Infection Control Guidelines: PPE, Precautions, and Pathogens
advertisement

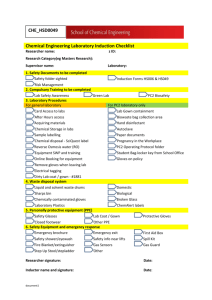
1. Differentiate universal and standard precaution. - Universal Precautions are guidelines developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that protect healthcare workers from exposure to potentially infectious materials. Standard Precautions are a more comprehensive set of safety protocols used to protect healthcare workers and patients from infection. Universal precautions are based on the principle that all blood and bodily fluids should be treated as if they are infectious, regardless of whether the source is known to be infected. Universal precautions are applicable to all patients, while standard precautions provide an additional layer of protection for those at higher risk of transmitting certain infections. Together, they create a comprehensive and effective strategy for reducing the risk of healthcare-associated diseases. Reference: Kelvas, D. MD (2023, March 10). Standard vs Universal Precautions: What’s the Difference? HIPAA Exams. https://www.hipaaexams.com/blog/universal-standardprecautions#:~:text=Universal%20Precautions%20are%20guidelines%20developed,w orkers%20and%20patients%20from%20infection. 2. Discuss the proper way of donning the ppe. a) Perform hand hygiene prior to donning PPE b) Put on gown. - gowns must fully cover a person’s torsos from neck to knees, arms to wrists and must wrap around their back. c) Put on mask or respirator. - Ties must be secured around the ears or the back of the head. - The flexible band must be fitted to the nose bridge. - Masks must fit snug to the face and below chin. d) Put on goggles or face shield. - Both must be placed over the face and eyes and adjusted to fit. e) Put on goggles or face shield. - Both must be placed over the face and eyes and adjusted to fit. f) Put on gloves. - Gloves must be extended to cover the wist of the gown that was already put on. 3. Discuss the proper way of doffing PPE a) Remove gown and gloves - Gowns are pulled away from the front of the body using only gloved hands so that the ties break. As the gown is pulled off, gloves are also peeled at the same time and only the inside of the gloves are touched in this process. b) Remove goggles or face shield. - Googgles and face shields are removed from the back of the head, lifting any bands without touching the front to avoid contamination. c) Remove mask or respirator. - Masks and respirators must be grasped from the ties or elastics in the back and removed without touching the front to avoid contamination. d) Immediately perform hand hygiene after doffing of PPE. Reference: Pondo, A. (2020, May 15). Donning and Doffing of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Tampa General Hospital. https://www.tgh.org/news/tgh-healthnews/2020/may/donning-and-doffing-of-personal-protective-equipment-ppe 4. List different PPE in the laboratory and their functions - Lab gowns/coats – protect skin and clothing from chemical splashes spills, and contamination. - Gloves – protect hands from chemical exposure, biological hazards, and sharp objects. - Masks/respirators – prevent inhalation of hazardous chemicals, dusts, fumes, and biological agents. - Closed-toe shoes – protect feet from chemical spills, dropped objects, and other hazards. - Hairnets – prevent hair from contaminating experiments or getting caught in equipment. - Face shields – provide additional protection to the face, particularly from splashes and flying debris. - Goggles – protect eyes from chemical splashes, dust, and flying debris. Reference: Personal Protective Equipment | Environmental health & Safety. (n.d.). https://www.ehs.gatech.edu/chemical/lsm/7-6 5. what to do in case of accidental needle prick injury? - A) wash it. rinse and wash the are well with running water and soap. No need to use antiseptics. Its also a good idea to flush out your eyes, nose,a nd mouth with water or sterile saline in case of splashes. - B) fact check it. find out as much as you can about the source patient of the needle. Find out if they have HIV, Hepa B or C - C) get treated immediately. This is an urgent situation and requires immediate treatment in a healthcare setting. Seek for a tailored treatment plan. It will be based on factors like depth and location of the needle stick. Reference: Ellis, R. R. (2023, May 16). Needle stick injury: What to do. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/hiv-aids/needle-stick-injury-what-do 6. List different blood-borne pathogens encountered in the laboratory. According to the british Columbia centre for disease control, blood borne pathogens include malaria, syphilis brucellosis Hepa B, Hepa C, and HIV. According to the CDC, the most common bbp are HIV, HEpa B and Hepa C. References: Bloodborne diseases. (n.d.). http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/disease-types/bloodbornediseases CDC - Bloodborne Infectious Diseases - Stop Sticks : Bloodborne Pathogens - NORA. (n.d.). https://www.cdc.gov/nora/councils/hcsa/stopsticks/bloodborne.html