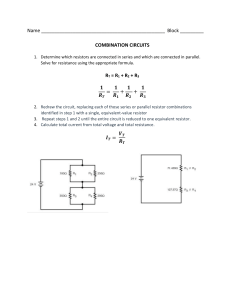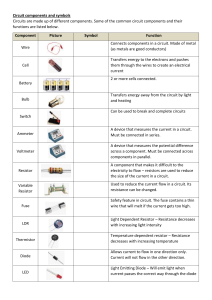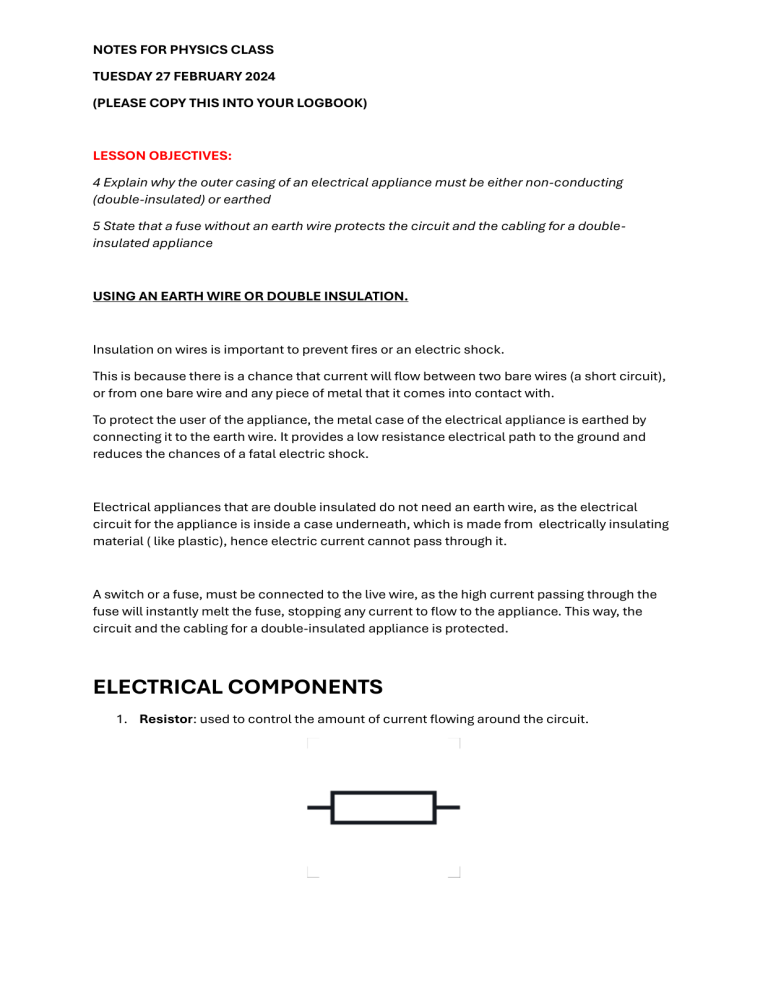
NOTES FOR PHYSICS CLASS TUESDAY 27 FEBRUARY 2024 (PLEASE COPY THIS INTO YOUR LOGBOOK) LESSON OBJECTIVES: 4 Explain why the outer casing of an electrical appliance must be either non-conducting (double-insulated) or earthed 5 State that a fuse without an earth wire protects the circuit and the cabling for a doubleinsulated appliance USING AN EARTH WIRE OR DOUBLE INSULATION. Insulation on wires is important to prevent fires or an electric shock. This is because there is a chance that current will flow between two bare wires (a short circuit), or from one bare wire and any piece of metal that it comes into contact with. To protect the user of the appliance, the metal case of the electrical appliance is earthed by connecting it to the earth wire. It provides a low resistance electrical path to the ground and reduces the chances of a fatal electric shock. Electrical appliances that are double insulated do not need an earth wire, as the electrical circuit for the appliance is inside a case underneath, which is made from electrically insulating material ( like plastic), hence electric current cannot pass through it. A switch or a fuse, must be connected to the live wire, as the high current passing through the fuse will instantly melt the fuse, stopping any current to flow to the appliance. This way, the circuit and the cabling for a double-insulated appliance is protected. ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS 1. Resistor: used to control the amount of current flowing around the circuit. 2. Variable resistor: used to change the current flowing around the circuit by changing the resistance. 3. Light-dependent resistor (LDR): a type of variable resistor whose resistance depends on the amount of light falling on it. In the dark, it has a very high resistance. When there is light, its resistance decreases. LDR is used in circuits to detect the level of light (for example, security lights that switch on automatically at night). 4. Thermistor: a type of variable resistor whose resistance depends on its surrounding temperature. The resistance changes by a large amount over a narrow range of temperatures. For NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors, the resistance decreases when they are heated.