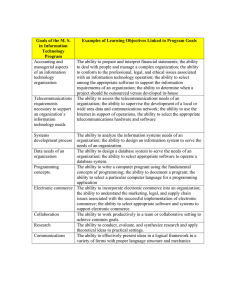
Introduction to Business and Management; Historical Perspectives and Theories Introduction to Business Goods and Services Goods are tangible items manufactured by businesses, such as laptops. Services are intangible offerings of businesses that can’t be held, touched, or stored. Physicians, lawyers, hairstylists, car washes, and airlines all provide services. Staple Food or Product A staple food, product, or activity is one that is basic and important in people's everyday lives. Rice is the staple food of more than half the world's population. Rice, wheat, maize (corn), millet, sorghum, roots and tubers (potatoes, cassava, yams and taro), and animal products such as meat, milk, eggs, cheese and fish. The tools, machinery, equipment, and buildings used to produce goods and services and get them to the consumer are known as capital. Revenue is the money a company receives by providing services or selling goods to customers. Costs are expenses for rent, salaries, supplies, transportation, and many other items that a company incurs from creating and selling goods and services. Profit = Revenue > Cost Loss = Cost > Revenue Risk is the potential to lose time and money or otherwise not be able to accomplish an organization’s goals. Four Factors of Production Four traditional factors of production are common to all productive activity: Land (Natural resources) Labor (human resources) Capital Organization / Entrepreneurship Trade The action of buying and selling goods and services. A trade occurs when two parties take part in buying or selling goods or services. The mechanism that allows trade to occur is called a market. Commerce Commerce is the exchange of goods or services among two or more parties. It is the subset of business that focuses on the sale of finished or unfinished products Commerce deals with the various aspects of business, trade, accounting, financial information/transactions and merchandising. Trade is referred to as a basic economic activity that involves buying and selling of different goods and services between two or more parties involved in the transaction. Commerce involves all the activities that aid in promoting the exchange of goods and services from the manufacturer to the last customers. Business A business is an organization that strives for a profit by providing goods and services desired by its customers. Businesses meet the needs of consumers by providing medical care, autos, and countless other goods and services. G Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurs are the people who combine the inputs of natural resources, labor, and capital to produce goods or services with the intention of making a profit or accomplishing a not-for-profit goal. These people make the decisions that set the course for their businesses; they create products and production processes or develop services. Because they are not guaranteed a profit in return for their time and effort, they must be risk-takers. Of course, if their companies succeed, the rewards may be great. https://turkishweekly.n et/they-are-therichest-in-kazakhstanin-2020-themagnificent-7-fromthe-forbes-list/ Management Management is essential for an organized life Good management is the backbone of successful organizations Managing life means getting things done to achieve life’s objectives Managing an organization means getting things done with and through other people to achieve its objectives. Definition of Management Management is a set of principles relating to the functions of planning, organizing, directing and controlling, and the application of these principles in harnessing physical, financial, human, and informational resources efficiently and effectively to achieve organizational goals. According to Van Fleet and Peterson define management, ‘as a set of activities directed at the efficient and effective utilization of resources in the pursuit of one or more goals.’ According to F.W. Taylor, ‘ Management is an art of knowing what to do when to do and see that it is done in the best and cheapest way ‘. According to Harold Koontz, ‘Management is an art of getting things done through and with the people in formally organized groups. It is an art of creating an environment in which people can perform and individuals and can co-operate towards attainment of group goals.‘ How the best manager in this world can teach us management? • For example, let us look at the managerial role of a mother and how she uses the managerial ingredients in managing the home. • First, she appraises her household and its needs. • She forecasts the needs of the household for a period of a week or a month or longer. • She takes stock of her resources and any constraints on these resources. • In a large household, she divides the work among other members and coordinates their activities. • She encourages and motivates them to do their best in completing their activities. Even the recorded history shows the application of some current management techniques as far back as 5000 BC. when the ancient Sumerians used written records in assisting governmental operations. The Egyptian pyramids, built as early as 3000 BC., required the organized efforts of over 1,00,000 workers. It would be natural to assume that all functions of modern management, namely, planning, organizing, directing, and controlling played a significant role in the construction of these monuments. Similarly, the early civilization of India bears witness to organized living. Management Can Be Defined In Detail In The Following Categories : • Management as a Process • Management as an Activity • Management as a Discipline • Management as a Group • Management as a Science • Management as an Art • Management as a Profession