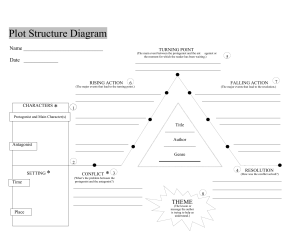
Elements of Drama 4 Elements Setting Place, time, weather, social conditions, mood Theme “Moral of the story” or central message Character Person’s qualities Antagonist Protagonist Plot How the author arranges the events Plot PLOT Click on the image. @Quizlet, hover over each bubble for the definition. Conflict Drives the Plot 1. Internal 2. External Struggle within one’s self. - Struggle with a force outside of one’s self. Character vs. Self - Character vs. Character Character vs. Nature Character vs. Society Setting Setting Place Geographical location the action is taking place Weather Rainy, stormy, sunny… Time = Mood Historical period, time of day, year… Social Conditions Daily life of characters, speech, dress, customs Character Characters & Characterization Protagonist Clear center of the story; all major events are important to this character Antagonist Opposition of the main character. Characteristics - Physical appearance What they say, think, feel, dream, does, does not do What others say about him/her and how others react to him/her How we know about a character Indirect The author explicitly tells the reader what he or she wants us to learn about the character. Direct The author implicitly shows the reader parts of the character that helps them understand the character's personality and the effect they have on other characters. Characters can be… Round Flat Dynamic Static Fully developed; they learn, grow, or deteriorate at the end. “Real” people. Character who goes through change in a positive way; “grows” One-dimensional character who is uncomplicated. Character does not go through a change; stays the same. Theme Theme is the central message, “moral of the story.” A theme is developed through 1. A story’s title 2. Figurative Language a. Symbolism b. Allusion c. Simile d. Metaphor e. Hyperbole f. Understatement g. Irony 7 Most common themes in plays 01 02 03 04 Fate or Destiny Hubris/Pride The protagonist's pride leads to their downfall as they ignore warnings or act recklessly. The protagonist's tragic fate is often predetermined, and they are unable to escape it despite their best efforts. Tragic Hero Flawed The protagonist has a character flaw or weakness that leads to their downfall, such as jealousy, greed, or ambition. The protagonist is often a noble or virtuous character who suffers a tragic fate due to their own actions or circumstances beyond their control. 7 Most common themes in plays 05 06 Irony Elicits strong emotions of pity, fear, and sadness in the audience, leading to a cathartic release of these emotions. 07 Catharsis Where the audience knows something the protagonist does not, adding to the pathos of the story. Moral Lesson Seeks to impart a moral lesson or commentary on the human condition, such as the dangers of unchecked ambition or the consequences of pride. Point of View Playwrights use only… Third Person In a live play, the point of view cannot be other than third person, as there is no real way for the author to make one character's inner thoughts and motivations accessible to the audience. The End