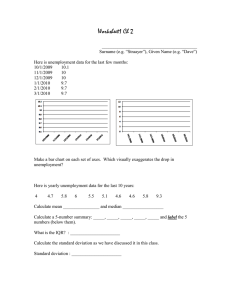
Powered by AI Copilot Certainly! When the economy experiences a contraction, it leads to various economic challenges. Let's explore the specific type of unemployment associated with this situation: Cyclical Unemployment is the term used for unemployment caused by a contraction in the economy. Here's how it works: 1. Definition: Cyclical unemployment occurs when there is a decline in national output (measured by Gross Domestic Product, or GDP). During an economic contraction, businesses produce less, leading to reduced employment opportunities. 2. Cause: It is triggered by a loss of confidence in the economy, which results in slower demand. While a specific event (such as a stock market correction or crash) may trigger it, the underlying cause often precedes the event. For example, an increase in interest rates can reduce capital spending, leading to layoffs and decreased consumer spending. 3. Impact: As businesses cut spending and lay off workers, unemployment rates increase. Individuals lose jobs due to reduced demand for goods and services. 4. Duration: Fortunately, no economic contraction lasts forever. The cycle eventually ends when prices fall enough to attract renewed demand. Remember that cyclical unemployment is just one aspect of the broader business cycle, which includes stages like expansion, peak, contraction, and trough1 2 4. So, the correct answer is b. cyclical unemployment. Source(s) 1. What Is an Economic Contraction? - The Balance 2. Contraction: Definition, How It Works, Examples, and Stages - Investopedia 3. Economic Cycle: Definition and 4 Stages of the Business Cycle 4. Frictional Unemployment: Definition, Causes, and Quit Rate Explained