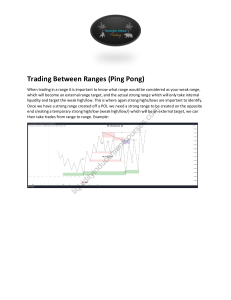
Powered by AI Copilot The Smart Money Concept (SMC) in trading revolves around understanding the behavior of institutional players, such as banks and hedge funds. These market makers, often referred to as the “smart money,” leave footprints of their trading decisions on the chart. Here are the key points about SMC: 1. Market Structure and Supply-Demand Dynamics: SMC focuses on supply, demand, and market structure. It suggests that market makers manipulate the market against retail traders. Institutions like banks and hedge funds can allegedly move substantial capital and set traps for retail traders. Retail traders, unaware of these activities, may fall victim to unpredictable market swings. 2. Liquidity: Liquidity is a crucial factor in SMC trading. It refers to specific price points where orders accumulate in the market, making an asset class “liquid.” Different types of liquidity include: Trendline liquidity: Points where orders cluster around trendlines. Buy-side liquidity: Areas where buy orders are waiting. Sell-side liquidity: Areas where sell orders are waiting. Double tops and double bottoms: Price levels where liquidity accumulates. 3. Smart Money’s Hunt for Liquidity: SMC suggests that the “smart money” hunts for liquidity provided by retail traders. Skeptics argue that retail traders’ liquidity is relatively insignificant compared to institutional capital. Market makers have access to vast pools of capital, making it unlikely they would specifically target small retail traders . In summary, while the Smart Money Concept has gained attention, it’s essential to understand its theory and apply it to your trading strategy. Remember that liquidity plays a pivotal role, and recognizing patterns related to supply and demand can enhance your trading decisions.