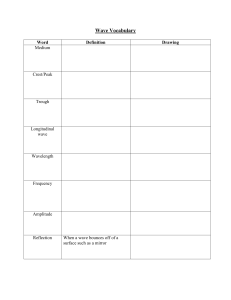
DEFINITION LIST: WAVES Normal – the imaginary line perpendicular to the surface between two different optical media. Medium – The substance or material that carries a wave. Laws of reflection – the incident ray, refracted ray and normal are all in the same plane. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Refraction – the bending of light as it moves from one medium to another medium with a different optical density. Optical density – a measure of the speed of light or other electromagnetic waves through a medium. Refractive index – the ratio of the speed of light in air to the speed of light through another medium. Snell’s Law – the ration of the sine’s of the angles of incidence and refraction of a wave are constant when it passes between two given media. Critical angle – the angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction is 90°. Total internal reflection – The reflection of light on the inside surface of a medium when light is travelling towards a medium of lower optical density and the angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle Interference – A phenomenon in which two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater or lower amplitude Diffraction – The ability of a wave to spread out in wavefronts as they pass through a small aperture or around a sharp edge OR the bending of a wave as it passes around the edges of an object. Huygen’s priniciple – Every point on a wave may be considered as a source of secondary wavelets which spread out in all directions at the same speed as the wave itself.