑦
5𝑐𝑚
.
D
©
Y
M
T
A
M
A
H
𝑧
E
D
CA
L
L
A
𝑥
Question:
Construct the locus of point that
are equidistant from the lines
XZ & ZY (Construct perpendicular bisector of Angle XZY).
Construct the locus of point
that are 5cm away from point z.
S
T
H
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
Shade the region inside the field
XYZ that is
- More than 5cm from z
- Closer to XZ than XY
𝑁𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ
𝑁
99𝑜
𝑊𝑒𝑠𝑡
𝐸𝑎𝑠𝑡
𝑥
𝑦
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
The bearing of y from x is 099 degree
𝑆𝑜𝑢𝑡ℎ
E
D
CA
Student is required to familiarize
themselves with the compass
direction.
Additionally, bearing that’s less
than 100 degree will have
additional 0 in front of it.
For example:
.
D
©
Y
M
𝑁
The bearing of y from
x is 065 degree.
A
H
T
A
M
𝑁
𝑦
65𝑜
𝑥
The bearing of x from
y is 180 + 65 = 245
degree.
𝑇
𝑃
65𝑜
The angle of elevation is the
angle measured upwards
from the horizontal.
E
D
CA
A
H
T
A
The angle
of depression is
M
. measured
theD
angle
©downwards from the
L
L
A
G
I
R
Find the angle of elevation of T from Q
Step 1: Find value of TP
Y
M
65𝑜
horizontal.
𝑄
S
T
H𝑅
tan ∠𝑇𝑆𝑃 =
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃
𝑃𝑆
PQRS is a rectangular
sized swimming pool.
PT is a vertical watch
out post with a CCTV
installed on it.
𝑆 PS = 50m and PQ =
40m. The angle of
elevation of T from S
is 8 degree.
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
𝑇
𝑃
tan 8 = 50
𝑇𝑃 = tan 8 × 50 ≈ 7.03
𝑆
𝑇
Step 2: Find the angle of elevation
tan ∠𝑇𝑄𝑃 =
7.03
𝑇𝑃
𝑄𝑃
tan−1 40 = ∠𝑇𝑄𝑃
∠𝑇𝑄𝑃 = 9.97𝑜
𝑄
𝑃
D. MATH ACADEMY
MATHEMATICALLY
SIMILAR
“Mathematically Similar”
Keyword to remember:
Two method to solve it.
Congruent: identical in form
1st Identify the SCALE FACTOR
-Student is required to understand the use of scale factor on different type of units.
- Power of 2 on Scale factor if it’s use to identify Area & Surface Area
- Power of 3 on Scale factor if it’s use to identify Volume, Litres, Density or Capacity
Y
M
E
D
CA
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
2nd Compare & identify the terms involve
- Student is required to put SQUARE ROOT for Area & Surface Area
- Student is required to put CUBE ROOT for Volume, Litres, Density or Capacity
- Student is not required to make any changes to single unit
(E.g. length of side, perimeter, radius, height, width etc.)
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
Solution guide [Method 1]:
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎: 𝐺 𝑐𝑚2
𝑥
𝐴
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎: 50 𝑐𝑚2
? 𝑐𝑚
13𝑐𝑚
12𝑐𝑚
5𝑐𝑚
𝑦
S
T
H
𝐵
𝑧
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R 𝐶
R
E
Above is two triangle that’s mathematically similar to each other.
• Find the area of the smaller triangle.
5 × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 13
E
D
CA
Y
M
L
L
A 𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑆𝑖𝑑𝑒
• Find the side AC of the larger triangle
12 × 2.6 = ? 𝑐𝑚
? 𝑐𝑚 = 31.2𝑐𝑚
Smaller Area × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 2 = 𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎
𝐺 = 𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 ÷ 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 2
13
𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = = 2.6
5
.
D
©
50
= 2
2.6
T
A
M
A
H
= 7.3964497 ≈ 7.4𝑐𝑚2
Solution guide [Method 2]:
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎: 𝐺 𝑐𝑚2
𝑥
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎: 50 𝑐𝑚2
? 𝑐𝑚
𝐴
13𝑐𝑚
12𝑐𝑚
5𝑐𝑚
𝑦
S
T
H
𝐵
𝑧
G
I
R
Above is two triangle that’s mathematically similar to each other.
• Find the area of the smaller triangle.
Y
M
𝐺
50
=
5
13
E
D
𝐺=
= 7.4𝑐𝑚 CA
A
• Find the side T
ACH
of the larger triangle
A
= . M
D
©? = 13 × 12 ÷ 5 = 31.2𝑐𝑚
5× 50
13
?
13
12
5
2
2
L
L
A
S
E
R 𝐶
R
E
D
E
V
Density = Litre = Volume: ? 𝑐𝑚3
Solution guide [Method 1]:
Density = Litre = Volume: 5924𝑐𝑚3
Height: 15𝑐𝑚
Height: 8𝑐𝑚
S
T
H
G
I
R
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
Above is two cylinder that’s mathematically similar to each other.
• Find the radius of the larger triangle
• Find the volume of the cylinder.
Y
M
8 × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 15
L
L
A
𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟:
𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ = 5924
E
D
A
𝑟=
= 15.35𝑐𝑚
C
𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒
𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟
=
𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
A
5924 × 1.875 T=H
𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 × 𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 𝐵𝑖𝑔𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠
A
M
= 39049.8𝑐𝑚
.
15.35 × 1.875 = 28.78 𝑐𝑚
D
©
𝑆𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 =
15
= 1.875
8
2
3
3
3
5924
8𝜋
Density = Litre = Volume: ? 𝑐𝑚3
Solution guide [Method 2]:
Density = Litre = Volume: 5924𝑐𝑚3
Height: 15𝑐𝑚
Height: 8𝑐𝑚
S
T
H
Above is two cylinder that’s mathematically similar to each
other.
G
I
R
• Find the volume of the cylinder.
L
L
A
=
Y
M
E
D
?=
= 39049.8𝑐𝑚
A
C
A
• Find the radius of the
larger cylinder
H
T
A
𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟: 𝜋𝑟 ℎ = 5924
=
M
.
D
= 15.35𝑐𝑚
𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑙𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟 =
©𝑟 =
3
5924
8
S
E
R
R
E
3
?
15
3
15× 5924
8
3
3
2
2
D
E
V
5924
8𝜋
15.35
8
?
15
15.35 × 15
= 28.78𝑐𝑚
8
D. MATH ACADEMY
MATRIX
&
VECTOR
𝑎
𝑐
𝑒
𝑎
𝑐
𝑏
𝑑
𝑥
𝑧
𝑦
𝑟
(2 x 2) (2 x 2)
Final result: (2 x 2)
T
A
M
.
D
©
Y
M
E
D
CA
𝑎×𝑦+𝑏×𝑟
𝑐×𝑦+𝑑×𝑟
A
H
𝑎𝑦 + 𝑏𝑟
𝑐𝑦 + 𝑑𝑟
𝑎
𝑐
𝑒
𝑎
𝑐
(3 x 2)
3 Rows & 2 Columns
𝑎
𝑐
𝑒
𝑎×𝑥+𝑏×𝑧
=
𝑐×𝑥+𝑑×𝑧
𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑧
=
𝑐𝑥 + 𝑑𝑧
𝑏
𝑑
𝑓
𝑏
𝑑
𝑓
𝑥
𝑧
𝑝
𝑦
𝑞
𝑗
𝑏
𝑑
𝑓
L
L
A
𝑥
𝑦
𝑏
𝑑
𝑧
𝑝
G
I
R
𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦
= 𝑐𝑥 + 𝑑𝑦
𝑒𝑥 + 𝑓𝑦
𝑎𝑧 + 𝑏𝑝
𝑐𝑧 + 𝑑𝑝
𝑒𝑧 + 𝑓𝑝
R
E
(2 x 2)
2 Rows & 2 Columns
S
T
H
𝑞
𝑗
S
E
R
(3 x 2) (2 x 3)
Final result: (3 x 3)
𝑎𝑞 + 𝑏𝑗
𝑐𝑞 + 𝑑𝑗
𝑒𝑞 + 𝑓𝑗
𝑎 𝑏
𝑐 𝑑
Find determinant of A
1. Find magnitude of A
𝐴 = 𝑎𝑑 − 𝑏𝑐
2. Determinant of A
1 𝑑 −𝑏
𝐴 −𝑐 𝑎
𝐴=
(3 x 2) (3 x 2)
Final result: Cannot
be solve because
the centre is
different
D
E
V
3 2
A= 6 1
3 4
2𝐵 = 2
6
=
10
.
D
©
B=
3
5
6
2
3 6
5 2
𝐵2 =
12
4
3×3+6×5
=
5×3+2×5
3 6
5 2
C=
3 6
5 2
Y
M
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
39 30
=
25 34
L
L
A
3×6+6×2
5×6+2×2
1 5
2 3
D=
3
5
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
3 R
2
3 6
𝐴𝐵 =TS
6 1
5 2
H
3 4
G
I
R
3×3+2×5 3×6+2×2
= 6×3+1×5 6×6+1×2
3×3+4×5 3×6+4×2
19 22
= 23 38
29 26
3 2
A= 6 1
3 4
𝐷 = 32 + 5 2
6
2
C=
Find determinant of B
1
𝐵
= 34 = 5.83
This arrangement is
different, simply adjust &
run calculation using
Pythagoras theorem to find
the result.
.
D
©
3
5
B=
1
=
−24
=
−𝑏
𝑎
Y
M
E
D
CA
A
H
T
A
M
𝑑
−𝑐
L
L
A
1 5
2 3
D=
S
T
H
G
I
R
3
5
S
E
R
𝐵 = 3 × 2 − 6 × 5 = −24
2 −6
−5 3
1
− ×2
24
1
− × −5
24
R
E
1
− × −6
24
1
− ×3
24
=
1
−
12
5
24
1
4
1
−
8
D
E
V
Matrix X Transformation *Please memorise
D
E
V
R
E
−1 0
Reflection on Y-axis
0 1
0
1
1 0
Reflection on X-axis
0 −1
0 1
Rotation of 90𝑜 clockwise
−1 0
0 1
Reflection on the line Y=X
1 0
Y
M
−1
Rotation of 90𝑜 anticlockwise
0
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
−1 0
Rotation of 180𝑜
0 1
E
D
0 −1
A
Reflection
on
the line Y=-X
C
−1 0
A
H
T
𝐾 0 A
Enlargement from Origin, K = Scale factor
M
0D.𝐾
©
𝑥
𝑥𝑜
=𝑘
՜=𝑗
𝑎
S՜ &
T
=
H
𝑏𝑧 𝑜𝑧
G
I
R
Hence,
𝑜
𝑧
𝑏
Find:
Y
M
1. ՜
𝑥𝑧
𝑥𝑜
+՜
.
D
©
E
D
CA
2. Vector position of a
1
=−
−k
A
H
𝑜𝑧
T
A
M
= 𝑘 + (−𝑗)
=𝑘−𝑗
S
E
R
a is the midpoint of the line 𝑥𝑦
: ՜ = 1: 3
=
D
E
V
R
E
𝑧𝑜
𝑜𝑎
=
1
2
2 𝑥𝑜
L
L
A
3.
=
𝑏𝑧
1
3 𝑜𝑧
4.
𝑥𝑏
𝑥𝑜
𝑜𝑏
+
𝑜𝑏
2
= 𝑘 + × −𝑗
3
2
=𝑘− 𝑗
3
2
3 𝑜𝑧
= ՜
𝑧𝑎
=՜+
𝑧𝑜
1
=𝑗+
2
𝑧𝑎
𝑧𝑎
=
𝑜𝑎
−𝑘
1
𝑗− 𝑘
2
D. MATH ACADEMY
MEAN
MODE
MEDIAN
The following numbers shows a group of workers working hour for a week:
56, 72, 28, 40, 60, 15, 84, 40
R
E
D
E
V
Mean:
*
A additional worker joined into
56+72+28+40+60+15+84+40
*
the group & the new mean is
8
*
now value at 52 hour. Find the
=49.375 Hours
*
******************************************************* * new worker working hour.
Mode: 40 Hours (40 hours occurs the most)
* 56+72+28+40+60+15+84+40+𝑥
= 52
******************************************************* *
9
Median: *Rearrange it first, then find the middle value *
* 𝑥 = 52 × 9 − 395 = 73
15, 28, 40, 40, 56, 60,72, 84
*
40+56
= 48
*
2
*
Hence, median is 48 Hours.
******************************************************* *
*
Range: Highest84 − Lowest15 = 69 Hours
*
Y
M
.
D
©
T
A
M
A
H
E
D
CA
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
T
H
S
E
R
The following numbers shows the time taken by 400 to complete a half marathon.
Minutes
45 <m ≤ 50
50 <m ≤ 60
60 <m ≤ 70
70 <m ≤ 90
90 <m ≤ 100
Frequency
23
64
122
136
26
Mean: Find the respective interval midpoint first
23×47.5 + 64×55 + 122×65 + 136×80 + 26×95 +(29×110)
S
T
H
G
I
R
400
=49.375 Hours
D
E
V
100 <m ≤ 120
R
E
29
S
E
R
L
L
A
Mode: 70 < m ≤ 90 group because it has the highest
frequency count.
Y
M
*****************************************************************************************
E
D
A
Median:
C
A
H frequency
*Identify it from cumulative
T
A
= 200𝑡ℎ
M
.
D
Hence,
median is 60 < m ≤ 70 group because the 200 fall under that group.
©
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
Minutes
Cumulative F
45 <m ≤ 50
50 <m ≤ 60
60 <m ≤ 70
70 <m ≤ 90
90 <m ≤ 100
100 <m ≤ 120
23
87
209
345
371
400
400
2
th
The following numbers shows days a group of student absences last month.
Number of Absences
0
1
2
Frequency
5
6
12
Mean:
* Simply multiply the number of absences with the respective frequency count
0×5 + 1×6 + 2×12 + 3×2
S
T
H
25
=1.44 absences
3
2
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
G
I
*****************************************************************************************
R
L
L
Mode: 2 Absences
A
Y
*****************************************************************************************
M
E
D
Median:
A
C
= 13𝑡ℎ
A
H1 into the total frequency before dividing it by 2.
*You’re required toT
add
A
Hence, median
M is 2 Absences.
.
D
*****************************************************************************************
©
25+1
2
Number of Absences
0
1
2
3
Cumulative F
5
11
23
25
Range: 3 − 0 = 3 Absences
D. MATH ACADEMY
CUMULATIVE
FREQUENCY &
FREQUENCY DENSITY
DIAGRAM
Minutes
45 <m ≤ 50
50 <m ≤ 60
60 <m ≤ 70
70 <m ≤ 90
90 <m ≤ 100
100 <m ≤ 120
23
87
209
345
371
400
Cumulative F
D
E
V
R
E
Y
M
Median
.
D
©
A
H
T
A
M
30th
Percentile
IQR =
-
E
D
CA
Number of person who took 91 minutes to complete the half marathon
L
L
A
G
I
R
S
E
*STARR
QUESTION*
S the number of people
Find
T
H took more than 91 minutes to
complete the half marathon.
400 − 350 = 50
Simply trace the amount of
people who took 91 minutes to
complete the half marathon
and minus it off by the total
headcount of 400 people.
Median:
Represented using this colored line
*Utilize the value below, draw & identify the median value from the cumulative frequency diagram
400 × 50% = 200
S
T
H
Value from the graph: 70 minutes
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
*****************************************************************************************
G
I
R
30th Percentile:
Represented using this colored line
*Utilize the value below, draw & identify the median value from the cumulative frequency diagram
Y
M
L
L
A
400 × 30% = 120
E
D
A
C
*****************************************************************************************
A
H Represented using this colored line
IQR:
Minus
T
Abelow, draw & identify the median value from the cumulative frequency diagram
*Utilize theM
value
.
D
[400 × 75% = 300] & [400 × 25% = 100]
©
Value from the graph: 62.7 minutes
Value from the graph: 80 − 61 = 19 minutes
Minutes
45 <m ≤ 50
50 <m ≤ 60
60 <m ≤ 70
70 <m ≤ 90
90 <m ≤ 100
100 <m ≤ 120
Frequency
23
64
122
136
26
29
R
E
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 𝐷𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝐻𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 ℎ𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚
Frequency Density Diagram
S
E
R
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
14
12
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
122
=
= 12.2
10
10
Y
M
8
6
4
A
H
AT
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
23
=
= 4.6
5
2
©
0
0
M
.
D
45 .
E
D
CA
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
64
=
= 6.4
10
50.
L
L
A
S
T
H
G
I
R
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
136
=
= 6.8
20
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
26
=
= 2.6
10
60.
70.
D
E
V
90 .
100 .
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
29
=
= 1.45
20
120
= 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
Minutes
45 <m ≤ 50
50 <m ≤ 60
60 <m ≤ 70
70 <m ≤ 90
90 <m ≤ 100
100 <m ≤ 120
Frequency
23
64
122
136
26
29
D
E
V
R
E
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 𝐷𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝐻𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 ℎ𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚
Frequency Density Diagram
S
E
R
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
70
60
122
𝐹𝐷 = 10
= 12.2
50
12.2 × 5 = 61
40
30
AT
𝐹𝐷 =
D
©
10
.M
E
D
CA
64
= 6.4
10
A
H
𝐹𝐷 =
20
Y
M
23
= 4.6 6.4 × 5 = 32
5
L
L
A
S
T
H
Always check the height of the
histogram given by the question.
G
I
R
* Highlighted in ORANGE
The height shown is 23cm
However, the FD we calculated is 4.6.
This situation indicate the present of
SCALE FACTOR.
136
𝐹𝐷 = 20
= 6.8
29
𝐹𝐷 = 20
= 1.45
6.8 × 5 = 34
1.45 × 5 = 7.25
4.6 × 5 = 23
𝐹𝐷 =
26
= 2.6
10
2.6 × 5 = 13
45 .
50.
60.
70.
90 .
100 .
? = Scale Factor
4.6 × ? = 23
?=
0
0
= 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙
120
23
=5
4.6
D. MATH ACADEMY
CORRELATION &
LINE OF BEST
FIT
Scatter Diagram – Positive Correlation
Scatter Diagram – Zero Correlation
1.4
1.4
1.2
1.2
1
1
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
L
L
A
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Y
M
E
D
CA
Scatter Diagram – Negative Correlation
3.5
A
H
3
2.5
2
1.5
.
D
©
1
0.5
T
A
M
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
0
S
T
H
G
I
R
0.5
1
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
1.5
2
2.5
Student may be asked to construct
“LINE OF BEST FIT”
• Identify whether it’s correlated
• Follow the general trend of the points
• Have similar number of point above and
below the line.
• If the data is irrelevant to each other then
it’s zero correlated
D. MATH ACADEMY
PROBABILITY
There is 9 orange flavor sweets, 8 apple flavor sweets and 10 grape flavor sweets in a
bag. Utilize the information given and answer the following question.
9
9
1
=
=
9+8+10
27
3
G
I
R
S
T
H
R
E
S
E
R
1. What’s the probability of a orange flavor sweets is chosen by Ali?
D
E
V
L
L
2. If Ali draw 6 sweets from the bag. FindA
how many sweet will be in orange flavor.
Y
M
E
6x =2
D
A
C
A
H
T
A
M
.
3. Find
the probability of Ali getting a coconut flavor sweets from the bag.
D
©
Probability of getting orange flavor sweets is 1/3.
1
3
Out of 6 draw, 2 sweets may be in orange flavor.
Answer is 0, because there’s no coconut flavor sweets in the bag.
There is 9 orange flavor sweets, 8 apple flavor sweets and 10 grape flavor sweets in a
bag. After each sweets drawn, it will be place back into the bag.
D
E
1. What’s the probability of a orange or apple flavor sweets is chosen by Ali if he
only
V
R
drawn once?
E
S
E
+ =
R
S
T
H
Probability of getting orange & apple flavor sweets is 17/27.
G
I
R
2. If 2 sweets were drawn from the bag. Find
L the probability of getting grape &
L
A
orange flavor.
Y
M
2
x
=
E
D
A
C
A
H
T
3. If 2 appleA
flavor sweets were drawn from the bag. Find the probability of getting it.
M× =
.
D
©
9
27
8
27
10
27
17
27
9
27
20
81
The final result will be 20/81.Things to take note is that you’re required to multiply it twice because #sequence matters
8
27
8
27
64
729
Answer is 64/729. You’re not required to multiply it by 2 because #sequence matters rule doesn’t apply if it’s repeating variable.
There is 9 orange flavor sweets, 8 apple flavor sweets and 10 grape flavor sweets in a
bag. Utilize the information given and answer the following question.
D
E
• Ali drawn 2 sweets from the bag. He didn’t replace the sweets back into the bag
V
R
after drawing it out. Find the probability of the sweets drawn is grape & E
apple
S
E
flavor. #Sequence matters
R
S
T
10
8
8
10
80 H
×
+
×
= IG
27 26 27 26 R351
L
L
A
The answer is 80/351. You’re required to reduce
the
total after each drawn.
Y
M
E
• Ali drawn 2 sweets from the bag. He didn’t replace the sweets back into the bag
D
A
after drawing it out. Find
the probability of the both sweets drawn is apple flavor.
C
A
H
8
7
28
T
A
×
=
M
27 26 351
.
D
©
The answer is 28/351. You’re required to reduce both the denominator & numerator after each drawn.
Not Late 0.65
0.7
Cycle
Late
0.35
Not Late 0.25
0.3
S
T
H
Walk
G
I
R
Late
L
L
A
D
E
V
S
E
R
R
E
0.75
Utilize the information given and filled up the missing component of the tree
diagram.
Y
M to school and not late for class.
1. Find the probability that Ali E
walks
D
0.3 × 0.25 = 0.075 𝑜𝑟CA
A
H
T
2. Find the A
probability that Ali is late for class.
M
47
.
0.7 × 0.35 + 0.3 × 0.75 = 0.47 𝑜𝑟
D
100
© cycle late walk late
3
40
ξ
D
E
V
Car
9
28
4
Bicycle
8
3
7
3
Motorcycle
L
L
A
G
I
R
DEBRIEF:
The Venn Diagram shows the mean of transportation of 80 household.
Y
M
S
T
H
18
R
E
S
E
R
1. Find the probability that the household uses car & motorcycle as their mean of transport.
.
D
©
E
D
CA
(𝑈𝑠𝑒 𝐶𝑎𝑟 & 𝑀𝑜𝑡𝑜𝑟)
8+3
=
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙
9 + 28 + 4 + 3 + 8 + 3 + 7 + 18
11
=
𝑜𝑟 0.1375
80
A
H
T
A
M
2. Find the probability that out of those household that uses car, how many of them also uses bicycle as their mean of
transport.
(𝑇ℎ𝑜𝑠𝑒 𝑤ℎ𝑜 𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑏𝑖𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑜𝑠𝑒 𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑟)
4+8
12
=
=
𝑜𝑟 0.2791
(𝑇ℎ𝑜𝑠𝑒 𝑤ℎ𝑜 𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑟)
28 + 4 + 8 + 3 43
This is a histogram which shows the math result of 50
student in Class 2A. Utilize the information given and
answer the following question.
Mathematics Exam Result of Class 2A
35
30
25
20
10
T
A
M
5
E
D
CA
A
H
10
.
D
©
S
T
H
G
I
R
S
E
R
First, identify the total of student which secured more than 60 marks.
Key things to take note is that, you’re required to minus it off the
student that you have picked. Both denominator & numerator will
decrease.
L
L
A
Y
M • Find the probability that 2 student chosen at random,
15
0
R
E
• Find the probability that 2 student chosen at random
secured a score of that’s more than 60 .
15 14
3
×
=
50 49 35
30
5
D
E
V
5
30 - 60
5
15
15 5
3
×
+
×
=
50 49
50 49
49
<30
Student's Math Exam Score
0 - 30
one scored less than 30 and the other secured more
than 60.
60 -80
80 - 100
>60
>60
<30
Similar process with the previous question. Keyword here is “AND”.
Hence, student is required to repeat the process twice.
D. MATH ACADEMY
GRAPH
DRAWING
Click here for more:
https://youtu.be/fjsMoChLtpA
D. MATH ACADEMY
SIN, COS, TAN
GRAPH
0
2
0
2
S
T
H
𝑦 = 2 sin 𝑥
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 2 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑆𝑖𝑛 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ
L
L
A
Y
G
I
R
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠𝑛′ 𝑡 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑. 𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑡 𝑓𝑜𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 ( 2𝜋 )
𝑎𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒
TH
A
.M
𝑦 = sin 𝑥 − 1
D
©
M
E
D
A
C
A
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑒 𝑆𝑖𝑛 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ 𝑠ℎ𝑖𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑𝑠 𝑏𝑦 𝑎𝑠
𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 − 1
𝑦 = sin 2𝑥
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑.
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒 ℎ𝑎𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑤 𝑏𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝜋 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦.
′
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠𝑛 𝑡 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑. 𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑡 𝑓𝑜𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘 𝑡ℎ𝑒
𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 ( 2𝜋 ) 𝑎𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒
2𝜋 ÷ 2 = 𝜋
𝑦 = cos(𝑥)
𝑦 = 2cos(𝑥)
S
T
H
𝑦 = 2 c𝑜𝑠 𝑥
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 2 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝐶𝑜𝑠 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ
L
L
A
Y
G
I
R
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠𝑛′ 𝑡 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑. 𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑡 𝑓𝑜𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 ( 2𝜋 )
𝑎𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒
M
E
D
𝑦 = cos(𝑥)
TH
𝑦 = cos 𝑥 − 1
A
.M
𝑦 = cos 𝑥 − 1
D
©
A
C
A
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ 𝑠ℎ𝑖𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑𝑠 𝑏𝑦 𝑎𝑠
𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 − 1
𝑦 = cos 2𝑥
𝑦 = cos 2𝑥
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑.
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒 ℎ𝑎𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑤 𝑏𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝜋 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦.
′
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑠𝑛 𝑡 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑. 𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑡 𝑓𝑜𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘 𝑡ℎ𝑒
𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 ( 2𝜋 ) 𝑎𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒
𝑦 = cos(𝑥)
2𝜋 ÷ 2 = 𝜋
S
T
H
D
E
V
R
E
S
E
R
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 2 𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ
G
I
R
𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒 𝑏𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝜋.
L
L
A
Y
1
2
𝜋÷2= 𝜋
D
©
H
T
A
.M
A
C
A
M
E
D
1
𝑦 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛 2 𝑥 + 1
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑒 tan 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ 𝑤𝑎𝑠 𝑠ℎ𝑖𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑢𝑝𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑏𝑦 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑏𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒
𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 + 1.
𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒 ℎ𝑎𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑤 𝑏𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 2𝜋.
1
2
𝜋 ÷ = 2𝜋
D. MATH ACADEMY
COMPLETING
THE
SQUARE
2020
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑎𝑎 & 𝑏𝑏
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑎𝑎 2 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
Step 1: Expand the unknown
MATH HACK TO DOUBLE CHECK ANSWER:
𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 + 𝑎𝑎2 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 + 𝑎𝑎2 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 +
2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 = −5𝑥𝑥
𝑎𝑎2 + 𝑏𝑏
𝑎𝑎 = −5𝑥𝑥 ÷ 2𝑥𝑥
H
T
A
.M
5
𝑎𝑎 = −
2
D
©
L
L
A
Y
= 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
A
C
A
M
E
D
E
R
Step 3: Compare the integer value available in the equation.
[Variable that doesn’t have x].
Can only be done at the last step because you need to
identify one of the unknown value of “a” first.
S
T
2H
𝑎𝑎G
+ 𝑏𝑏 = 3
RI 5 2
Step 2: Adjust the unknown accordingly to make the first variable 𝑥𝑥 2 is
the same. Only uses the first 2 variable in the equation to run the
comparison & identify the first unknown value.
R
E
S
D
E
V
−
2
+ 𝑏𝑏 = 3
25
𝑏𝑏 = 3 −
4
13
𝑏𝑏 = −
4
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑎𝑎 & 𝑏𝑏
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑎𝑎 2 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
Method 2:
2
𝑥𝑥 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
= 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
Step 1:Make adjustment if needed to the first
unknown (x) to make it the same as the one
given by question.
*MOST IMPORTANTLY*
Simply expand the (x + a)^2 accordingly.
L
L
A
Y
Utilize the formula & focus on the first two variable
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑎𝑎 2 = 𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥 + 𝑎𝑎2
−5𝑥𝑥 = 2𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥
−5𝑥𝑥 ÷ 2𝑥𝑥 = 𝑎𝑎
H
T
A
.M
5
𝑎𝑎 = −
2
D
©
A
C
A
M
E
D
R
E
S
E
R
Step 3: Remember to minus the squared value of a.
Reason being, according to the formula you added a
square into it. Hence, you need to minus it off at the end
of the calculation
S
T
H
G
I
R 𝑏𝑏 = 3 − 𝑎𝑎 2
Step 2: Uses the first 2 variable in the equation & identify which core
formula you should use. Identify the “a” value accordingly.
*Do take note on the ± signage use*
D
E
V
𝑏𝑏 = 3 −
13
𝑏𝑏 = −
4
5 2
−
2
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓 𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒:
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑎𝑎 2 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 2 − 5𝑥𝑥 + 3
Utilize the a & b value we gotten earlier
2
5
13
𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥 −
−
2
4
5
𝑥𝑥 − = 0
2
5
𝑥𝑥 =
2
A
C
A
M
E
D
E
R
L
L
A
Y
When x = 5/2, substitute into the equation again
5 2
1
H
T
𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥 −A −
4
16
M
.
D
13
©
𝑦𝑦 = −
4
R
E
S
D
E
V
S 5 13
T
H
𝑇𝑇𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢
𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝:
,−
G
2
4
I
R
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑎𝑎 & 𝑏𝑏
𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥 + 𝑏𝑏 2 + 𝑐𝑐 = 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
Method 1:
2
Step 1: Expand the unknown
𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥 + 2𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑏𝑏 2 + 𝑐𝑐 = 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 + 𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 2 + 𝑐𝑐 = 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 +
𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 = 8𝑥𝑥 2
𝑎𝑎 = 8
𝑎𝑎𝑏𝑏 2 + 𝑐𝑐
H
T
A
M
.
16𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏
= −18𝑥𝑥
D
©𝑏𝑏 = − 18 = − 9
2𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 = −18𝑥𝑥
16
8
E
R
Step 3: Compare the integer value available in the
equation. [Variable that doesn’t have x].
2
G
I
𝑎𝑎𝑏𝑏
+ 𝑐𝑐 = 4
R
= 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
M
E
D
A
C
A
L
L
A
Y
S
T
H
Step 2: Simply compare each variable expended with the
respective one. Identify the a & b variable value first before
proceeding with the integer value calculation.
R
E
S
D
E
V
9 2
8 −
+ 𝑐𝑐 = 4
8
81
𝑐𝑐 = 4 −
8
49
𝑐𝑐 = −
8
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑎𝑎 & 𝑏𝑏
𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥 + 𝑏𝑏 2 + 𝑐𝑐 = 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
Method 2:
2
Step 1:Make adjustment if needed to the
first unknown (x) to make it the same as
the one given by question.
8𝑥𝑥 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
18
4
𝑥𝑥 +
8
8
9
1
2
𝑥𝑥 − 𝑥𝑥 +
4
2
= 8 𝑥𝑥 2 −
=8
L
L
A
Y
*MOST IMPORTANTLY*
Simply expand the (x + b)^2.
M
E
Utilize the formula & focus on the first two variable
D
A
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑏𝑏 = 𝑥𝑥 + 2𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥
+ 𝑏𝑏
C
9
− 𝑥𝑥 = 2𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥 H A
4
T
A
9
M
.
− D𝑥𝑥 ÷ 2𝑥𝑥 = 𝑏𝑏
4
©
𝑎𝑎 = 8
𝑏𝑏 = −
2
9
8
2
R
E
S
Step 3: Remember to minus the b squared value.
Additionally, remember to multiply the entire result
with the “a” value you identified.
Reason being, in the equation arrangement given, you’re
only required to extract a from the ( x + b )^2 part only.
S
T
H
E
R
G
1
I
R 𝑐𝑐 = 8 − 𝑏𝑏 2
2
Step 2: Uses the first 2 variable in the equation & identify which
core formula you should use. Identify the b value accordingly.
*Do take note on the ± signage use*
D
E
V
=8
=8
2
1
−
2
9 2
−
8
1
81
−
2
64
49
=8 −
64
49
=−
8
𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓 𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒:
𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥 + 𝑏𝑏 2 + 𝑐𝑐 = 8𝑥𝑥 2 − 18𝑥𝑥 + 4
Utilize the a ,b & c value we gotten earlier
2
9
49
𝑦𝑦 = 8 𝑥𝑥 −
−
8
8
9
𝑥𝑥 − = 0
8
9
𝑥𝑥 =
8
A
C
A
M
E
D
L
L
A
Y
When x = 9/8, substitute into the equation again
9 2
49
H
−
T
8
8
A
.M
𝑦𝑦 = 8 𝑥𝑥 −
D
49
©𝑦𝑦 = −
8
E
R
R
E
S
D
E
V
S 9 49
T
H
𝑇𝑇𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢𝑢
𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝:
,−
G
8
8
I
R
D. MATH ACADEMY
FUNCTION
GRAPH
IDENTIFICATION
0
2
0
2
𝐼𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑦𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ:
D
E
V
Utilize the function given (Set random x value & identify the respective y value)
𝑦 = 𝑥 + 1 ; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐸
4
𝑦 = ; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐹
𝑥
Y
1
0
Y
0
4
2
-4
-2
x
0
-1
x
0
1
2
-1
-2
𝑥
𝑦 = 1 − ; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐴
3
Y
1
0
x
0
3
𝑦 = 2𝑥 ; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐶
H
T
A
4
𝑦 = −. M
; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐷
𝑥
D
©
Y 0 2
M
E
D
A
C
A
2
2
x 0 1 -1
Y
0
-4
-2
4
2
x
0
1
2
-1
-2
L
L
A
Y
𝑦 = 2𝑥 2 − 2
; 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚 𝐵
Y
-2
0
0
x
0
1
-1
G
I
R
S
T
H
E
R
R
E
S
D. MATH ACADEMY
GRADIENT
FUNCTION &
TURNING
POINT
0
2
0
2
𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 & 𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (𝐿𝑜𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐿𝑜𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑛)
𝑑𝑦
𝐺𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐹𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑦
𝐻𝑜𝑤 𝑡𝑜 𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑑
:
𝑑𝑥
𝑃𝑎𝑟𝑡 1 (𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 & 𝑟𝑒𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑡 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡)
𝑦 = 𝑥 3 − 2𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 5
M
E
D
𝑦 = 1𝑥 3 − 2𝑥 2 + 1𝑥 1 + 5𝑥 0
L
L
A
Y
S
T
H
D
E
V
E
R
R
E
S
𝑥 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑓𝑦𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑖𝑠 𝑡𝑜 1
𝑥 = 𝑥1
&
𝑥 𝑎𝑙𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑏𝑒 𝑤𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑛 𝑎𝑠 1 𝑥
𝑥 𝑛 = 1𝑥 𝑛
&
𝑛 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑏𝑒 𝑤𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑛 𝑎𝑠 𝑛𝑥 0
𝑥 0 = 1 𝐻𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑛𝑥 0 = 𝑛
G
I
R
A
C
𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 2 (𝑇𝑎𝑘𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑝𝑙𝑦
𝑏𝑦 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑒𝑟 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 & 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑏𝑦 1 𝑑𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠)
A
H3−1
T
d𝑦
= 1M
× 3A× 𝑥
− 2 × 2 × 𝑥 2−1 + [1 × 1 × 𝑥 1−1 ]
𝑑𝑥
.
D
©
𝑑𝑦
= 3𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 1
𝑑𝑥
𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 & 𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (𝐿𝑜𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐿𝑜𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑛)
D
E
V
𝑑𝑦
𝑆𝑒𝑡
= 0 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑦 𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡
𝑑𝑥
R
E
𝐻𝑜𝑤 𝑡𝑜 𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡:
S 𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑒𝑑
𝑃𝑎𝑟𝑡 3 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑦 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑢𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑥
𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
E
Or 𝑥 − 1S
=R
0
3𝑥 − 1 = 0
𝑃𝑎𝑟𝑡 1 𝑆𝑒𝑡 = 0
T
𝑥=1
3𝑥
=
1
H
𝑑𝑦
G
I
1
= 3𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 1 = 0
R
𝑑𝑥
𝑥=
3LL
𝑃𝑎𝑟𝑡 2 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑦 𝑥 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑆𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑥A
= & 1 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑜 𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
Y
M
3𝑥
1
𝑦 = 𝑥 3 − 2𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 5
E
D
𝑥
1
A
𝑦=
−2
+ + 5 Or 𝑦 = 1 − 2 1 + 1 + 5
C
A
−𝑥
− 3𝑥
=5
H
=
5.15
T0
3𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 1
=
A
𝑇𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡:
, 5.15 𝐿. 𝑚𝑎𝑥 & 1 , 5 𝐿. 𝑚𝑖𝑛
M
.
3𝑥 −D1 𝑥 − 1 = 0
©
𝑑𝑦
𝑑𝑥
1
3
1 3
3
1 2
3
1
3
1
3
3
2
ACA
DEM
Y
FO
RE IN W E R E
O
M
U
FOR
N YO
SCAN N E E D E D WE RH E
D. M
BE W
HO Y
OU
ATH
YOU
NG
D. MATH ACADEMY
HOPE YOU FIND THIS HELPFUL
It took me months to compile all these sample question and key
points. Really hope that it will come in handy for your exam
preparation.
At D. Math Academy, I worship the hard-work and dedication a
student put in towards his preparation work more than the final
result of his examination.
Attitude is the key to everything.
"How you do anything is how you do everything"
If you wish to support our cause, you can donate to us. Donate
link is available at our website. Funds collected will be used to
fund the channel operation as well as funding our CSR activity
(An initiative to give back to the society).
D. MATH
ACADEMY
BE WHO YOU NEEDED
WHEN YOU WERE YOUNGER
YOUR IDEAL
MATH TUTOR
DIXON YAU
FOUNDER
Mobile: 010-268-5505
Email: dixonyau@dmathacademy.com
Website: www.dmathacademy.com
Youtube: www.youtube.com/c/dmathacademy