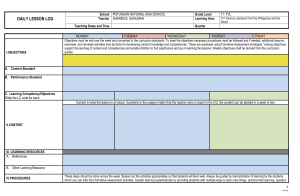
GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School Teacher/s Teaching Dates and Time SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR)portal Grade Level Learning Area Quarter November 7-11, 2016 SESSION 2 SESSION 3 SEVEN SCIENCE THIRD SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Describe in words the position of an object within the room or the school ground; 2. Elucidate position of moving objects using coordinates in number line and graphical representation; 3. Make a roadmap that shows how to get to school from their house; 4. Determine the speed of a moving object; 5. Calculate speed and velocity; and 6. Observe required speed limit in roads and highways The learners demonstrate an understanding of motion in one dimension. The learners describe the motion of an object in terms of distance or displacement, speed or velocity, and acceleration. S7FE-IIIa-1 The learners describe the motion of The learners differentiate quantities an object in terms of distance or in terms of magnitude and displacement, speed or velocity, direction. and acceleration. S7FE-IIIa-1 S7FE-IIIa-2 The learners create and interpret visual representation of the motion of objects such as tape charts and motion graphs. S7FE-IIIb-3 Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Descriptors of Motion -Where is it? a. Using Diagrams b. Using Graphs Descriptors of Motion -Distance and Displacement Descriptors of Motion -Speed and Velocity Descriptors of Motion - Acceleration - Motion Detectors Page 119-121 Page 130-134 Page 121-122 Page 134-136 Page 122-123 Page 136-139 Page 123-124 Page 139-143 B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. Name the common signage you find in highways and roads that gives direction? Review: When can we say that an object is in motion? From our previous lesson, what are the different ways to describe the motion of an object? Review: What is speed? What makes speed different from velocity? The teacher prepares beforehand the instructions to be given to the students. Instructions like a. It is right there b. Turn and it is there c. Walk slowly and you will get there d. It is from here and there Inform the class that the students should be able to make a roadmap that shows how the students get to school from the house. In this activity, students should be able to design ways to obtain the speed of each member of the group and decide how to used these values to determine who among them walks fast In this activity, students will analyze an example of motion wherein speed or velocity is changing by examining the record of the dots on a strip of paper. Divide the class into groups. Assigned members as Leader, Time keeper, Note taker, etc. Using the same group from the previous activity. Find a bigger space in the school where the class can perform Activity 3: Fun walk (page 137) Divide the class into 5 groups. Assigned members as Leader, Time keeper, Note taker, Reporters, etc. Perform Activity 1 : Where is It ? on page 131 C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson Using Figure 1 of page 131, describe the positions of the objects using number line. Using Figure 2 of page 132, The group performs Activity 2 : My describe the position of the ball at a Home to School Roadmap on page given time. 135 to 136. Following the instructions carefully. Each student should be able to draw its roadmap in short band paper. D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 1 During the processing, the teacher should emphasize that once the students have selected their point of reference, they can easily describe any change in the position Present Figure 5 on page 134 to the class. Let the students describe the motion of the dog. From the figure define distance and The teacher explains that after determining how far the object moves, the next question will be “How fast did it move?” This information can be provided by the The group performs Activity 4: Doing Detective Work on page 139 to 141. Following the procedure carefully. Each group should be able to record the distance travel, plot values as points in the graph. The teacher explains that the difference in length between two successive tapes provides the object’s acceleration or its change in speed or velocity for a time of an object. In other words, they can easily tell whether an object is moving or not. At this point, the definition of motion, which is the change in position over time, can be introduced. E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 displacement. objects speed or velocity. interval of 1 second. Define and differentiate Speed form Velocity. Define Average Speed and Instantaneous Speed Students will describe motion using motion graphs. Following the procedure below: Discuss Speed as distance travel divided by time of travel or 1. Using the values from figure 2 of page 132, complete Table 1: Position of the ball vs time; 2. Plot the values in Table 1 as points on the graph in Figure 3, page 134, using graphing paper 3. Lastly, draw a straight diagonal line through the points in the graph. Speed = The teacher also defines motion as a change in position. Gives the definition of Distance and Displacement. Velocity = Distance traveled Time of travel Students will describe the distance travelled by the car by plotting the values from the Table 3 on page 141 using motion graphs. The students also interpret the graph in terms of speed and acceleration of the moving car. Discuss Velocity as Speed with direction (displacement divided by time of travel) or Displacement F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) Students are asked to answer the Short Answer Questions (Q1 to Q14 on page131-132.) Select students to present their answers to the class. Time of travel Refer to figure 7 of page 135, displacement-time graph. Answer the following questions: 1. What is the distance of the object after 2 seconds? 2. What is its displacement after 6 seconds? 3. How will you describe the motion of the object between 0s and 2s, between 2s and 4s, and between 4s and 6s? Board Drill: 1. Who is travelling faster than the other, a person who covered 10 meters in 5 seconds or the one who took 10 seconds to cover 20 meters? 2. What is the speed of the car travelling 20 meters in 5 seconds? 3. What is the velocity of the boy running 15 km in 3 minutes Each group should answer the Short Answer Questions (Q1 to Q10 on page140-141.) going North? G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living Teacher emphasizes the significance that knowledge in describing motion of an object will help them understand common road signage. How far is your home from the school? What is the maximum speed limit allowed by law for road vehicles in the Philippines? In what instance you are required to increase your speed? - Cite instance like emergency cases. - Precaution on safe driving by using safety belts. H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Teacher makes the students realize the fact that understanding motion of the objects will be of great help to those who are lost and in need of clear guide for them to get to their destination safely. The students will answer the questions orally. Why is it important to attain the required speed limit in the road or highways? Teacher indicates that acceleration does not take place only on increasing speed along a straight line but could also takes place when a moving object reduces or decreases it speed or when it changes direction. 1. Is it possible to get zero displacement? 2. When can displacement be equal to zero? This is to correct the common conception among people that acceleration only refers to objects with increasing speed. I. Evaluating learning J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the Check students’ answer on Short Answer Questions (Q1 to Q14) Check students’ answer from the activities given (Developing Mastery) Check students’ answer : Board Drills Check students’ answer in the Short Answer Questions (Q1 to Q10 on page140-141.) Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: CHECKED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON NOTED BY: __________________________ School Teacher/s ______________________ School Principal Grade Level Learning Area SEVEN SCIENCE LOG Teaching Dates and Time SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References November 14-18, 2016 SESSION 2 Quarter SESSION 3 THIRD SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Analyze an example of motion wherein speed or velocity is changing by examining the record of the dots on a strip of paper; 2. Emphasize that any change in the velocity of an object an object results in an acceleration; 3. Cooperate actively in the group activity; and 4. Reports the answers of the short answer questions and graphical analysis to the class. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Explain that waves carry energy ; 2. Note that the energy produces by the waves creates movement; and 3. Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves; The learners demonstrate an understanding of motion in one dimension. The learners demonstrate an understanding of waves as a carrier of energy. The learners create and interpret visual representation of the motion of objects such as tape charts and motion graphs. S7FE-IIIb-3 The learner infer that waves carry energy S7FE-IIIc-4 The learners create and interpret visual representation of the motion of objects such as tape charts and motion graphs. S7FE-IIIb-3 The learners differentiate transverse waves from longitudinal waves, and mechanical waves from electromagnetic waves S7FE-IIIc-5 Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Descriptors of Motion - Acceleration -Motion Detectors (Group Reporting on Results) Summative Test Descriptors of Motion a. Distance and Displacement b. Speed and Velocity c. Acceleration Waves Around You - Warm up. What are waves? Types of Waves -Let’s Make Waves 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and Page 123-124 Page 139-143 Page 123-124 Page 139-143 Page 126-127 Page 144-145 Page 128-131 Page 145-149 These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. The teacher prepares the students to do the reporting of results to the class. He/she sees to it that all members of the group have the change to share his/her thoughts and understanding of the activity done Students should derive the definition of acceleration from the data gathered and present it logically to the class. Group Reporting on the Results of Activity no. 4: Doing Detective Work Students emphasizes that any change in the velocity of an object Teacher presents a demonstration to serve as motivation. What happens when waves pass by? Demonstration Activity: Introduction to Vibrations Please see TG page 126-127 for the procedure. Students are expected to answer the given questions in the Summative Test. Interpret the change of speed/velocity using graphical presentation. In this activity, students should be able to observe how waves are produced. In this activity, students should be able to observe and draw the different types of waves and describe how they are produced. From the activity, ask the students the following questions: 1. What two things are vibrating? 2. What caused the salt to move? Using the same groupings from the previous group activity. Students are to perform Activity 1: Let’s Make Waves! on page 145- 149. They are required to follow accurately the procedure to be able to differentiate and draw the different types of waves. Solicit from the students the idea about waves are caused by a After the activity, the group presents its Group Output in the practicing new skills # 1 E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) an object results in an acceleration. Acceleration is either increasing or decreasing of speed and changing directions. Each group presents their answer the Short Answer Questions (Q1 to Q10 on page140-141.) Summative Test (See Attachment: Summative Test Unit 3 Module 1.1.) source of a vibration and waves can set objects into motion. class. Sharing in their own understanding on the different types of waves. Oral Recitation: 1. What do you do when you wave your hand? 2. Think of a still lake. How would you generate water waves on the lake? Ask the students to answer Summary Questions on Page 149 How engineers and architects designed skyscrapers and bridges to address the problem regarding the stability of constructed building whenever earthquakes occur? G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living Teacher tell the student that there are some parts in the country that uses motion detectors to detect the speed of vehicle passing by, example in Subic Laguna The teacher explains that waves observed in the activity are like other types of waves that are observed in the nature. Waves like earthquake and water waves (tsunami). H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson What is needed in order for an object to move? The teacher stress that waves are What are the different types of created by a source and as the waves and how one differs from the waves travel it carries energy within other? it and cause movement I. Evaluating learning Evaluate the Group Reporting Check the answer of students in the Summative Test. Evaluate the explanation of students in the oral recitation Check the answer of students in the Summary Questions (See Rubric Attached: Title: Reporting Rubric) J. Additional activities for application or remediation I. REMARKS II. REFLECTION Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: CHECKED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON NOTED BY: __________________________ School Teacher/s ______________________ School Principal Grade Level Learning Area SEVEN SCIENCE LOG Teaching Dates and Time SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES November 21-25, 2016 SESSION 2 Quarter SESSION 3 II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Explain how waves carry energy from one place to another; 2. Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves; 3. Distinguish between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves; and 4. Create a model to demonstrate the relationship among frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and wave velocity. A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) THIRD At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Demonstrate how sound is produced; 2. Identify factors that affect the pitch and loudness of the sound produced; The learners demonstrate an understanding of waves as a carrier of energy. The learners differentiate transverse waves from longitudinal waves, and mechanical waves from electromagnetic waves S7FE-IIIc-5 The learners differentiate The learners relate the transverse waves from longitudinal characteristics of waves waves, and mechanical waves from S7FE-IIId-6 electromagnetic waves S7FE-IIIc-5 The learners describe the characteristics of sound using the concept of wavelength, velocity and amplitude. S7FE-IIIc-7 Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Characteristics of Waves - Amplitude - Wavelength - Wave Velocity Mechanical Waves vs. Electromagnetic Waves Summative Test on: a. Types of Waves b. Characteristics of Waves - Amplitude - Wavelength - Wave Velocity c. Mechanical Waves vs. Electromagnetic Waves Production of sound Page 131-134 Page 134-137 Page 128-137 Page 142-144 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 3. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 1 Page 150-153 Page 154-156 Page 145-156 Page 161-165 These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. Review: What are the different types of waves discussed from the previous lesson? Review: 1. What is am amplitude of a wave? 2. What is wavelength? 3. How to measure the speed of a wave? Ask students to place their palm on their throat then say loudly, “Mom! Phineas ad Ferb are making a title sequence!” The teacher asks the students the question: How do you describe waves? The teacher asks the students the question: How do waves propagate? Using the same groupings from the previous group activity. Students are to perform Activity 2: Anatomy of a wave on page 150- 149. They are required to follow accurately the procedure to be able to describe waves through amplitude, wavelength, and wave frequency. Before the discussion, the teacher show the large images of mechanical waves, which the students were able to generate from Activity 1, and a chart of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be used by the students in answering the questions in the Activity sheet. Teacher calls students to present their output (My Sounding Box) to the class. Let them demonstrate how sound is produced. The students within the group create a model to demonstrate the relationship among frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. Students should: - Define mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. The teacher discusses that sounds are caused by vibrations. Vibration are considered as a disturbance that travels through a medium Students are expected to answer the given questions in the Summative Test honestly. Students create their own sounding box using shoe box and rubber bands with different thickness. They will demonstrate how sound is produced. They will different the sound produced by each band. - Identify the common name of electromagnetic waves shown in the chart (solid, liquid, or gas), This vibratory motion causes energy to transfer to our ears and interpreted by our brain. - Draw waves to re[present each electromagnetic waves. Illustration must represent the wavelength of a wave relative to others. E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 The teacher demonstrates how to measure speed of the wave using the frequency and the wavelength of the wave. F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) Ask the students to answer the short answer questions: Summary on page 153 Present the speed of sound in different materials. Sound need medium for it to travel, thus it cannot travel through a medium. Students will answer the activity sheet provided by the teacher that contains the identification of common names and illustration of the different electromagnetic waves. Summative Test (See Attachment: Summative Test Unit 3 Module 1.2) G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living The teacher shares to the class that the Sun is an important source of ultraviolet (UV) waves, which is the main cause of sunburn. Sunscreen lotions are transparent to visible light but absorb most UV light. The higher a sunscreen’s solar protection factor (SPF), the greater the percentage of UV light absorbed. The principles of propagation of sound are used in the creation of musical instruments H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Why UV rays are harmful to the skin compared visible light? How sounds propagated? Can sound waves travel through a medium? I. Evaluating learning Evaluate students’ answers in the short answer questions: Summary on page 153 Check the answers in the activity sheet. Check the answer of students in the Summative Test. J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the VI. REFLECTION students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: CHECKED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON NOTED BY: __________________________ School Teacher/s ______________________ School Principal Grade Level Learning Area SEVEN SCIENCE LOG Teaching Dates and Time SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 3. Additional Materials from November 28- December 2, 2016 SESSION 2 Quarter SESSION 3 THIRD SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Demonstrate how sound is produced; 2. Identify factors that affect the pitch and loudness of the sound produced; 3. Describe the characteristics of sound from the sounding box and compare them with the sound produced by a guitar; and 4. Explain sound production in the human voice box and how pitch, loudness and quality of sound vary from one person to another. The learners demonstrate an understanding of the characteristics of sound. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1. Create musical instruments using indigenous products ;and 2. Use these instruments to compose tunes and present a Gig. The learners explain sound production in the human voice box and how pitch, loudness and quality of sound vary from one person to another. S7FE-IIIe-8 The learners describe how organisms produce, transmit, and receive sound of various frequencies (infrasonic, audible, and ultrasonic sound). S7FE-IIIe-9 The learners describe how organisms produce, transmit, and receive sound of various frequencies (infrasonic, audible, and ultrasonic sound). S7FE-IIIe-9 The learners describe how organisms produce, transmit, and receive sound of various frequencies (infrasonic, audible, and ultrasonic sound). S7FE-IIIe-9 Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Characteristics of Sound - Pitch Characteristics of Sound - Loudness - Quality The Human Ear Summative Test on: Production of sound Characteristics of Sound - Pitch - Loudness - Quality The Human Ear Production of Sound Activity 3 : Big Time Gig Page 144 Page 165-167 Page 144 Page 167-170 Page 142-144 Page 161-170 Page 145 Page 170-172 Learning Resource (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. How are sounds produced? A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 1 Using the sound box made by the students, they will describe the characteristics of sound and compare it with the sound produced by a guitar. The students will perform Activity 2: Properties and Characteristics of Sound From the activity, the students listen and observe the different pitch of the rubber band of different thickness and the from the string of the guitar. From your Biology lesson, can you still remember the anatomy of a human ear? Recalls that sound are produced by vibration. Students are expected to answer the given questions in the Summative Test honestly. Given the picture of the human ear, teacher asks the students to name the different parts of the ear. Form a group of four (4) students. One student can play stringed instruments, the other one can play the drum, and the third member can use other instruments aside from stringed and drums, while the last member is the solo performer. Each member of the group creates its own improvised instruments according to its assigned task. Teacher discusses the function of the different parts of the human ear. The members of the group practice their composed song using their improvised musical instruments. The teacher then discuss about sound pitch. E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) Teacher explains about loudness and sound intensity. The students will answer the Short Answer Question (Q1 to Q 16) including the table for pitch of the guitar strings. on page 166-167 Initiating students’ creativity, they will make improvised / localized musical instruments. Using the materials available in the locality. The group comes up with their own song composition which will be accompanied by the instruments they have created. Summative Test (See Attachment: Summative Test Unit 3 Module 1.3) G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson I. Evaluating learning What sound level is audible to human ear? How would you relate pitch and frequency Check answers (Q1 to Q16) There are many localized instruments known like those used by our Ethics Brothers in the Provinces of Bukidnon. Can you name some of these? Is loud music like rock music healthy to the ears? Check the answer of students in the Summative Test. Use Scoring Rubric found in page 171. J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the VI. REFLECTION students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: CHECKED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON NOTED BY: __________________________ School Teacher/s ______________________ School Principal Grade Level Learning Area SEVEN SCIENCE LOG Teaching Dates and Time SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES December 5-9, 2016 SESSION 2 Quarter SESSION 3 THIRD SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1 Demonstrate how light produced by common sources ; 2. Relate characteristics of light such as color and intensity to frequency and wavelength; 3. Design and implement an experiment that shows that light travels in a straight line; and 4. Investigate the relationship between light intensity and the distance of the light source. A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard The learners demonstrate an understanding of the characteristics of light. C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) The learners relate characteristics of light such as color and intensity to frequency and wavelength. S7FE-IIIf-10 The learners relate characteristics of light such as color and intensity to frequency and wavelength. S7FE-IIIf-10 The learners shall be able to suggest proper lightning in various activities. The learners infer that light travels in a straight line. S7FE-IIIg-11 The learners relate characteristics of light such as color and intensity to frequency and wavelength. S7FE-IIIf-10 The learners infer that light travels in a straight line. S7FE-IIlg-11 II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Characteristics of Light - Intensity and Brightness Characteristics of Light - Color Properties of light - light travels in a straight line Summative Test on: Characteristics of Light - Intensity and Brightness - Color Properties of light - light travels in a straight line Page 146-148 Page 173-176 Page 147-148 Page 177-181 Page 185-186 Page 185-186 Page 146-186 Page 173-186 3. Textbook pages 3. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 1 E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living H. Making generalizations and These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. Do you still remember Sir Isaac Newton? What about Christian Huygens? Did you meet them in your earlier grades? In this activity, students are going to create an improvised Photometer to determine which among the chemical substance produces brightest light. Group the students to perform Activity 1: Light Source: Langis Kandila or Lampara Data processing may be done by group presentation and class discussion of the guide questions to probe the concept of common light source and how light is produced and propagated Discussion should also be extended to cover differences and similarities of brightness and intensity. Group reporting on the results of the activity Introduce light as a wave, especially as a major component of the Electromagnetic Theory of Light by James Clark Maxwell. Students will create a Spectrum Wheel and explore the characteristics of light such as energy, frequency and wavelength. Review the different characteristics of light discussed from the previous lesson. Group the students to perform Activity 2: My Spectrum Wheel Group the students to perform Activity 4: Light up Straight Data processing may be done by group presentation and class discussion of the data and results in tabular form and guide questions to the characteristics of electromagnetic spectrum. Extend the discussion to include dispersion as a special kind of refraction In the quest to come up with the design, students will be able to discover and apply the different characteristics and properties of light. Group reporting on the results of the activity. Students design an experiment to show that light travels in a straight line. What is our main source of light? Using the Electromagnetic Students will design an experiment given several materials to show that light travels in a straight line Students are expected to answer the given questions in the Summative Test honestly. Summative Test (See Attachment: Summative Test Unit 3 Module 1.4) abstractions about the lesson I. Evaluating learning Use Reporting Rubric to evaluate the group reporting. Spectrum, at what frequency color is visible to human eyes? Use Reporting Rubric to evaluate the group reporting. Use Scoring Rubric found in page 186 Check the answer of students in the Summative Test. J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the VI. REFLECTION students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: CHECKED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON NOTED BY: __________________________ School Teacher/s ______________________ School Principal Grade Level Learning Area SEVEN SCIENCE Teaching Dates and Time LOG SESSION 1 I. OBJECTIVES December 12-16, 2016 SESSION 2 Quarter THIRD SESSION 3 SESSION 4 Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. At the end of the session, the learners are expected to: 1 Describe the condition necessary for heat transfer to take place and trace the direction in which heat is transferred ; 2. Describe heat transfer by conduction and compare the heat conductvities of materials based on their relative coldness; 3. Observe and describe convection of heat through liquids; and 4. Observe transfer of heat through radiation. A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/Objectives (Write the LC code for each.) II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 3. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resource IV. PROCEDURES The learners demonstrate an understanding of how heat is transferred. The learners infer the condition necessary for heat transfer to occur. S7FE-IIIh-i-12 The learners infer the condition necessary for heat transfer to occur. S7FE-IIIh-i-12 The learners infer the condition necessary for heat transfer to occur. S7FE-IIIh-i-12 The learners infer the condition necessary for heat transfer to occur. S7FE-IIIh-i-12 Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. Heat Heat Transfer - Conduction Heat Transfer - Convection - Radiation Summative test on: Heat transfer - Conduction - Convection - Radiation Page 150-153 Page 187-192 Page 153-154 Page 192-194 Page 154-159 Page 194-198 Page 150-159 Page 187-98 These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/Instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 1 E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills # 2 F. Developing mastery (leads to Formative Assessment 3) At the start, the teacher ask the students to give their ideas about heat In this activity, students will analyze changes in the temperature of the water inside the containers to answer the questions that follows Group the students to perform Activity 1: Warm me up, cool me down. Data processing may be done by group presentation and class discussion of the guide questions to describe the condition necessary for heat to transfer to take place and trace the direction in which heat is transferred. Group reporting on the results of the activity, including answers to the questions. (Q1-Q11) page 152. Have you tried placing your finger inside a freezer then it stuck? Review on heat transfer through conduction Students will describe heat transfer by conduction and compare the heat conductivities of materials based on their relative coldness. Group the students to perform Activity 2: Which feels colder? Is water a good conductor of heat? The students present to the class their observation. Extend the discussion about heat transfer through conduction Group reporting on the results of the activity. Group the students to perform Activity 3: Move me up Activity 4: Keep it cold The teacher discusses about heat transfer through convection and radiation. Students will answer Q1-Q6 in page 195 – Activity 3: Move me up Students will answer Q1-Q4 in page 197 – Activity 4: Keep it cold G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living How thermometers work? H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Students’ illustrate the transfer of heat to the class Perform Activity 5 : All at once at home. Practical application of heat transfer in that take place within the respective houses of the students Emphasize that different objects or materials conduct heat differently. Which among the metals observed conduct the highest heat conductivity Students are expected to answer the given questions in the Summative Test honestly. Summative Test (See Attachment: Summative Test Unit 3 Module 1.5) I. Evaluating learning Check answers of the students (QiQ11) Use Reporting Rubric to evaluate the group reporting. Check students answers Q1-Q6 in page 195 – Activity 3: Move me up Check the answer of students in the Summative Test. Check students answers Q1-Q4 in page 197 – Activity 4: Keep it cold J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the VI. REFLECTION students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? PREPARED BY: ___________________________ Science Teacher CHECKED BY: NOTED BY: __________________________ ______________________ School Principal