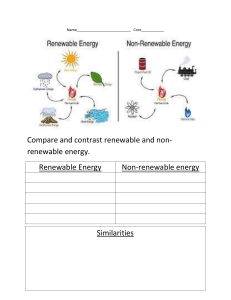
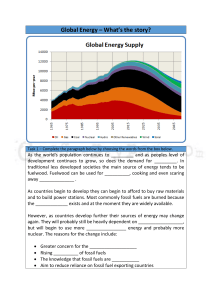
itle: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Energy Issues: Challenges, Solutions, and the Path Forward Introduction: Energy is the lifeblood of modern civilization, powering our homes, industries, and economies. Yet, as the demand for energy continues to soar, we are confronted with a myriad of complex issues that threaten the sustainability, security, and environmental integrity of our energy systems. In this essay, we delve into the multifaceted landscape of energy issues, exploring the challenges we face, the innovative solutions emerging to address them, and the imperative for collective action to forge a sustainable energy future. 1. The Growing Demand for Energy: The global population is on an upward trajectory, accompanied by rapid urbanization and industrialization. Consequently, the demand for energy is escalating, exerting pressure on finite resources and exacerbating environmental degradation. Meeting this burgeoning demand while mitigating the adverse impacts on the planet poses a formidable challenge for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and society at large. 2. Fossil Fuel Dependence and Climate Change: One of the most pressing energy issues of our time is the pervasive reliance on fossil fuels, which account for the majority of global energy consumption. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and its attendant consequences, including rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and ecological disruptions. Transitioning away from fossil fuels towards cleaner, renewable sources of energy is imperative to mitigate the climate crisis and safeguard the planet for future generations. 3. Energy Poverty and Social Equity: Despite the abundance of energy resources, millions of people around the world lack access to reliable and affordable energy services, perpetuating a cycle of poverty and deprivation. Energy poverty disproportionately affects marginalized communities, exacerbating social inequalities and hindering socioeconomic development. Bridging the energy access gap requires concerted efforts to deploy decentralized, off-grid solutions, enhance energy efficiency, and promote inclusive policies that prioritize the needs of vulnerable populations. 4. Energy Security and Geopolitical Risks: The geopolitics of energy is fraught with complexities, as nations jostle for control over scarce resources and strategic transit routes. Dependence on energy imports exposes countries to geopolitical risks, including supply disruptions, price volatility, and geopolitical tensions. Enhancing energy security necessitates diversifying energy sources, investing in domestic production capacity, and fostering regional cooperation to mitigate geopolitical risks and enhance resilience to external shocks. 5. Technological Innovation and Disruption: The rapid pace of technological innovation is reshaping the energy landscape, unlocking new possibilities for efficiency, sustainability, and decentralization. Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, are becoming increasingly costcompetitive and scalable, challenging the dominance of conventional fossil fuels. Meanwhile, advancements in energy storage, smart grid infrastructure, and digitalization are revolutionizing the way we produce, distribute, and consume energy, paving the way for a more decentralized and democratized energy system. 6. The Imperative for Transitioning to Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy is not merely an environmental imperative but an economic opportunity and a moral imperative. Renewable energy sources offer a clean, abundant, and inexhaustible alternative to fossil fuels, with the potential to catalyze economic growth, create jobs, and foster sustainable development. Moreover, by harnessing the power of the sun, wind, and water, we can reduce our reliance on finite resources, mitigate climate change, and safeguard the health and well-being of current and future generations. 7. Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Effective policy and regulatory frameworks play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of energy transitions and driving the adoption of clean energy technologies. Governments have a responsibility to enact ambitious climate policies, establish robust regulatory mechanisms, and provide incentives to spur investment in renewable energy infrastructure. Moreover, international cooperation and multilateral initiatives are essential to address transboundary energy challenges, promote technology transfer, and mobilize financial resources for sustainable energy projects. 8. The Role of Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness and fostering a culture of energy literacy are indispensable for driving meaningful change and empowering individuals to make informed choices about energy consumption. Educational initiatives, public outreach campaigns, and community engagement programs can help dispel myths, debunk misconceptions, and promote energy-efficient behaviors. By empowering citizens to become active participants in the energy transition, we can accelerate the shift towards a more sustainable and equitable energy future. 9. Corporate Responsibility and Sustainable Practices: Businesses have a critical role to play in advancing the transition to clean energy and adopting sustainable practices across their operations. Corporate sustainability initiatives, renewable energy procurement strategies, and supply chain transparency efforts can drive market transformation, spur innovation, and enhance corporate reputation. By embracing renewable energy solutions and integrating sustainability into business models, companies can simultaneously reduce their carbon footprint and create long-term value for shareholders and stakeholders alike. 10. Conclusion: Embracing the Energy Transition: In conclusion, navigating the complex landscape of energy issues requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technological innovation, policy reform, public engagement, and corporate responsibility. By embracing the energy transition and accelerating the shift towards renewable energy sources, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change, enhance energy security, and foster inclusive and sustainable development. As stewards of the planet, we have a collective responsibility to safeguard the health and well-being of current and future generations by forging a path towards a more resilient, equitable, and sustainable energy future.