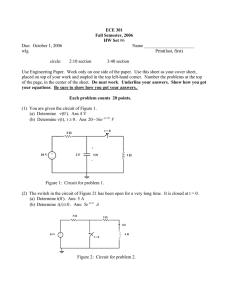
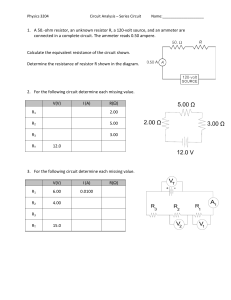
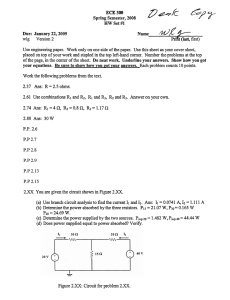
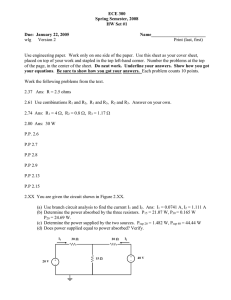
E M K 11203 E L E C T R I C CIRCUIT THE ORY 1 Chapter 2: Resistive Circuit (cont.) Delta (∆) - Wye (Y) Circuit ⦁ Circuit configuration are often encountered in which the resistor do not appear to be in series or parallel. ⦁ Need to convert the circuit form one form to another to solve. ⦁ Two circuit configuration that often account for these difficulties configuration: Wye (Y) ⦁ Delta (∆) ⦁ The bridge network 2 Delta (∆) - Wye (Y) Circuit (Cont…) ⦁ Delta (PI) configuration 3 Delta (∆) - Wye (Y) Circuit (Cont…) ⦁ Wye configuration 4 Delta (∆) - Wye (Y) Circuit (Cont…) ⦁ ∆ - Y transformation 5 Delta (∆) - Wye (Y) Circuit (Cont…) ⦁ Y - ∆ transformation 6 E xam ple ⦁ Convert the ∆ to a Y 𝑅𝐵𝑅𝐶 𝑅1 = 𝑅Æ + 𝑅𝐵 + 𝑅𝐶 (20Ω)(10Ω) 𝑅1 = = 3.3333Ω 30Ω + 20Ω + 10Ω 𝑅Æ𝑅𝐶 𝑅2 = 𝑅Æ+ 𝑅𝐵 + 𝑅𝐶 (30Ω)(10Ω) 𝑅2 = = 5Ω 30Ω + 20Ω + 10Ω 𝑅Æ𝑅𝐵 𝑅3 = 𝑅Æ + 𝑅𝐵 + 𝑅𝐶 𝑅3 = 7 (30Ω)(20Ω) = 10Ω 30Ω + 20Ω + 10Ω E xam ple ⦁ Convert the Y to a ∆ 𝑅1 𝑅2 + 𝑅 2 𝑅 3 + 𝑅1 𝑅 3 𝑅Æ = 𝑅1 (10 Ω)(5Ω) + (5Ω)(10Ω) + (10 Ω)(10Ω) 3 𝑅Æ = 3 = 30Ω 10 Ω 3 𝑅𝐵 = 𝑅1 𝑅2 + 𝑅 2 𝑅 3 + 𝑅 1 𝑅3 𝑅2 (10 Ω)(5Ω) + (5Ω)(10Ω) + (10 Ω)(10Ω) 3 𝑅𝐵 = 3 = 20Ω 5Ω 𝑅𝐶 = 𝑅1 𝑅2 + 𝑅 2 𝑅 3 + 𝑅 1 𝑅3 𝑅3 (10 Ω)(5Ω) + (5Ω)(10Ω) + (10 Ω)(10Ω) 3 𝑅𝐶 = 3 = 10Ω 10Ω 8 E xercise ⦁ Find the total resistance (RT) of the network Ans: RT = 2.889Ω 9 E xam ple ⦁ Find the current and power supplied by the 40V sources in the circuit shown below. We can find this equivalent resistance easily after replacing either the upper Δ (100, 125, 25Ω) or the lower Δ (40, 25, 37.5Ω) with its equivalent Y. We choose to replace the upper Δ. Thus, 100125 = 50 250 125 25 R2 = = 12.5 250 100 25 R3 = = 10 250 R1 = 10 Equivalent resistance, Req = 55 + 50 50 = 80 100 Then, the current and power values are, 40 = 0.5A 80 p = 40 0.5 = 20W i= 11 E xercise ⦁ Find the equivalent resistance (Rab) & current i. Ans: Rab = 9.632Ω i = 12.458A 12 Practice 1 ⦁ Find i and Vab Ans: i = -1A Vab = 56V 13 Practice 2 ⦁ Find Rab, Is, Vx and Power at 80 V. Ans: Rab = 40Ω IS = 2A Vx = -60V 14 Practice 3 ⦁ Find V1, V2 and Is using star-delta transformation technique Ans: V1 = 10V V2 = 5V IS = 1.0476A 15 Practice 4 ⦁ Find V1, V2 and power in 5kΩ and 20kΩ using voltage divider rule or current divider rule Ans: V1 = 45V V2 = 60V P5 = 0.18W P20 = 0.18W 16 Practice 5 ⦁ Find Vx, Vy and Ix using voltage divider rule or current divider rule Ans: Vx = 10.8 V Vy = 4.8V Ix = 6A 17 Practice 7 ⦁ Find Req, IT and power developed by 30V. Ans: Req = 8.963Ω IT= 3.347A P30V= 100.41W 18 Practice 8 ⦁ Find Vo and power absorbed by 10Ω. Ans: Vo= 4.376V P10= 748.03mW 19 Practice 9 ⦁ Find I1, I2, I3 and I4 using current divider rule and Kirchhoff Current Law. Ans: I1= 5A I2= 2.5A I3= -2.5A I4= 1.25A 20 Practice 10 ⦁ Find V0 using voltage divider rule. Ans: Vo= 14.084V 21 Practice 11 ⦁ Find RT and Vx Ans: RT=36.25Ω Vx= 9.310V 22 Practice 12 ⦁ Find VX and VY using voltage divider rule and power at 2 Ω. Ans: Vx= 5V VY= 3V P2= 2W 23