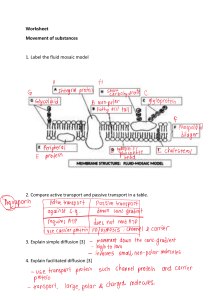
• Print slide 22 per student • Diffusion practical- agar cubes • Demo- potassium permanganate / starch in visking tubing Behaviour targets: 1. Remain silent when the teacher is talking. 2.Stay on task throughout the lesson. 3. Speak to staff and other students in a polite way. 4.Refrain from unnecessary contact with others. DO THIS NOW… Compare the diagram to a typical animal and/or plant cell. Are there differences? Are there similarities? 04/05/2024 Learning Objectives Understand how particles move by diffusion and why it is important for living things Success Criteria – 1-4: state that diffusion is the spreading of the particles of any substance in solution, or particles of a gas. list the factors that affect the rate of diffusion. write a simple hypothesis. 5-6: predict which way substances will move across a cell membrane. explain why surface area affects the rate of diffusion. write a hypothesis using scientific knowledge. 7-8: explain how temperature and concentration gradient affects rate of diffusion. write a hypothesis using detailed scientific knowledge and explain how it could be tested. Discuss… What do cells need? Water Hormones Oxygen Glucose Urea Amino acids Carbon dioxide What do cells need to get rid of? Discuss… How do substances, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, get into and out of cells? Key Concept • In order for the cell to carry out the many chemical reactions it needs to, substances must enter and leave the cell. • This happens in the following 3 ways: New information- Diffusion • Diffusion is a natural process that happens all around us. • It is simply where molecules spread out from each other. • We say that they are moving from a high concentration to a low concentration. • Dissolved substances and gases can move into and out of cells across the cell membrane by diffusion. New information- Diffusion Demonstrate understanding Task: Copy and complete the definition for diffusion. Diffusion is the net movement of Diffusion is the net ______________ of particles from a region of high _______________ from a region of _______ concentration region of low ___________ to a regionto of a ________ ____________. concentration. High Particles Concentration Movement Low Practical demo- Diffusion in action When you can smell the perfume hold up your hand! Task: Draw a particle diagram to explain what is happening during diffusion. Discuss… Dissolved substance move into and out of your cells by diffusion across the cell membrane. How could you increase the rate of diffusion? End 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Practical activity-Investigating diffusion You are going to in investigate the factors that affect the rate of diffusion Experiment 1: Remember to record your results accurately How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion? Experiment 2: Can diffusion occur across a membrane? 20 minutes Practical activity-Investigating diffusion You are going to in investigate the factors that affect the rate of diffusion Remember to record your results accurately https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/diffusion/latest/diffusion_all .html What happens when the temperature increases? What happens when it cools? What happens when you increase the concentration of particles? What happens when you decrease it? New information- Rates of diffusion Concentration In general, the greater the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of diffusion. The difference between two areas of concentration is called the concentration gradient. Surface area The larger the surface area the faster the rate of diffusion. Temperature An increase in temperature means the particles in a gas or a solution move around more quickly, so diffusion takes place more rapidly as the random movement of particles speeds up. New information- Rates of diffusion New information- Rates of diffusion New information- Rates of diffusion Demonstrate understanding Task: List three things that can affect the rate of diffusion. The rate of diffusion is affected by the difference in concentrations, the temperature, and the available surface area. New information- Diffusion in living organisms Dissolved substances move into and out of cells by diffusion across the cell membrane. These include: • simple sugars, such as glucose • gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide • Waste products, such as urea from the breakdown of amino acids in your liver. Task: over the next few slides you will be shown some examples of diffusion in living organisms. Annotate the diagrams provided with some brief notes to explain what is happening. New information- Digestive system Digested food products move from the gut cavity to the blood in the capillaries of the villi. The food products are in higher concentration in the small intestine. capillary network Villi small intestine blood vessels New information- Respiratory system Oxygen moves from the air space in the alveoli to the blood vessels around the lungs.... There is a large amount of oxygen in the alveoli as it is breathed in. There is a small amount of oxygen in the blood vessel as it gets transported around the body. deoxygenated blood (from body tissues) capillary air in/out alveolus oxygenated blood (to body tissues) red blood cell New information- The placenta The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. The umbilical cord connects the placenta to the foetus. Blood from the mother is high in O2 but low in waste. Blood from the foetus is low in O2 but high in waste. umbilical cord blood to mother • low in O2 • high in CO2/waste blood from mother • high in O2 • low in CO2/waste New information- Nervous system A synapse is a junction between two nerve cells across which electrical signals must pass. Chemical messages diffuse Synapse across the gap. Chemical message Moving from an Nerve impulse area of high concentration to low concentration. New information- Stomata Carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant through the stomata. During photosynthesis CO2 is used so the level of CO2 inside the leaf is low. Demonstrate understanding Task: Describe two examples of diffusion occurring with the body. Any relevant examples: Food diffusing out of the gut into the bloodstream, oxygen diffusing into the bloodstream form the lungs, carbon dioxide diffusing into the lungs from the bloodstream. Review and reflect Which outcome did you reach? What skills do you do well? What could you do to progress even further/ reach the next outcome? 1-4: state that diffusion is the spreading of the particles of any substance in solution, or particles of a gas. list the factors that affect the rate of diffusion. write a simple hypothesis. 5-6: predict which way substances will move across a cell membrane. explain why surface area affects the rate of diffusion. write a hypothesis using scientific knowledge. 7-8: explain how temperature and concentration gradient affects rate of diffusion. write a hypothesis using detailed scientific knowledge and explain how it could be tested. For printing…… capillary network Villi deoxygenated blood (from body tissues) capillary small intestine blood vessels umbilical cord blood to mother • low in O2 • high in CO2/waste blood from mother • high in O2 • low in CO2/waste air in/out alveolus oxygenated blood (to body tissues) red blood cell