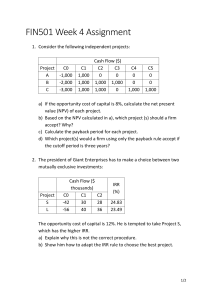
Real estate investment and analysis Submitted by: Jerryson Anyawoe Student ID:21015318 Own or Lease Analysis Own Lease Lease Payments -1,500,000 Lease payment Tax Shield 375,000 Interest Payments -1,350,000 Interest Tax Shield 337,500 Depreciation Tax Shield 200,000 After-tax cash flow -812,500 -1,125,000 Reversion Net Sales Proceeds Loan Balance BTER Tax After Tax equity reversion 15,520,000 7,500,000 8,020,000 2,080,000 5,940,000 Difference 1,500,000 -375,000 -1,350,000 337,500 200,000 312,500 Original Basis Adjusted Basis Gain Tax 0 1 2 3 4 5 IRR -2,500,000 312,500 312,500 312,500 312,500 6,252,500 28.24% 10,000,000 7,200,000 8,320,000 2,080,000 Internal Rate of Return (IRR): An IRR of 28.24% from the own or lease differential is considered financially viable, as it suggests a potential positive return on the investment. The IRR exceeds the cost of debt which suggest potentially higher returns than the cost debt (18%). IRR Is significantly higher than the cost of debt used in financing the project. Return on Equity (ROE): The ROE of 30% indicates high positive returns from equity. This is likely to be more than the cost of equity which mostly likely less than 18% Cost of Debt: The cost of debt is 18%, indicating the interest expense associated with borrowing funds. Conclusion Based on the computations above, it will financially viable to OWN than to lease based on reasons below: 1.The IRR of the differential of cashflows of indicates the after-tax yield on capital invested positive. 2.The IRR differential is higher than cost of debt required to finance the project indicating returns asset generate enough returns to cover the cost of debt. 3.Both IRR and ROE are higher than cost of debt indicating greater returns financially from the asset. 4.There could be other considerations in arriving at the decision to own or lease, but strictly from the financial perspective, OWNING is the best option.