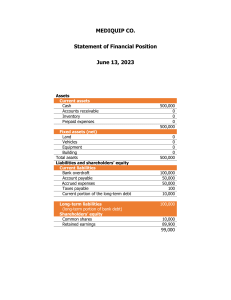
The objective of FS IASB Accounting standards for preparing FS FASB Relevance Qualitative characteristics Faithful representation Comparability Verifability The international FS standard framework Enhancing qualitative characteristics Timeliness Understandability Cost of providing and using information Constraint on FS Important information might not be included in the FS Assets Elements related to the measurement of financial position Liabilities Equity Introduction to FS Income Elements related to the measurement of performance Expenses Accrual accounting Underlying assumptions in FS Going concern The elements of FS Means that an item is included in the FS Recognition of FS elements Items are recognized when it meets the definition and satisifies the criteria for recognition Historical cost Amortized cost Current cost Measurement of FS element Realizable value Present value Fair value BS IS Other comprehensive income (OCI) Major FS CF Introduction to FS and FSA Statement of changes in equity Evaluate the past, current and potential performance and financial performance and position of a company Use FS prepared by companies, combined with other information FSA For the purpose of making decisions Articulate the purpose and context of the analysis Collect data FSA framework 6 phases of FSA Process data Analyze/ Interpret the data Follow - up Theme of FSA Depends on the economic decision after FSA Whether to include the company's stock in a portfolio or not Scope of FSA Making investment recommendation Determine the creditworthiness of the company for making/extending a loan Example of economic decision Assigning a debt rating Introduction to FSA Evaluating a M&A decision ... Require listed companies to provide FS information to public regularly Stock exchanges MD&A Auditor's reports Company's investor relation Interim report Company's earning calls Sources of information Presentation/ Press releases/ Speaking with managements/ Company website, fanpage/ Company visit Business and geographic segment reports/ Industry reports Other financial analysts' report Economic or industry indicators Other sources Identify the contract(s) with a customer Identify the separate or disticnt performance obligations in the contract Rev. recognition 5 steps in recognizing rev. Determine the trasaction price Allocate the transaction price to the performane obligation in the contract Recognizing rev. when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligations. Revenue Gross revenue Deduction of rev. Net rev. Understand Rev. via company's business model Break down rev. into company's business line Cost from purchasing raw materials/ WIPs/ FG Direct labour cost D&A Understand costs included in COGS Overhead costs Utilities costs Maintenance cost COGS Others Relationship between COGS and inventory Selling expenses SG&A General and administrative expenses Some companies provide information of expenses grouped by nature or grouped by function. Expenses IS Fixed cost Variable cost Capitaization of Interest costs Component of IS Capitalization Capitalization of Internal development costs Capitalization vs. Expensing Expensing Doubtful accounts Issues in expense recognition Warranties Straight line method D&A Base on the D&A accounting policy Accellerated methods Diminishing balance method Financial income/ Financial expenses Interest expense Operating profit Financial income/ expenses Non - operating items IS and IS analysis Other income/ expense EBIT/ EBITDA Profit before tax Tax expense and Effective tax rate Net income Basic EPS EPS Diluted EPS Unusual or infrequent items Discontinued operations Non - recurring items Changes in accounting policy Changes in scope and exchange rates IS analysis Vertical common size Common - size analysis Horizontal common size IS analysis techniques Net profit margin Gross profit margin IS ratios Operating profit margin Pretax margin FSA Current vs. Non current classification FS of financial institutions (Banks/ Brokerage companies/ Insurance companies) Liquidity - based presentation A=L+E E=A-L Cash & cash equivalents Marketable securities/ Short term investment Account receivables Prepayments to suppliers Current assets Short term trade receivables The allowance for doubtful account .... BS Inventories Inventories Provision for decline in value of inventories Other CA Assets Long - term trade receivables Historical cost Tangible assets Accumulated depreciation PP&E Historical cost Intangible assets Non - current assets Accumulated amorization Investment property Financial instruments Deferred tax assets Goodwill Components and format of BS Others ST borrowing ST trade payables ST advances from custoers Current liabilities Accrued expenses BS and BS analysis Deferred income Provision for ST liabilities Liabilities Long term borrowing Long - term financial liabilities Long term account payable Non - current liabilities Deferred tax liabilities Provision for Long - term payable Capital contributed by owners Preferred shares Treasury shares Equity Retained earnings Accumulated OCI Noncontrolling interest Statement of changes in equity Vertical common size BS Common size analysis Horizontal common size BS BS analysis Liquidity ratios Financial ratios Solvency ratios Capital structures Direct CF statement CF classifications Indirect CF statement Preferred Linkages between the FS Non cash items D&A Non - operating items CFO under indirect method NI adjusted for Changes in DTA/DTL CF statement Changes in NWC CFO CFO under direct methods Conversion of CFO under direct and indirect methods CF and CF analysis CFI Changes in non - current non operating assets CFF Changes in non - current non operating liabilities & Equity Summarize Evaluate sources and the use of cash Common size analysis CF analysis Financial ratios FCFE Free cash flow FCFF Evaluating past performance FSA applications Projecting future financial performance Assessing credit risk Screening for potential equity investment FS quality vs Earning quality Quality spectrum of FS Biased accounting choices in preparing FS Conservatives vs. Aggressive accounting Motivations Context for assessing FS quality Conditions conductive to issuing low quality FS Market regulatory authorities FS quality Mechanisms that discipline FS quality Auditors Private contracting Detection of FS quality issue Accounting choices and its impact on FS items Warning signs Introduction to FS modelling