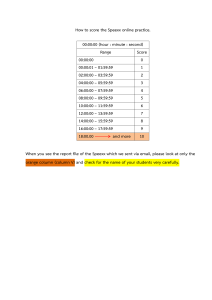
CHME 401 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY II EXPERIMENT 401-5 GAS ABSORPTION OBJECTIVE The objective of the experiment is to investigate absorption of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) to water in a packed bed column. Effect of chemical reaction on absorption mechanism will be investigated. PRELIMINARY WORK 1. Study on absorption mechanism in packed bed absorption column especially absorption of solute (CO2) from vapor phase to liquid phase through a non-diffusing gas (air). Familiarize with concepts of film resistances, experimental estimation of mass transfer coefficients and importance of understanding film resistances in multiphase reactors including gas and liquid phases. 2. Visit the lab. in advance to experiment and familiarize yourself with the experimental set-up with the consent of the teaching assistant. DESCRIPTION OF THE EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP In this unit, the gaseous phase (CO2) is contacted with the liquid phase (water or NaOH solution) in a packed column filled by an inert packing material (raschig rings) in order to increase the contact area. Unit is mainly composed of a column, feed tank and centrifugal pump for feeding the liquid phase, a rotary compressor for mixing the gas with air (air is used as carrier medium) and the Hempl apparatus for analyzing gaseous mixtures absorption of CO2 can also be measured by taking liquid samples from the column outlet and feed tank. CO2 analysis is made by NaOH titration. Experimental set-up is given in Figure 1. 1 Figure 1. Absorption Column EXPERIMENTATION Inlet and outlet CO2 concentrations in gas and liquid phases will be measured during the experiment. Procedure 1) Fill the feed tank with pure water 2) Fill the spheres in hempl apparatus with 1 M NaOH solution 3) Turn compressor (P1) on set air flow rate to 30 L/min 4) Feed CO2 set regulator to 0.5 and flow rate to 15 L/min 5) Turn pump (G1) on set flow rate of the water to 200 L/h 6) Wait 15 min until steady state conditions are reached 7) Take samples from V4 (column bottom) and V6 (feed tank) 8) Analyze inlet and outlet CO2 concentrations in gas mixture by using Hempl apparatus (instructions are given in Appendix A). 9) Repeat Steps 1-8 but fill the feed tank with 0.2 M NaOH solution (caustic soda) this time only gas phase will be analyzed 2 Analysis 1) Estimate total mass transfer coefficients for both of the runs 2) Estimate enhancement factor 3) Using the first run determine whether gas or liquid film mass transfer resistance is controlling the absorption rate (Hint: you may use a similar approach as in example 10-8-1 in “Transport Processes and Separation Process Principles”, Christie John Geankoplis, 4th Edition) Useful Data About the Apparatus S (surface area of the column) = 0.005 m2 H (height) = 1.5 m a = 500 m2/m3 3 APPENDIX A Gas Phase Carbon Dioxide Analysis (from the Manual of Equipment) 4 5 6 7 8 APPENDIX B Analysis of Carbon Dioxide in Liquid Phase by Titration Required Chemicals Phenolphthalein Indicator: dissolve 0.5 g of phenolphthalein in 60 ml of ethanol in a 100 ml graduated flask and add water up to the mark. Standard NaOH Solution (0.03 M) Analysis Take 150 ml of samples from feed tank and exit of the column. Transfer 100 ml of samples in flasks add 3-5 drops of indicator (colorless) and titrate with NaOH solution until persistent pink color obtained. Record the volume used for titration. 9