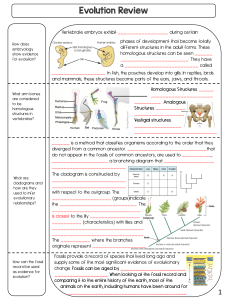
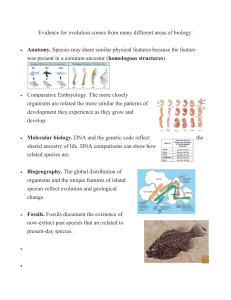
General Biology 2 Quarter 3: Evidence of Evolution Target In this lesson, it explicitly discusses the various concepts on pieces of evidence in evolution on how changes in organisms occurred starting from the simple origin of life to the wide variety of plants, animals and microorganisms existing today which are intended for you to enjoy learning in biology. Through diverse fun-filled activities, you will explore and describe the different evidence used in biology to show that evolution did take place. You will also learn to infer the evolutionary relationship between organisms using the evidence of evolution. After accomplishing this lessom, you are expected to: 1. Explain evidence of evolution (e.g., biogeography, fossil record, DNA/protein sequences, homology, and embryology) (STEM_BIO11/12- IIIc-g-12) 2. Infer evolutionary relationships among organisms using the evidence of evolution (STEM_BIO11/12-IIIc-g-13) Before going on, check how much you know about the lesson. Do the next activity on a separate sheet of paper. Jumpstart In the next activity you will appreciate a body structure that is present in us and in some organisms related to humans. Activity: What a Thumb Can Do For You Do you understand how important your thumbs are? Only primates have hands capable of grasping objects. The grasp is created possible by the opposable thumbs. Are you aware that you simply perform plenty of tasks using your thumb and fingers? have you ever experienced doing a series of tasks without the help of your thumb? Ask a companion to tape your thumbs to the palms of each hand with masking tape. Be cautious not to wrap the tape too tightly because it will cut off the blood circulation to your hand. Then do the following: a. pick up your pen b. write your name on a paper c. turn the doorknob d. pick up any plastic container e. unbutton or rebutton a shirt Question: How has having an opposable thumb helped primates, especially humans to adapt to their environment and survive better than other animals? Sounds interesting! Let us go to another scientific journey. Lesson Pieces of Evidence for Evolution 1 In the previous lessons, it is said that evolution is the process of change in species over time. Some changes are easily visible. Other changes occur so gradually through time and are not easily observed. Darwin’s theory of evolution was eventually recognized when scientists were able to supply verifications that Darwin himself had been unable to specify. Natural selection gives us with an outline in understanding the ideologies of evolution. Darwin’s idea of evolution has been improved by new evidence that have been gathered by modern scientists. Moreover still, modern scientists are at an interminable expansion on collecting data and evidence that may verify or invalidate the information about evolution of life that we have now. And these pieces of evidence are significant in the field of biology. Discover Previously, you have studied the patterns of descent with modification from our common ancestor to the present organismal diversity. As well as you also have traced the development of evolutionary thoughts from a few notable individuals in the field of evolution. Before we begin, try some more activity to boost your vocabulary. Activity: Word Parts Directions: Below are words that have been divided into halves. Find the pieces that fit together and write them in your answer sheets. spe igin riod adap or inhert sils fos em homo gans lohous cies ry theo igial tation tance evo its bryology vest lution pe tra CONCRETE EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION AND HOW TO INFER USING ITS EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIP A. Fossils Fossils are preserved remnants of once living organisms trapped in rocks, tar pits, frozen in ice or embedded in amber. The most common fossils are bones, shells and seeds or pollen grains. Most fossils are formed in sedimentary rock. Paleontologists (a specialist in the study of the forms of life existing in prehistoric or geologic times), use the fossils found in rocks to track the evolutionary history of many organisms. (a) (b) Figure 1. (a) Fossilized shrimp. (b) Mammalian (peccary) fossil Source: http://www.citruscollege.edu/lc/archive/biology/Pages/Chapter17-Rabitoy.aspx By identifying the age of rocks in which fossils appear, we can obtain an accurate idea of how old the fossils are. Geologists use Relative dating rocks were dated by their position with respect to one another; rocks in deeper strata are generally older. On the other hand, in absolute dating rocks are dated by measuring the degree of decay of certain radioisotopes contained in the rock; the older the rock, the more its isotopes have decayed. Since radioactive isotopes decay at a constant rate unchanged by temperature or pressure, the isotopes in a rock act as an internal clock, determining the time after the rock was formed. Hence, the records found in the rocks show a gradual evolutionary descent from simpler to more complex life forms. Furthermore, the fossil record provides a clear record of the major evolutionary transitions that have occurred through time. B. Embryology An embryo is an organism in its initial phases of development. While embryology is the study of the development of the anatomy of an organism to its adult form also gives evidence of relatedness between now widely different groups of organisms. Scientists observed that at some point during the development process, embryos of many different animals appeared so similar that it was difficult to tell them apart. During development, at some time all vertebrates have a supporting dorsal rod, called a notochord, and demonstrate paired pharyngeal pouches. This could indicate that an organism passes through some of the embryonic stages that its ancestors passed through. Then numerous variations occur in ways appropriate to an organism’s final form. However, the similarities in the early stages of embryo development are further evidence that living organisms have evolved from earlier living things and that they do share a common ancestry. Figure 2. Vertebrate embryonic development Source: http://www.geo.arizona.edu/Antevs/nats104/00lect12.html C. Anatomical Evidence In comparing the anatomy and the development of organisms, it shows a unity of plan among those that are closely related. The more body structures that two species have in common, the more closely they are related. It adopts the idea of “descent from a common ancestor”. Similar structures in different species irrespective of their functions are called homologous structures. Homology seems to indicate descent from common ancestor. The limb skeletons of vertebrates are homologous structures. Figure 3. The limb skeletons of vertebrates are homologous structures. Source: http://www.geo.arizona.edu/Antevs/nats104/00lect12.html Analogous structures are structures which are different in appearance but have the similar function. Analogy does not indicate common ancestry. Examples of are the limbs of insects and mammals, and wings of butterflies and birds. Figure 4. Analogy of bat & bird wings Source: http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/ Analogy_of_forelimbs.htm Vestigial structures seem like to give more evidence for evolutionary change. Vestigial structures are anatomical features that are usually reduced and have no function in many organisms. These are organs that were previously functional in the ancestors of the species but are only remnants in the present-day species. For example, skeletal extremities discovered in certain snakes have no known use to these animals. In humans, appendix is thought to have no use, but in other mammals it aids in the digestion of cellulose. Table 1. Some Vestigial Organs in Man Coccyx (tail bone) Appendix Ear muscles for wiggling Wisdom teeth D. Biochemical Living organisms shared numerous related biochemical molecules, such as DNA, ATP, amino acids, and enzymes. This finding supports descent from a common ancestor. The more closely linked organisms are the more related is their biochemical genetic makeup. 1. DNA/Nucleic acids Genes are located in the chromosomes, which are made of DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid. The more closely related two living organisms are, the more similar the sequence of their DNA molecules will be. Figure 5. The phylogenetic tree of the hemogobin gene (with its branches) shows the number of nucleotide changes that have occurred. Source: https://evidenceforevolution13bio.weebly.com/biogeography.html 2. Proteins Proteins are molecules that are used to build up and repair body parts. Scientists believe that the more similar the structure of protein molecules of different organisms is, the more related they are and the more recent the existence of their common ancestor. Unrelated species have different amino acids. E. Biogeography Table 2. Cytochrome c Biogeography is the study of the geographic distributions of organisms. Darwin’s trip around South America allowed him to observe the diversity of organisms in different areas and the resemblance of such species of birds and tortoises in an island to nearby mainland. Darwin believed that the group of organisms in each island is adapted to a distinct way of life. The common ancestors of these organisms had come from one place, expanding out into other accessible regions. Figure 6. Pangolins share similar characteristics with anteaters and armadillos Need another activity! Try the next activity on the next page. Explore Activity 1: Complete the Map! Direction: Complete the concept map. Use a separate piece of paper. Evidence for Evolution Activity 2: Practice Test Directions: Fill in the puzzle. The puzzle contains terms used in the lesson. Use the letter clues below to complete the spelling of each word. 1. _ _ _ _ E _ _ _ 2. V________ ______ 3. _O_____ 4. ____L_____ 5. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _U _ _ _ _ _ ____ 6. ___T____ 7. _I__________ 8. _____O____ 9. _N_______ Clues: a. b. c. d. A proof or testimony Non-functional or partly functional organs Preserved remains of an ancient organisms Similar structures from the same ancestral body parts but have different functions e. The major constituent of genes f. Made up of amino acids g. The study of the geographic distributions of organisms h. The study of the development of the anatomy of an organism to its adult form i. Have similar functions but different anatomical structures Deepen Activity: Self -Test Directions: Write a short explanation on each question below. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Can you describe why certain extinct plants and animals were not fossilized? 2. A friend informs you, “man came from apes” since many structural and biochemical similarities are observed between them. How would you respond to this? 3. On the left are the structural palms of various organisms or species of primates. Tarsiers are one of the small species of primates generally found at tropical islands like Bohol, Philippines. Gibbons are small apes usually found in the forests of Southeast Asian regions, Chimpanzees are few of the assumed “smart” animals and humans are considered to be the highest form of “thinking organisms” on Earth. One of the assertions of the theory of Evolution is these organisms evolved from the related ancestor. By examining at the picture how will you support or reject the said claim? 4. In the book, Jurassic Park, by Michael Crichton, scientists are able to reconstruct dinosaurs by getting dinosaur DNA from a mosquito that had been well-preserved in amber since the era of dinosaurs. Do you believe this can actually happen in real life? Why? Well done! Now get ready to measure your mastery on the next page. ASSESSMENT Directions: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. 1. DNA of the life-forms on Earth are almost universal and seem to be templated from one original source, this line of inferring can be based from what evidence of evolution? A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C. Molecular Biology D. Embryology 2. Exactly different organisms such fish and humans may have resemblances during the early stage of their development and will lose some key likenesses as they grow in later stage of development, which among the following is the line of evidence and field of study that underlie the said concept for evolution? A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C Molecular Biology D. Embryology 3. Preserved bodies of cave dwelling man from cold and icy places suggested that humans look different in the past, what evidence of evolution is used? A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C. Molecular Biology D. Embryology 4. Identify what evidence of evolution is used: vertebrate animals such as humans, chickens and fish have gill slits and tails during their embryonic stage. A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C. Molecular Biology D. Embryology 5. Boa constrictors, a kind of snake has a remnant of what appears to be rudimentary hind legs, what type of body structure are these? A. Analogous structures B. Homologous structures C. Embryonic structures D. Vestigial structure 6. These body structures indicate that organisms descended from a close common ancestor. A. Analogous structures B. Homologous structures C. Embryonic structures D. Vestigial structures 7. Fox and polar bears which are distant relatives both developed white colored fur to adapt to the snowy environment where they habituate. These body structures are identified as: A. Analogous structures B. Homologous structures C. Embryonic structures D. Vestigial structures 8. This is the study of body structures of organisms to compare and infer evolutionary links. A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C. Embryology D. Biogeography 9. Which among the following best explains the fossil records as an evidence of evolution? A. Recorded events from the past indicates that the Earth was once filled with water. B. Fossils suggest that the Earth is not the same as it is today, for instance there were once a huge massive interconnected land termed as Pangaea. C. Fossils recorded the history of life on Earth and indicates that ancient life forms were different from modern day species. D. Recorded activities of animals from prehistoric times suggest that people came from monkeys. 10. How will you differentiate analogous structures from homologous structures as evidence of evolution? A. Analogous structures indicate common ancestry while homologous structures suggest evolution because of same environmental factors. B. Analogous structures are structures which indicates that organisms might developed structures with same function as needs arise while homologous structures showed pattern of common descent from different body structures of closely related specie. C. Both analogous and homologous structures are body structures used by researchers to study the evolutionary development of organisms while vestigial organisms showed different result. D. B and C 11. What evidence of evolution is portrayed by the unique species on islands which are usually isolated from another mainland? A. Fossil record B. Comparative Anatomy C. Embryology D. Biogeography 12. Mapping of DNA allows scientist to compare the genes of organisms from the past and organisms present today, the evidence of evolution used is: A. Fossil record B. Molecular Biology C. Analogous structures D. Comparative Anatomy 13. Which is NOT true about fossils? A. They suggest that life has a history. B. They are proofs of life in the past. C. The older the fossil, the less it looks like modern day species. D. They seem precisely like modern-day species, regardless of their age 14. How will you use biogeography as an evidence to infer evolutionary relationship? A. Organisms living closer at each other and sharing the same niche are also closely related to each other. B. The unique characteristics of the organisms living on a secluded area is indicative of their ancestry and speciation. C. Biogeography revealed that organisms with similar developmental pattern even if found at different places might once live together before they were separated due to natural events or forces. D. All of the above 15. The following are the pieces of evidence of evolution that may be used to infer the evolutionary relationship between organisms, EXCEPT . A. Comparative Anatomy C. Molecular Bonds B. Fossil record D. Embryology