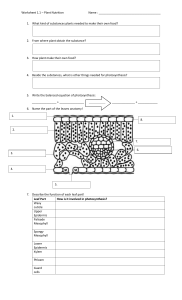
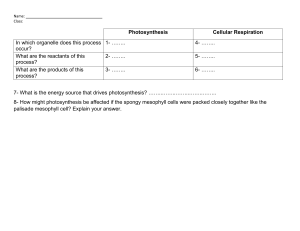
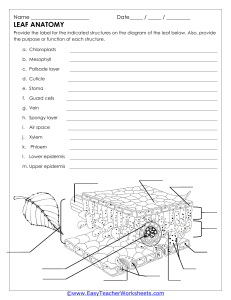
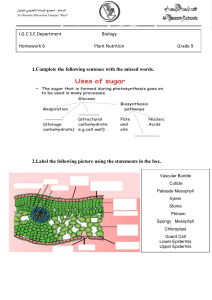
PLANTS STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGY PART 1 PLANT NUTRITION 1. Green leaf structure a/ What is mesophyll? Mesophyll is the internal tissue located between the two epidermal cell layers of a green leaf. The mesophyll of a plant carries out photosynthesis. b/ Types of mesophyll cells Palisade cells are responsible for photosynthesis and therefore contain many chloroplasts. Spongy mesophyll is made up of cells that also photosynthesise, but this area of the leaf is primarily important for gas exchange and therefore has many spaces. c/ Stoma and guard cells Stoma and stomata are the two structures mostly found on the underside of the epidermis of plant leaves. Stoma is involved in the gas exchange between the plant body and the external environment. The main difference between stoma and stomata is that: -stoma is the pore, which is surrounded by two guard cells -stomata are the collection of stoma found inside the lower epidermis of plant leaves. 2. Plants nutrition (Photosynthesis) a/ What is photosynthesis?- Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae and certain bacteria to turn sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into food (sugars) and oxygen. b/Uses of glucose-Little free glucose is produced in plants; instead, glucose units are linked to form starch (stored in the leaf)or are joined with fructose, another simple sugar, to form sucrose. Sucrose is the ideal sugar for transport in plants. c/ Testing green leaves for starch. PART 2 TRANSPORT IN PLANTS 1. Transport system of plants: xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots. b/ Water uptake through the roots c/ Transpiration- This is the evaporation of water from a plant, mostly from its leaves. d/ Potometer It’s difficult to measure how much water is lost through transpiration from the leaves. It’s easier to measure how fast the plant takes up water. The rate of water uptake depends on the rate of transpirationthe faster the plant transpires , the faster it takes up water. PART 3 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS 1. Plants reproduction- asexual reproduction 2. Plants reproduction- sexual reproduction Flowers-the reproductive organs of plants a/Flower structure stigma anther style stamen filament ovary ovule petal sepal peduncle receptacle carpel b/ Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. c/ Fertilisation and fruit development It is the process of fusion of the female gamete, the ovum or egg and the male gamete produced in the pollen tube by the pollen grain. Once pollination occurs a tube grows from the pollen grain down through the style to the ovule stigma style carpel ovary ovule Note: Petals not shown in order to simplify diagram Fertilisation occurs when the male gamete fuses with the ovule (the female gamete) d/ After fertilization: e/ Germination: