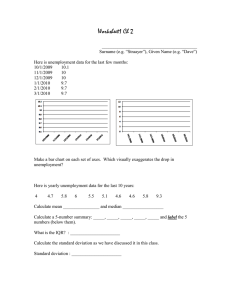
Unemployment Unemployment is a term referring to individuals who are employable and actively seeking a job but are unable to find a job [1]. It does not include stay-at-home parents, retirees or students. Types of unemployment Structural unemployment is a form of involuntary unemployment caused by a mismatch between the skills that workers in the economy can offer, and the skills demanded of workers by employers.[2] It remains for long periods and is caused due to technological changes, government policies or competition. Frictional unemployment is a type of short-term unemployment that occurs when workers look for new employment or transition out of old jobs and into new ones.[3] This could occur due to seasonal employment patterns, geographic mobility and voluntary transition. Cyclical unemployment is tied with business cycles and fluctuation in the overall economy, the downturns lead to a less demand of goods and services which increases the job loss. Seasonal unemployment is caused when people are unemployed during certain time periods of an year because of the environment and natural cycles. FACTORS RELATED TO UNEMPLOYMENT Economic factors: Economic factors significantly influence unemployment levels. Fluctuations in the business cycle, technological advancements, globalization, labour market regulations, and skill mismatches all play a role. Demographic factors: Demographic factors also play a crucial role in shaping unemployment rates. Population growth rates, particularly in relation to job creation, have a significant impact on unemployment levels. Additionally, the age structure of the population, including trends such as an aging workforce or a youth bulge, can influence labour force participation rates and overall unemployment figures. Social & Cultural factors: Social and cultural factors are important determinants of unemployment rates. Education and skill levels greatly impact employability, with higher levels of education often correlating with lower unemployment rates. Moreover, factors like geographical mobility, influenced by housing affordability and transportation, can affect individuals' ability to access employment opportunities. Government policies: Government policies, including unemployment benefits and job creation initiatives, play a vital role in mitigating unemployment. These measures influence job seekers' incentives and enhance workforce skills to address unemployment rates effectively. Additionally, monetary and fiscal policies aim to stimulate economic growth and reduce unemployment during downturns. CONSEQUENCES OF UNEMPLOYMENT 1. Financial Difficulties: This leads to a lack of regular income, making it difficult for individuals to meet their basic needs and sustain a decent standard of living. 2. Reduced Purchasing Power: It decreases personal purchasing power, as individuals have limited or no income to spend on goods and services. 3. Social Stigma and Psychological Impact: It can result in social stigma and a sense of social exclusion. Individuals may face criticism, low selfesteem, and psychological stress due to the inability to find work. 4. Increased Inequality: The lack of job opportunities and income disparities can widen the gap between the rich and the poor, leading to social unrest and dissatisfaction. 5. Brain Drain: Qualified professionals may seek employment opportunities abroad, causing a loss of skilled workforce and hindering the country’s overall development. 6. Social Unrest: Frustrations arising from a lack of jobs can manifest in protests, strikes, and demonstrations, demanding better employment opportunities and government intervention. 7. Economic Burden: The government has to bear the burden of providing social welfare programs, unemployment benefits, and job creation initiatives. Additionally, the loss of productive human capital hampers economic growth and development. [4] RATE OF UNEMPLOYMENT The unemployment rate is the percentage of the labor force without a job. It is a ,lagging indicator meaning that it generally rises or falls in the wake of changing economic conditions, rather than anticipating them. When the economy is in poor shape and jobs are scarce, the unemployment rate can be expected to rise. When the economy grows at a healthy rate and jobs are relatively plentiful, it can be expected to fall.[5] The 2023 global unemployment rate stood at 5.1 per cent, a modest improvement from 2022 when it stood at 5.3 per cent.[6] SOLUTION: Indeed, implementing a multifaceted approach is crucial in addressing unemployment effectively. By adapting industrial techniques to match market demands, adjusting policies to mitigate seasonal unemployment, and reforming the education system to align with industry needs, opportunities for employment can be expanded. Strengthening employment exchanges and providing support for self-employed individuals can also enhance job prospects. Emphasizing full and productive employment, increasing production rates, and prioritizing employment programs further contribute to tackling unemployment. Additionally, managing population growth can play a vital role in addressing the long-term sustainability of employment opportunities in the country. These measures, when implemented in conjunction, can foster a more resilient and inclusive economy with reduced unemployment rates. Sources1.https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/economics/unemployme nt/#:~:text=What%20is%20Unemployment%3F,not%20have%20an%20ap propriate%20job.- corporate finance institute 2.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Structural_unemployment- Wikipedia 3.https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/frictionalunemployment.asp#:~:text =Frictional%20unemployment%20is%20the%20result,workforce%20contri bute%20to%20frictional%20unemployment.- Investopedia 4.https://www.nextias.com/blog/unemployment/#:~:text=What%20are%20th e%20Effects%20of,in%20social%20unrest%20and%20crime. - Nextias 5.https://www.investopedia.com/terms/u/unemploymentrate.asp – Investopedia 6. https://www.ilo.org/global/about-theilo/newsroom/news/WCMS_908068/lang-en/index.htm#:~:text=The%202023%20global%20unemployment%20rate,s tood%20at%205.3%20per%20cent.- ILO BY- Rishit Ranjan