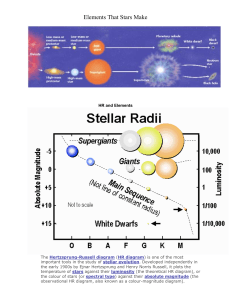
STAR Stars are giant, luminous spheres of plasma. There are billions of them — including our own sun — in the Milky Way Galaxy. And there are billions of galaxies in the universe. Stars are the most widely recognized astronomical objects, and represent the most fundamental building blocks of galaxies. The age, distribution, and composition of the stars in a galaxy trace the history, dynamics, and evolution of that galaxy. Moreover, stars are responsible for the manufacture and distribution of heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Facts about STARS 1. There could be over a Septillion stars in the universe. 2. No, the stars do not twinkle. 3. The sun, the closest star to earth is moving. 4. It would take roughly 35,000 years to reach the nearest sun next to the Sun. 5. The Sun produces the energy equivalent to 100 billion typical hydrogen bombs every second. 6. One day, the sun will die. 7. All you need are clouds of dust with great turbulence within to create a star. 8. You would need 1,100 years to circle the largest known star in the universe. Types of Stars 1. Main Sequence Stars Is the point in a stars evolution during which it maintains a stable nuclear reaction. In this stage during which a star will spend most of its life. Sun is a main sequence star. 2. Red Giants Stars Is a large star that is reddish or orange in color. A star that has a low surface temperature and a diameter that is large relative to the sun. 3. White Dwarfs Stars Is a remnant of average-sized star that has passed through the red giant stage of its life after the star has used up its remaining fuel. 4. Brown Dwarfs Stars It is also called a failed star. During the process of star formation, some protostars never reach the critical mass required to ignite the fires of nuclear fusion. 5. Variable Stars A star whose brightness changes usually in more or less regular period. 6. Binary Stars A system of two stars that revolve around each other under their natural gravitation. Multiple Star System 9. The larger the star, the shorter the life span. 1. Open Star Cluster 10. If you look at the stars, you are actually looking back in time. An open, or galactic, cluster is a group of relatively young, loosely bound stars. Astronomers have cataloged more than 1,000 galactic clusters within the Milky Way. An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud, and are still loosely gravitationally bound to each other. 1|Page 2. Globular Star Cluster CONSTELLATION A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Constellations are fixed star groups or clusters of stars arranged in a definite pattern. These clusters of stars were named in honor of mythological characters, great heroes and even animals. A constellation is a group of stars that, when seen from Earth, form a pattern. The stars in the sky are divided into 88constellations. The brightest constellation is Crux (the Southern Cross). Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. A globular cluster is sometimes known more simply as a globular. Globular clusters, which are found in the halo of a galaxy, contain considerably more stars and are much older than the less dense galactic, or open clusters, which are found in the disk. STELLER EVOLUTION Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these proto stars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star. In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These areas had their origins in star patterns from which the constellations take their names. There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky. The brightest constellation is Crux (the Southern Cross). The constellation with the greatest number of visible stars in it is Centaurus (the Centaur - with 101 stars). Constellations are formed of bright stars which appear close to each other on the sky, but are really far apart in space. The shapes you see all depend on your point of view. Many societies saw patterns among the stars with gods and goddesses or stories from their culture. The stars allowed farmers to plan ahead and form agriculture, and constellations made it easier to recognize and interpret the patterns in the sky. The constellations also helped with navigation. BLACK HOLE Black hole is an object whose surface gravity is exceedingly high that nothing, even light can escape. Any ray of light or object that enters the black hole is trapped. It can take in radiation and objects but can never send anything back. 2|Page