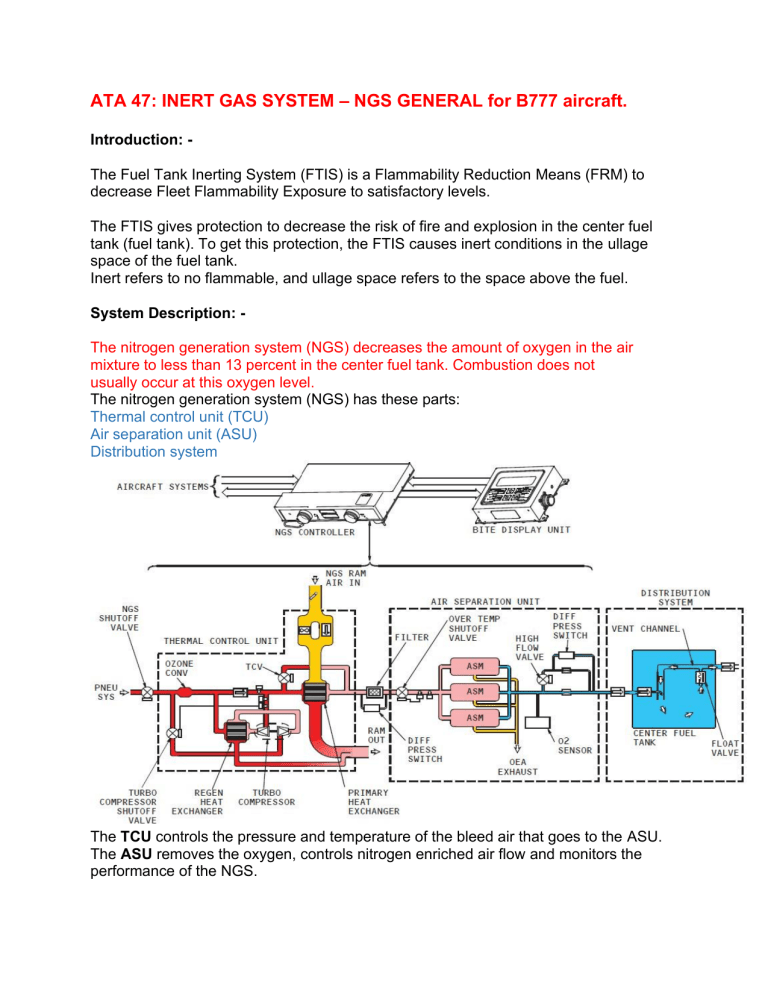
ATA 47: INERT GAS SYSTEM – NGS GENERAL for B777 aircraft. Introduction: The Fuel Tank Inerting System (FTIS) is a Flammability Reduction Means (FRM) to decrease Fleet Flammability Exposure to satisfactory levels. The FTIS gives protection to decrease the risk of fire and explosion in the center fuel tank (fuel tank). To get this protection, the FTIS causes inert conditions in the ullage space of the fuel tank. Inert refers to no flammable, and ullage space refers to the space above the fuel. System Description: The nitrogen generation system (NGS) decreases the amount of oxygen in the air mixture to less than 13 percent in the center fuel tank. Combustion does not usually occur at this oxygen level. The nitrogen generation system (NGS) has these parts: Thermal control unit (TCU) Air separation unit (ASU) Distribution system The TCU controls the pressure and temperature of the bleed air that goes to the ASU. The ASU removes the oxygen, controls nitrogen enriched air flow and monitors the performance of the NGS. The Distribution system uses ducts and valves to move the NEA to the center fuel tank. The nitrogen generation system (NGS) operates without the pilot interface during all phases of flight. The NGS controller commands the NGS for all modes of operation. The NGS controller uses the aircraft configuration and system inputs to choose the NGS mode. The NGS operates in two flow modes, low flow and high flow modes. The low flow mode supplies a minimum amount of nitrogen enriched air (NEA) to the distribution system. The high flow mode supplies an increased NEA flow by opening the high flow valve. The open high flow valve provides an additional NEA path to the distribution system. The NGS also operates in the boost or non-boosted mode. The boost mode is selected by opening the turbo compressor shutoff valve to allow the thermal control unit (TCU) bleed air to enter the turbo compressor. This will increase the bleed pressure to the air separation unit (ASU). The nitrogen generation system uses hot bleed air and changes it to nitrogen enriched air for the center fuel tank. The thermal control unit controls the bleed air pressure and temperature and delivers the air to the air separation modules. The NGS shutoff valve (SOV) gets bleed air from the left side of the pneumatic manifold. The NGS SOV controls the flow of air to the nitrogen generation system. During descent and ground operations, the NGS operates in the Boosted mode. The turbo compressor shutoff valve opens and lets bleed air go to the turbo compressor. Air that goes through the turbine side of the turbo compressor is cooled through expansion and then used to precool the air entering the compressor side of the turbo compressor. The boosted air then goes to the primary heat exchanger and TCV. The ASM reduces the oxygen quantity of the air to a level that is too low to support combustion. This nitrogen enriched air (NEA) goes to the center fuel tank. The distribution section sends the NEA to the center fuel tank. The distribution section has these parts: Tubes Check valves. Float valve Vent channel Drain When the NEA goes into the fuel tank, it pushes the air with oxygen through the vent line out of the fuel tank and causes the inert conditions in the fuel tank. The nitrogen generation system (NGS) turbo-compressor boosts the NGS pressure. The nitrogen is a chemically unreactive gas because it does not support the hydrocarbon combustion reaction, and it is non-reactive with the materials of the fuel system components and equipment. The pressure sensor monitors the bleed air inlet pressure to the nitrogen generation system (NGS). It protects the system and the center fuel tank from an overpressure condition. The oxygen sensor measures the oxygen content and absolute pressure of the nitrogen enriched air (NEA). This information is sent to the nitrogen generation system (NGS) controller. The oxygen sensor monitors air separation module (ASM) performance. Ground: - NGS begins a cold start prior to first flight. The total run time is 15 minutes. The cold start function operates the NGS. The purpose of the cold start or ground run is to ensure the proper concentration of NEA in the center fuel tank before takeoff. Climb: - The NGS system begins operating at takeoff. During climb and for the initial phase of cruise the NGS system will operate in the low flow, non boosted mode. 35 seconds after take off the NGS BIT is initiated. 39 minutes after takeoff the NGS controller initiates the ASM performance test. Cruise: - Cruise shutdown occurs 60 minutes after takeoff, if Cruise shutdown logic is true. The NGS system will begin operating the low flow, non-boosted mode when the aircraft is in cruise and less than 90 minutes from the top of descent (TOD). Descent/Approach: - Descent mode occurs after the aircraft as descended by more than 1000 feet from the top of descent. The initial NGS mode during descent is the high flow non-boosted mode. After 31 seconds the NGS mode changes to the high flow, boosted mode. After the aircraft lands in this condition the NGS will change to the low flow boosted mode Landing (Ground): - After the aircraft lands and the ambient temperature is greater than 60 F (16 C), the NGS will operate for 15 minutes in the low flow, boosted mode. If the temperature is less than 60F (16 C) then NGS will stop 5 seconds after weight on wheels. On B777 aircraft. The two EICAS messages are: NITROGEN GEN PERF NITROGEN GEN SYS 1) NITROGEN GEN PERF: - The nitrogen generation (GEN) performance (PERF) EICAS message is a status level message. The message indicates the system is operational. However, the performance is degraded. The NGS can continue to operate for 10 consecutive days before a repair is necessary. 2) NITROGEN GEN SYS: - The nitrogen generation system (SYS) EICAS message is a status level message. The message indicates the system is not operational. Maintenance action is required to use the system or dispatch the aircraft with the system when not operational. BITE display unit (BDU) to troubleshoot the nitrogen generation system (NGS) components. The bite display unit has no processing ability. The BDU communicates with the NGS controller over the RS422 interface. The BITE display unit is in the forward section of the right air conditioning compartment. You get access to the unit through the access door to the pneumatic ground connector. The nitrogen generation system (NGS) controller controls and monitors the NGS. It also provides an interface to other aircraft systems. The NGS controller is behind the sidewall liner on the right side of the forward cargo compartment. The GROUND TEST menu lets you do a series of tests of the nitrogen generation system. ELECTRICAL TEST SYSTEM TEST GSE PERF NON-BOOSTED (low flow mode) GSE PERF BOOSTED (high flow mode) DISPLAY TEST When you select a particular test, the message TEST IN PROGRESS shows. If there is no fault during the test, the display shows SYSTEM OK. If there is a fault during TESTING, the display shows EXIST FAULTS for 2 seconds. Then the display shows the EXISTING FAULTS menu.