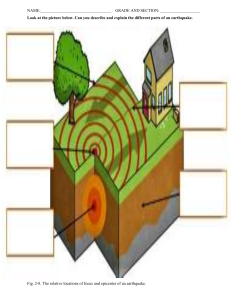
POWER PLANT Maintenance and Safety PRESENTED BY: ENGR. JEROME CUZ JR Guide Questions 1. Why is knowing safety precautions important? 2. What is the difference between RISK and HAZARD? 3. Identify 3 Risks and 3 Hazards in your house hold 4. Make an Emergency Plan for Earthquake or Typhoon when your at home. 5. As an Augustinian, how can you share what you have learned today to others? A power plant, also referred to as a power power station and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. WHAT IS A POWER PLANT? DIFFERENT TYPES OF POWER PLANT Nuclear Hydroelectric Geothermal DIFFERENT TYPES OF POWER PLANT Solar Wind Gas/Diesel fired DIFFERENT TYPES OF POWER PLANT Coal-fired A coal-fired power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity by heating water and turning it to steam that drives a turbine connected to electic generator COAL-FIRED POWER PLANT PROCESS OF POWER GENERATION Rankine Cycle 2 1 3 4 PUMP MAINTENANCE Coal-fired Power Plant Plant maintenance is an execution process of repairing or servicing the asset to avoid breakdown TYPES OF PLANT MAINTENANCE Preventive Maintenance Preventive maintenance is a scheduled maintenance that is usually done during a Plant Scheduled Shutdown Corrective Maintenance Corrective maintenance is an unscheduled maintenance that is usually done during a Plant Scheduled Shutdown Emergency Maintenance Emergency maintenance is an unscheduled maintenance that is performed during a Plant Ermegency Shutdown TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT Crane Welding Machine Cutting Tools TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT Measuring Tools Camera Scaffolding PROCESSES INVOLVED Welding Cutting Lifting SAFETY Coal-fired Power Plant Plant Safety encompasses the SOCIAL, MENTAL, PHYSICAL well-being of workers, that is, the “Whole Person” Conduct Preliminary orientation with workers safety Conduct Daily Safety Meetings with the workers Ensure that every group of workers has their own Licensed Safety Officer Actual inspection of each work areas. WHAT WE DO? to ensure safety PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) P L A N T S A F E T Y Importance To Employees Prevention of Injuries and Illnesses Reduced Stress and Anxiety Career Longevity To Employers Improving employee morale and Reducing workers' compensation costs Enhancing reputation and trust How do we ensure SAFETY? We practice Indusrial Hygiene, it is the control of hazards to acceptable limits thru following the Three Steps to Control Hazards: 1. Identify the hazard 2. Evaluate the hazard 3. Correct/Control the hazard Trivia! HAZARD VS RISK Hazard- Potential of an act or condition that can lead to an accident Risk- The Likelihood and severity of Accident Occuring “In essence, Hazard is the Potential SOURCE of accident while Risk is the CHANCE and IMPACT of the accident” Trivia! HAZARD VS RISK EXAMPLE You spilled your water on the floor made out of tiles. Identify the Hazard and Risk associated in this situation. HAZARD Wet Floor causing less friction with anything it is in contact with RISK Someone MIGHT slip on the wet floor and may cause Injury EMERGENCY Preparedness and Program Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program Preparedness Familiarize with emergency exits and assembly area Serious participation in earthquake drills Look around places where you usually stay, identify safe places such as sturdy piece of furniture where you can perform, DROP, COVER and HOLD ON Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program During Earthquake inside a building Drop down to the ground and cover your head and neck using your arms Find a sturdy structure that can cover you from falling objects Stay away from glass and light fixtures or furnitures that might fall Hold on to the sturdy structure and stay until the shaking stops. Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program During Earthquake outside or in an open space If you are outdoors when shaking starts, move away from buildings, streetlights, and utility wires. Once in the open, do the “Tripod Position”. Stay there until the shaking stops. Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program During Earthquake when inside your car Stop as quickly and safely as possible and stay in the vehicle. Avoid stopping near or under buildings, trees, overpasses, and utility wires. Earthquake Emergency Preparedness and Response Program After an Earthquake When shaking stops, look around. If there is a clear path to safety, leave the building and go to an open area away from damages areas, or if applicable proceed to assembly area. If you are trapped do not move about or kick up dust, if you have cellphone use it to call of help, if not applicable tap on something or whistle so rescuers can locate you. If you are trapped inside the car, turn off the engine and use the carn horm to signal the rescuers Stay in the Evacuation Centers until it is announced that it is safe to be back to your house or office. Typhoon Emergency Preparedness and Response Program Before the Typhoon Stay updated - Closely monitor weather updates through legitimate sources like PAGASA. Ensure adequate supply of emergency kits (batteries, flashlights, medicine, first aid kits, etc.) Ensure adequate supplies of backup fuels like diesel or bunker fuel to operate generators or boilers if power supply is disrupted. Inspect infrastructure for any possible breakdown Secure outdoor equipment Review emergency protocols Typhoon Emergency Preparedness and Response Program During the Typhoon Make sure everyone is updated regarding the weather updates from PAGASA Activate emergency power systems Halt non-critical outdoor operations Lessen or remove the manpower working on the field Typhoon Emergency Preparedness and Response Program After the Typhoon Once safe, thoroughly inspect plant and surrounding infrastructure for any weather damages Safely address any damaged components like power lines, generators, transformers before bringing plant back online Remove any debris around transmission lines or blocking critical access paths to the plant. Analyze typhoon response and identify any potential safety or preparedness improvements for future events. Update emergency plans accordingly. Guide Questions 1. Why is knowing safety precautions important? 2. What is the difference between RISK and HAZARD? 3. Identify 3 Risks and 3 Hazards in your house hold 4. Make an Emergency Plan for Earthquake or Typhoon when your at home. 5. As an Augustinian, how can you share what you have learned today to others? SAFETY is not just a Common Sense Let’s make it a COMMON PRACTICE