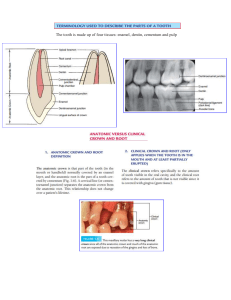
Oral Histology and Embryology Laboratory 1. Label the Microscopic Structure of Dentin: Draw a diagram of dentin under a microscope and label its various components, such as dentinal tubules, dentin matrix, odontoblasts, and peritubular dentin. 2. Illustrate Dentinogenesis: Draw a series of illustrations depicting the process of dentinogenesis, from the differentiation of odontoblasts to the deposition of dentin matrix. Illustrate how odontoblasts form dentin along the inner surface of the pulp chamber and pulp canal. 3. Create a Cross-Sectional View of a Tooth: Draw a cross-sectional diagram of a tooth and illustrate the different layers of dentin, including primary dentin, secondary dentin, and tertiary dentin (or reparative dentin). Depict variations in dentin thickness and morphology in different regions of the tooth. 4. Label the Anatomy of Dental Pulp: Draw a diagram of a tooth and label the different components of the dental pulp, including the pulp chamber, pulp horns, pulp canal(s), apical foramen, and pulpdentin complex. 5. Illustrate Pulpal Blood Supply and Innervation: Draw a schematic representation of the blood vessels and nerves that supply the dental pulp. Illustrate branches of the trigeminal nerve and major blood vessels entering the pulp through the apical foramen and branching within the pulp tissue. 6. Create a Cross-Sectional View of Pulp Tissue: Draw a cross-sectional diagram of a tooth and illustrate the different layers of pulp tissue, including the cell-rich zone, cell-free zone, and pulp core. 7. Label the Microscopic Structure of Cementum: Draw a diagram of cementum under a microscope and label its various components, such as cementocytes, cementoid, cementoenamel junction (CEJ), and incremental lines. 8. Illustrate Cementogenesis: Draw a series of illustrations depicting the process of cementogenesis, from the differentiation of cementoblasts to the deposition of cementum matrix. Illustrate how cementoblasts form cementum on the root surface of a tooth and the role of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath in guiding cementum formation. 9. Create a Cross-Sectional View of a Tooth Root: Draw a cross-sectional diagram of a tooth root and illustrate the different layers of cementum, including acellular cementum and cellular cementum. 10. Label the Microscopic Structure of the Periodontal Ligament: Draw a diagram of the periodontal ligament under a microscope and label its various components, such as fibroblasts, collagen fibers, blood vessels, and nerve endings. 11. Illustrate the Attachment of the Periodontal Ligament: Draw a schematic representation of how the periodontal ligament attaches the tooth root to the surrounding alveolar bone. Illustrate Sharpey's fibers anchoring the PDL to the cementum and bone, and the arrangement of fibers within the ligament. 12. Create a Cross-Sectional View of the Periodontal Ligament: Draw a cross-sectional diagram of a tooth and surrounding periodontal tissues and illustrate the location and structure of the periodontal ligament. 13. Illustrate PDL Fibers Orientation: Draw a series of illustrations illustrating the orientation of different types of collagen fibers within the periodontal ligament, such as principal fibers (alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical), transseptal fibers, and interradicular fibers.