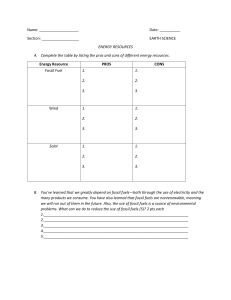
Title: A Finite Resource or a Sustainable Solution? Author: Méndez Flores José Guadalupe Introduction: Fossil fuels have been the cornerstone of human civilization for centuries, powering our industries, transportation systems and homes. However, due to their finite nature and detrimental environmental impact, concerns have been raised about their long-term viability. This essay will explore the debate surrounding the future of fossil fuels, examining whether they will endure beyond 30 years or be permanently replaced by alternative energy sources. Development: Proponents of fossil fuel longevity argue that these resources possess immense reserves that can sustain our energy needs for decades to come. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the world's proven reserves of coal, oil, and natural gas could last for centuries at current consumption rates. Moreover, advancements in extraction technologies, such as hydraulic fracturing, have unlocked vast new reserves, particularly in shale formations. Furthermore, fossil fuels offer several advantages over alternative energy sources. They provide a high energy density, making them ideal for transportation and industrial applications. Additionally, fossil fuel infrastructure is well-developed and widely distributed, ensuring a reliable and consistent energy supply. Despite their abundance and advantages, fossil fuels face significant challenges that threaten their long-term sustainability. The primary concern is their environmental impact. The combustion of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, which trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. The consequences of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems, are already being felt worldwide. Moreover, the reliance on fossil fuels poses geopolitical and economic risks. The uneven distribution of these resources often leads to conflicts and instability, while price fluctuations can have severe economic repercussions. Additionally, the transition to a low-carbon economy could render fossil fuel investments obsolete, stranding assets and causing financial losses. The debate surrounding the future of fossil fuels is reflected in the opinions of experts. Fatih Birol, Executive Director of the International Energy Agency, stated, "The world is at a crossroads. We can either continue on our current path, which leads to a future of climate instability and economic hardship, or we can choose to transition to a clean energy future." On the other hand, Daniel Yergin, Vice Chairman of IHS Markit, argues that "Fossil fuels will continue to play a major role in the global energy mix for decades to come, even as renewables grow." Conclusion: The future of fossil fuels is uncertain and hinges on the world's collective response to climate change and the development of viable alternatives. While fossil fuels may remain a significant energy source for the next 30 years, their long-term sustainability is doubtful. The transition to a low-carbon economy is inevitable, driven by environmental imperatives, economic considerations, and technological advancements. The key lies in accelerating the development and deployment of renewable energy sources while ensuring a just and equitable transition for those reliant on fossil fuel industries. APA References: Natalichio, D. R., Natalichio, D. R., & Natalichio, D. R. (2024, 22 enero). ¿Hasta cuándo dependeremos de los combustibles fósiles? EcoPortal.net. https://www.ecoportal.net/temas-especiales/combustibles-fosiles-2/ Muñoz, R. P. (2021, 20 enero). Energías renovables vs. combustibles fósiles. Gaceta UDG. https://www.gaceta.udg.mx/energias-renovables-vs-combustibles-fosiles/