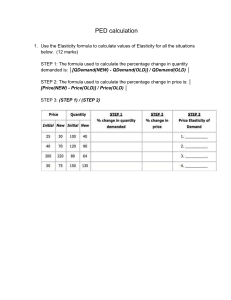
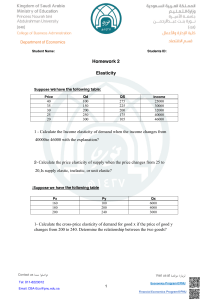
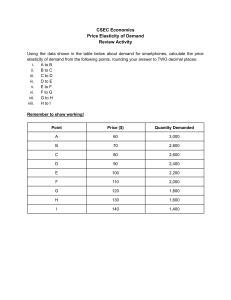
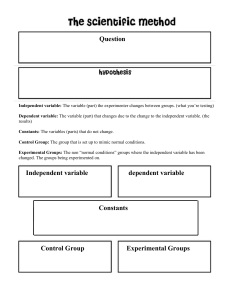
Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Materials for Mechanical Design Part 1: 3 Types of Material Properties Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Professor Dr. Mazharul Islam Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 2 / 44 Bibliography Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/) 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Learning Outcomes for the Class Session Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 3 / 44 Bibliography After duly participating in this class session and studying the related contents on the accompanying online course site, the students will be expected to classify engineering materials; define the elasticity constants; explain the key physical properties of the engineering materials; explain the key chemical properties of the engineering materials; explain the key mechanical properties of the engineering materials; and address the variability of materials properties data in design works. 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Brain Storming Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 5 / 44 Bibliography How the engineering materials can be classified? Common Types Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 6 / 44 Bibliography Ductile Vs Brittle Metal Vs Non-Metal Ferrous Vs Non-Ferrous Material Families and Classes [1, Table 2-5, pp. 81-82] Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 7 / 44 Bibliography Metals Ceramics Glasses Polymers Elastomers Hybrids Composites Foams Natural Materials "Materials Data Book" from Cambridge University Engineering Department, 2011 Learning Outcomes Review Available at http://teaching.eng.cam.ac.uk/sites/teaching. eng.cam.ac.uk/files/Documents/Databooks/MATERIALS% 20DATABOOK%20(2011)%20version%20for%20Moodle.pdf Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 8 / 44 Bibliography "V. CLASSIFICATION AND APPLICATIONS OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS" 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Brain Storming Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 9 / 44 Bibliography Which properties of materials are important for mechanical design? 3 Types of Properties Learning Outcomes Review Physical Properties Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Chemical Properties Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 10 / 44 Bibliography Mechanical Properties 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Elasticity Constants Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 11 / 44 Bibliography Poisson’s Ratio (µ) Young’s Modulus or Modulus of Elasticity (E) Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity (G) Bulk Modulus (K) Flexural Modulus Poisson’s Ratio (µ or ν) −Lateral Strain −ϵL = =ν Axial Strain ϵa (adopted from Mott and Tang [4]) "When a material is subjected to a tensile strain, there is simultaneous shortening of the cross-sectional dimensions perpendicular to the direction of the tensile strain" [4] "The ratio of the shortening strain to the tensile strain is called Poisson’s ratio" [4] Typical values based on [4] Poisson′ s ratio = Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Cast Iron: 0.25 to 0.27 Steel: 0.27 to 0.30 Aluminum and Titanium: 0.30 to 0.33 Post-Assessment Summary 12 / 44 Bibliography Please refer to Figure 2-4 of [4, p. 36] for more insights. Young’s Modulus or Modulus of Elasticity (E) Learning Outcomes Review E= Introduction stress σ = strain ϵ (Eq. (2-1) from Mott and Tang [4]) Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Derived from the Hooke’s Law [2] Physical Properties Unit is GPa Chemical Properties Please consult Table 4.1 of [2] for the typical values of E for some of common engineering materials Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 13 / 44 Bibliography Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity (G) Learning Outcomes Review G= Introduction Shear Stress τ = Shear Strain ϕ (as per [2, p. 94]) Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Based on experimental investigations [2] Physical Properties Unit is GPa Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 14 / 44 Bibliography Please consult Table 4.2 of [2] for the typical values of G for some of common engineering materials Bulk Modulus (K) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 15 / 44 Bibliography K= Direct Stress σ = Volumetric Strain δV /V (as per [2, p. 112]) "When a body is subjected to three mutually perpendicular stress, or equal intensity, then the ratio of the direct stress to the corresponding volumetric strain is known as bulk modulus" [2] Bulk Modulus (K) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 16 / 44 Bibliography K= Direct Stress σ = Volumetric Strain δV /V (as per [2, p. 112]) "When a body is subjected to three mutually perpendicular stress, or equal intensity, then the ratio of the direct stress to the corresponding volumetric strain is known as bulk modulus" [2] Flexural Modulus or Modulus of Elasticity in Flexure[4, p. 37] Learning Outcomes Review "another stiffness measure often reported, particularly for plastics" [4] Introduction "a specimen of a material is loaded as a beam in flexure (bending) with data taken and plotted for load versus deflection" [4] Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants "The ratio of stress to strain is a measure of the flexural modulus " [4] Physical Properties "the stress pattern in the specimen is a combination of tension and compression " Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 17 / 44 Bibliography Relationships between Elastic Constants Learning Outcomes Review Introduction K= E 3(1 − 2µ) (as per [2, p. 112]) G= E 2(1 + µ) (as per [2, p. 112]) Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 18 / 44 Bibliography 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Physical Properties Melting (of Softening) Temperature Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Density Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 19 / 44 Bibliography Thermal Conductivity Electrical Resistivity 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Chemical Properties 1 Heat of Combusion Learning Outcomes Review Chemical Stability Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Preferred Oxidation State(s) Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Ability to Corrode Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 20 / 44 Bibliography 1 Adopted from https://www.samaterials.com/physical-and-chemical-properties.html 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Mechanical Properties [2, 3] Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 21 / 44 Bibliography Strength Stiffness Elasticity Plasticity Ductility Brittleness Malleability Toughness Machinability Resilience Creep Fatigue Hardness Tensile Test Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 22 / 44 Bibliography "Strength, elastic, and ductility properties for metals, plastics, and other types of materials are usually determined from a tensile test" [4] "a sample of the material, typically in the form of a round or flat bar, is clamped between jaws and pulled slowly until it breaks in tension" [4] Please refer to "Section 2-1 Material Strength and Stiffness" in the Textbook [1] Tensile Strength (Su ) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants "The peak of the stress-strain curve is considered the ultimate tensile strength (Su )" [4] "sometimes called the ultimate strength or simply tensile strength" [4] Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 23 / 44 Bibliography (Eq. 1.11 [4]) Yield Strength (sy ) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 24 / 44 Bibliography "That portion of the stress-strain diagram where there is a large increase in strain with little or no increase in stress" [4] "The property indicates that the material has, in fact, yielded or elongated plastically, permanently, and to a large degree" [4] Shear Strength (sy s or su s) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties "Both the yield strength and the ultimate strength in shear (sy s and su s, respectively) are important properties" [4] "Unfortunately, these values are seldom reported" [4] "We will use the following estimates" [4] sys = sy /2 = 0.50sy = yield strength in shear (Eq. (2-3) from Mott and Tang [4]) Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 25 / 44 Bibliography sus = 0.75su = ultimate strength in shear (Eq. (2-3) from Mott and Tang [4]) Fatigue Strength or Endurance Strength (sy s or su s) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 26 / 44 Bibliography "Parts subjected to repeated applications of loads or to stress conditions that vary with time over several thousands or millions of cycles fail because of the phenomenon of fatigue" [4] "Materials are tested under controlled cycle loading to determine their ability to resist such repeated loads" [4] "The resulting data are reported as the fatigue strength" [4] "also called the endurance strength of the material" [4] Stiffness or Rigidity Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 27 / 44 Bibliography "It is the ability of the material to resist deformation under stress" [2] "The modulus of elasticity is the measure of stiffness" [2] Elasticity Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 28 / 44 Bibliography "the property of a material to regain its original shape after deformation when the external forces are removed" [2] "desirable for materials in tools and machines" [2] "steel is more elastic than rubber " [2] Plasticity Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 29 / 44 Bibliography "property of a material which retains the deformation produced under load permanently " [2] "necessary for forging, in stamping images on coins and in ornamental works" [2] Ductility Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 30 / 44 Bibliography "degree to which a material will deform before ultimate fracture" [4] "When ductile materials are used in machine members, impending failure is detected easily, and sudden failure is unlikely" [4] "ductile materials normally resist the repeated loads on machine elements better than brittle materials" [4] "The usual measure of ductility is percent elongation of the material after fracture in a standard tensile test" [4] Lf − LO × 100% LO (Eq. (2-1) from Mott and Tang [4]) Percent Elongation = Brittleness Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 31 / 44 Bibliography "The opposite of ductility is brittleness" [4] "shows negligible plastic deformation before fracture takes place" [3] "Brittle material fail by sudden fracture" [3] Example: Cast Iron Malleability Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 32 / 44 Bibliography "a special case of ductility which permits the material to be rolled or hammered into thin sheets" [2] "The malleable materials commonly used in engineering practice (in order of diminishing malleability) are lead, soft steel, wrought iron, copper and aluminium" [2] Toughness Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 33 / 44 Bibliography "The property of the material to resist fracture due to high impact loads like hammer blows" [2] "desirable in parts subjected to shock and impact loads" [2] "Tough materials have the ability to bend, twist or stretch before failure takes place" [3] "Modulus of toughness is the total area under stress-strain curve in tension test" [3] Machinability Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 34 / 44 Bibliography "the property of a material which refers to a relative case with which a material can be cut" [2] "reported in comparative terms, relating the performance of a given material with some standard" [4] "brass can be easily machined than steel" [2] Resilience Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 35 / 44 Bibliography "ability of the material to absorb energy when deformed elastically and to release this energy when unloaded" [3] "A resilient material absorbs energy within the elastic range without any permanent deformation" [3] "essential for spring materials" [3] "measured by a quantity called modulus of resilience" [3] "represented by area under stress-strain curve from origin to elastic limit point" [3] Creep Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 36 / 44 Bibliography "When a part is subjected to a constant stress at high temperature for a long period of time, it will undergo a slow and permanent deformation called creep" [2] "considered in designing internal combustion engines, boilers and turbines" [2] Fatigue Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 37 / 44 Bibliography "When a material is subjected to repeated stresses, it fails at stresses below the yield point stresses" [2] "Such type of failure of a material is known as fatigue" [2] "The failure is caused by means of a progressive crack formation which is usually fine and microscopic size" [2] "considered in designing shafts, connecting rods, springs, gears, etc." [2] Hardness Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 38 / 44 Bibliography "defined as the resistance of the material to penetration or permanent deformation" [3] "an important property in selection of materials for parts which rub on one another such as pinion and gear, cam and follower, rail and wheel and parts of the ball bearings" [3] "four primary methods of measuring hardness - Brinell hardness test, Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test and Shore scleroscope" [3] Please read Section "2-4 Hardness" of [1] for more information 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Variability of Material Properties Data Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 39 / 44 Bibliography "As the designer, you must carefully judge the reliability of the data that you use" [4] "you should evaluate the reliability of the final product by considering the actual variations in material properties, the manufacturing considerations that may affect performance, and the interactions of various components with each other" [4] Please read Section "2-2 The Statistical Significance of Material Properties" of [1] "Materials Data Book" from Cambridge University Engineering Department, 2011 Learning Outcomes Available at http://teaching.eng.cam.ac.uk/sites/teaching. eng.cam.ac.uk/files/Documents/Databooks/MATERIALS% 20DATABOOK%20(2011)%20version%20for%20Moodle.pdf Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 40 / 44 Bibliography "It must be realised that many material properties (such as toughness) vary between wide depending on composition and previous treatment. Any final design should be based on manufacturers’ or suppliers’ data for the material in question, and not on the data given here." 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Lessons Learned in Today’s Class Session Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 41 / 44 Bibliography What are the key lessons you have learned today? 1 Learning Outcomes 2 Review 3 Introduction 4 Properties of Materials 5 Elasticity Constants 6 Physical Properties 7 Chemical Properties 8 Mechanical Properties 9 Variability of Material Properties Data 10 Post-Assessment 11 Summary Summary Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 42 / 44 Bibliography Classification of engineering materials; Physical properties of the engineering materials; Chemical properties of the engineering materials; Mechanical properties of the engineering materials; and Variability of materials properties data in design works. Summary of the Mechanical Properties Strength (yield/ultimate/shear/fatigue) Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Stiffness or Rigidity (Young’s Modulus/Flexural Modulus) Elasticity (elastic regions) Machinability (comparative terms) Plasticity (plastic regions/Flexural Modulus) Resilience (modulus of resilience) Chemical Properties Ductility (Percent Elongation) Mechanical Properties Brittleness (fracture point) Variability of Material Properties Data Malleability (compressive stress at breaking point) Post-Assessment Summary 43 / 44 Bibliography Toughness (Modulus of Toughness) Creep (creep strain) Fatigue (fatigue strength) Hardness (BHN/HB) References I Learning Outcomes Review Introduction Properties of Materials Elasticity Constants Physical Properties Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Variability of Material Properties Data Post-Assessment Summary 44 / 44 Bibliography [1] R. G. Budynas and J. K. Nisbett, Shigley’s MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DESIGN. McGraw-Hill Education (India) Private Limited, eleventh e ed., 2021. [2] R. S. Khurmi and J. K. Gupta, A Textbook of Machine Design. S. Chand Publishing, low priced students’ paperback edition ed., 2019. [3] V. B. Bhandari, Design of MACHINE ELEMENTS. McGraw-Hill Education (India) Private Limited, silver jubilee ed., 2021. [4] R. L. Mott and J. Tang, Machine Elements in Mechanical Design. Pearson India, 2020.