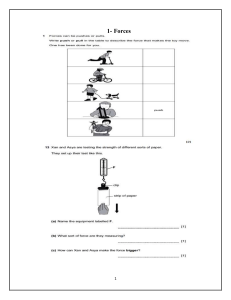
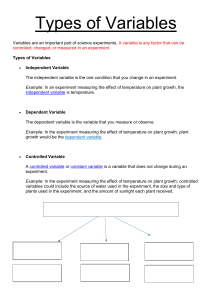
INTRODUCTION: Natural resources are materials that support life and provide energy for living beings and machines, sourced from the sun or Earth's natural processes within the environment's atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. WHERE DOES ENERGY COME FROM? Source of Materials for Living Things: Different spheres of the Earth provide essential materials for living organisms. Sunlight is the only external source, crucial for life processes. Role of Sunlight: Plants and algae (producers) utilize sunlight for photosynthesis to produce food. Sunlight's energy is converted into chemical energy in plants, forming various compounds like wood, starch, and oil. Impact of Sunlight: Sunlight generates heat, influencing wind movement, waves, ocean currents, and weather patterns. It dictates the climate in different regions and serves as a renewable energy source for electricity generation. Recyclability of Sunlight: While various resources supporting life can be recycled, sunlight is an exception and cannot be recycled. Energy Resources: The sun is the primary energy source for Earth, essential for sustaining life. Plants utilize solar energy through photosynthesis to produce food, a process also seen in ancient plants that became fossil fuels. Earth's internal heat, stemming from radioactive elements and planetary formation, can be utilized for electricity generation. Nonrenewable Resources: Nonrenewable resources are finite substances that cannot be easily replaced or regenerated within a short span. Fossil Fuels: Formed from ancient plants and animals over millions of years, buried deep within the Earth's layers. Intense heat, pressure, and chemical reactions transformed plant and animal remains into hydrocarbons like coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Coal: Solid fossil fuel, primarily composed of carbon, derived from fossilized dead plants in oxygen-deprived swamps. Main source of global electricity generation with advantages including ample supply and high net energy yield, but disadvantages such as land disturbance, pollution, and emissions of CO2 and air pollutants. Peat to Coal Development: Peat is an initial coal stage, consisting of decayed plant fibers, generating more smoke than energy. Pressure transforms peat into lignite (brown coal) with low heat energy output. Further compression leads to bituminous coal, a sedimentary rock with impurities, and then anthracite coal, nearly pure carbon and exceptionally hard. Oil (Petroleum): Liquid fossil fuel formed from deceased sea-surface organisms, preserved under layers of sediments over time. Refined oil yields gasoline, diesel, kerosene, used for fuel and various products like plastics and fertilizers. Advantages of Oil: Abundant supply for decades. High net energy yield, though declining. Minimal land disruption with an efficient distribution system. Disadvantages of Oil: Water pollution risks from spills and leaks. Excludes environmental costs from market prices. Emission of CO2 and air pollutants upon burning. Susceptibility to international supply disruptions. Natural Gas: Comprised mainly of methane, a hydrocarbon. Often found above oil deposits and used for cooking, heating, and power generation. Advantages include ample supply, high net energy yield, and lower CO2 emissions than other fossil fuels. Disadvantages involve low net energy for liquefied natural gas, emissions upon burning, and challenges in international transportation. Nuclear Energy: Nuclear fission involves splitting an atom's nucleus to release nuclear energy, primarily in the form of heat. Heat from nuclear reactions converts water into steam, driving turbines to generate electricity. Advantages: Comparable cost to coal, minimal greenhouse gas emissions, efficient energy production, small waste generation, and reliability. Disadvantage: Management of radioactive waste poses significant risks and requires long-term secure storage. Renewable Resources: Solar, wind, geothermal, hydro, and biomass energy sources are continually available unlike dwindling fossil fuels. Solar Energy: Sunlight converted into electricity using solar cells made of silicon layers. Advantages: Moderate environmental impact, no direct emissions, lower cost with natural gas backup. Disadvantages: Low net energy, high initial cost, need for backup systems on cloudy days, and high water use for cooling. Wind Energy: Wind power, derived from the sun's energy, has historical use for grinding grains and pumping water. Generates electricity as wind turns turbines, exemplified by the Bangui wind Farm in Ilocos Norte. Advantages: Moderate to high net energy, widely available, low electricity cost, minimal emissions, and easy expansion. Disadvantages: Requires backup or storage, potential visual and noise pollution, and risk to birds if not properly located. Geothermal Energy: Heat from the earth's crust, fueled by radioactive decay, harnessed by tapping hot water underground to produce electricity. Advantages: Moderate net energy, low CO2 emissions, and cost-effective in suitable locations. Disadvantages: High cost and efficiency challenges except at specific sites, limited suitable locations, and some emissions. Hydrothermal Energy: Utilizes water's kinetic energy from waterfalls or dams to run turbines for electricity generation. Advantages: Moderate to high net energy. Disadvantages: Land disturbance, ecosystem disruption, and emissions in certain conditions. Dendrothermal Energy (Biomass): Biomass, recent plant and animal matter, burned directly for heating or processed into biofuels. Advantages: Availability, potential for sustainable use, and land restoration. Disadvantages: Environmental impact, increased emissions if not sustainable, habitat loss, and inefficient burning practices. Biodiesel: Derived from crops like oil palm or soybeans, offering reduced emissions and better mileage. Advantages: Lower CO and CO2 emissions, high net energy yield for oil palm, reduced hydrocarbon emissions, and improved mileage. Disadvantages: Increased NO2 emissions, competition with food crops, habitat loss, and potential biodiversity reduction. Energy from Tides: A dam is constructed across an estuary or bay to harness tides for electricity. Turbines on both sides of the dam generate electricity by allowing water through during high and low tides. Greater water level differences result in increased electricity generation. Advantages: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cost-effective: Tidal power is free once infrastructure is in place. Environmentally friendly: Produces no greenhouse gases or waste. No fuel required: Relies on natural tidal movements. Reliable electricity production: Consistent energy generation. Low maintenance costs: Not expensive to upkeep. Predictable: Tides follow a known pattern. Disadvantages: 1. High initial cost: Building a barrage across an estuary is expensive. 2. Limited power generation: Only active for about 10 hours daily during tidal movements. Energy Conservation: Goal: Conserve energy to extend the lifespan of non-renewable sources and reduce environmental impact. Approaches: Use less energy and increase energy efficiency. Ways to Use Energy More Efficiently: Where Energy is Used Transportation Residential How to Use Less Energy How to Use Energy More Efficiently - Ride a bike or walk instead of driving. - Reduce the number of trips made. - Carpool or use public transportation. - Increase fuel efficiency in cars. - Opt for smaller, lighter cars. - Drive at speeds below 90 kilometers per hour. - Turn off lights when not in use. - Use appliances only when necessary. - Unplug appliances when idle. - Upgrade to newer, more efficient appliances. - Insulate the home. - Ensure windows and doors are well-sealed. - Use LED or compact fluorescent light bulbs. Where Energy is Used How to Use Less Energy How to Use Energy More Efficiently - Opt for activities not involving electronics. - Utilize natural light over artificial lighting. Industrial - Recycle materials like tin cans, plastics, glass, and steel. - Reduce use of plastic, paper, and metal. - Reuse materials. - Design equipment for efficiency. - Practice conservation in plants/factories. Commercial - Turn off appliances and equipment when not in use. - Utilize fluorescent lighting. - Set thermostats to automatically adjust when buildings are closed. - Implement energysaving practices in business operations. Conclusion: Conservation: Preserve energy resources by reducing consumption and improving efficiency to avoid wasting non-renewable resources.