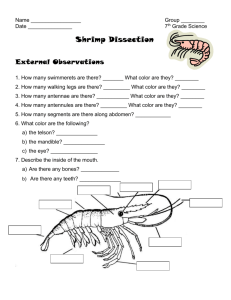
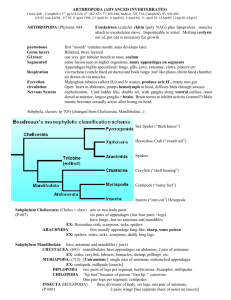
Unit 4C: Phylum Arthropoda Day 1- General Arthropod Traits & Subphylum Crustacea What traits do all Arthropods Share? Name ____________________ 1. Arthropod means “jointed foot” 2. Paired jointed appendages 3. Segmented bodies 4. ____________________________________- body regions have specific functions. a. Head- sensory/feeding (antennae, eyes, mouthparts) b. Thorax- locomotion (walking legs, wings) c. Abdomen- visceral organs 5. Exoskeleton a. Support & protection b. Prevents ______________________________ c. Two layers: i. ____________________- lipoprotein on outside; resists water loss ii. ____________________- chitin on inside; tough, leathery protein 6. Grow by shedding exoskeleton- ___________________ (molting) 7. ______________________ nervous system 8. ______________________ circulatory system 9. Complete digestive system with mouth and anus SUBPHYLUM CRUSTACEA What are some examples of crustaceans? We will focus our studies on crayfish. 1. _____________________________- fused head and chest region. Covered by Body Regions hard carapace. Pointy protrusion at anterior end is called a rostrum. 2. _____________________________- has some swimming appendages and visceral organs. In some becomes muscular tail. Head: 1st _____________________________________________- long; sense, feed, taste 2nd ____________________________________________- short; sense, feed, taste 3rd ____________________________________________- chewing & grinding 4th-6th _________________________________- small, hair-like; food handling & respiration 7th-8th ______________________________________- larger than maxillae; food handling Thorax: Paired Appendages 9th ______________________________- “claws”; food capture and defense 10th-13th ___________________________- walking legs for movement Abdomen: ____________________________- hair-like swimmerets may help with swimming; First 2 pairs at junction of thorax & abdomen are used to determine gender & for sexual reproduction ____________________________- tail-like structure at end of abdomen where anus is located. ____________________________- 2 flipper-like structures on either side of telson; aid in steering & swimming 1. Scavengers & predators- eat other invertebrates, some plants 2. ___________________________________- enlarged part of stomach in cephalothorax; contains tooth-like structures (gastric teeth) for grinding food. Digestion/Feeding 3. ___________________________________- large yellow gland in cephalothorax that secretes digestive enzymes into stomach 4. ___________________________________- embedded in muscular abdomen/tail 5. ________________________ Circulation Respiration Excretion Nervous/Sensory Reproduction Economic/Environmental Importance 1. _________________ circulatory system 2. Have _________________ with short blood vessels 1. _____________________- feathery structures on either side of cephalothorax directly under carapace 2. ______________________- push water over gills while resting. 3. ______________________- push water over gills while moving. 1. ________________________- kidney-like organs located behind antennae. 2. ________________________- ammonia liquid waste released through this pore in front of head. 1. ______________________________- fused trilobed brain in head. 2. ______________________________- runs along belly with small ganglia masses. 3. ______________________________- attached to movable stalks; may see fuzzy images. 4. ________________________- hair-like structures on mouth & antennae; can detect food & pheromones. 1. __________________________ 2. Mating occurs after females molt in fall. 3. Male inseminates female using 2 stiff anterior pleopods. 4. In the spring, as the female passes eggs out of her body, they become fertilized. 5. Eggs attach to the hair-like pleopods on abdomen where they stay until hatching. 1. Part of the ______________________________________ 2. Control animal populations 3. Major source of _____________ for many regions of the world’s human population. 4. ________________________________ (rolly polly)