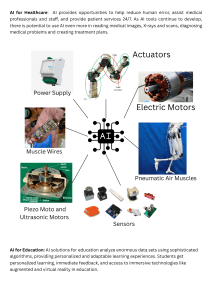
Benefits of AI Disadvantages of AI Automating repetitive tasks: AI can be used to automate repetitive tasks, which can save time and reduce errors. Job loss: As AI is used to automate tasks that were previously done by humans, there is a risk of job loss. Improved decision making: AI can process large amounts of data quickly and identify patterns that humans may miss, leading to better decision making. Dependence on technology: As more tasks are automated by AI, humans may become overly dependent on technology and lose important skills. Increased efficiency and productivity: AI can work around the clock and perform tasks more quickly and accurately than humans, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Bias: AI algorithms can be biased if they are trained on biased data, which can lead to unfair decisions. Personalization: AI can be used to personalize experiences for users, such as recommending Lack of creativity: While AI can be used to products or content based on their interests and generate new ideas and solutions, it is not behaviors. capable of true creativity like humans are. Improved healthcare: AI can be used to analyze medical data and identify patterns that may Privacy concerns: As AI processes large indicate disease or other health issues, leading amounts of data, there are concerns about how to earlier detection and better treatment. that data is used and who has access to it. Improved safety: AI can be used to monitor and detect potential safety hazards in various Security risks: As AI becomes more advanced, industries, such as manufacturing and there is a risk of it being used for malicious transportation. purposes, such as hacking and cyber attacks. It's worth noting that this is not an exhaustive list, and there may be additional benefits and disadvantages of AI depending on the specific context in which it is being used. Ethical issues related to AI: 1. Bias: AI algorithms can be biased if they are trained on biased data, which can lead to unfair decisions. 2. Privacy: As AI processes large amounts of data, there are concerns about how that data is used and who has access to it. 3. Autonomous weapons: There are concerns about the development of autonomous weapons, which could potentially make life-and-death decisions without human input. 4. Job displacement: As AI is used to automate tasks that were previously done by humans, there is a risk of job loss. 5. Accountability: As AI makes more decisions, there is a question of who should be held accountable if something goes wrong. 6. Transparency: It can be difficult to understand how AI makes decisions, which can make it hard to detect and address biases. 7. Responsibility: There is a question of who is responsible if AI causes harm, particularly if the harm is the result of a decision made by an AI system. 8. Equity: There are concerns that AI could widen existing inequalities, such as by reinforcing systemic biases or by favoring certain groups over others. 9. Autonomy: As AI becomes more advanced, there is a question of whether it can truly be considered autonomous and what that means for how it should be treated. 10. Manipulation: There are concerns about the use of AI to manipulate people, such as through the use of deepfakes or targeted advertising. Here are some examples of AI technologies: 1. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a field of AI that focuses on the interaction between humans and computers using natural language. Examples include chatbots and virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. 2. Machine Learning (ML): ML is a type of AI that enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. Examples include fraud detection, recommendation systems, and image recognition. 3. Computer Vision (CV): CV is a field of AI that focuses on enabling machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world around them. Examples include facial recognition, object detection, and autonomous vehicles. 4. Robotics: Robotics is a field that combines AI and engineering to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks autonomously. Examples include drones, self-driving cars, and industrial robots. 5. Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze data and make predictions about future outcomes. Examples include predicting customer behavior and predicting equipment failures in manufacturing. 6. Deep Learning: Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to process large amounts of data and learn complex patterns. Examples include speech recognition, language translation, and image processing. 7. Cognitive Computing: Cognitive computing is a type of AI that uses machine learning algorithms to simulate human thought processes. Examples include IBM Watson, which is used in healthcare and finance. 8. Sentiment Analysis: Sentiment analysis uses natural language processing and machine learning to analyze text and determine the sentiment behind it. Examples include analyzing social media posts and customer reviews. Here are some of the areas where AI could be used: 1. Healthcare: AI can be used for medical image analysis, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and telemedicine. 2. Finance: AI can be used for fraud detection, risk assessment, credit scoring, and trading. 3. Manufacturing: AI can be used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. 4. Retail: AI can be used for personalized recommendations, inventory management, and supply chain optimization. 5. Transportation: AI can be used for autonomous vehicles, traffic management, and logistics optimization. 6. Education: AI can be used for personalized learning, student assessment, and curriculum development. 7. Agriculture: AI can be used for precision farming, crop monitoring, and yield prediction. 8. Energy: AI can be used for predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and demand forecasting. 9. Entertainment: AI can be used for personalized recommendations, content creation, and virtual assistants. 10. Security: AI can be used for surveillance, threat detection, and cybersecurity. Here are some examples of how AI is currently being used in education: 1. Personalized Learning: AI-powered tools can analyze student data and provide personalized recommendations for learning materials, pace, and difficulty level. 2. Intelligent Tutoring Systems: These systems use AI to provide personalized feedback and guidance to students as they learn, based on their individual strengths and weaknesses. 3. Grading and Assessment: AI-powered tools can automate grading and assessment of assignments and exams, saving time for teachers and providing more consistent and objective feedback to students. 4. Adaptive Learning: AI can be used to adapt learning materials and assessments based on student progress, providing a more individualized and efficient learning experience. 5. Language Learning: AI-powered language learning tools can provide personalized feedback on pronunciation and grammar, and can adapt the level of difficulty to the student's proficiency level. 6. Educational Content Creation: AI can be used to generate educational content such as quizzes, summaries, and videos based on the learning objectives and target audience. 7. Predictive Analytics: AI-powered analytics can identify students who are at risk of falling behind or dropping out, allowing teachers and administrators to intervene and provide support. 8. Smart Classrooms: AI can be used to automate routine classroom tasks, such as taking attendance and managing classroom resources, allowing teachers to focus on teaching. Benefits of AI Reduction in Human Error Zero Risks 24 x 7 Availability Digital Assistance New Inventions Unbiased Decisions Perform Repetitive jobs Daily applications AI in Risky situations Ethical issues relating to the use of AI 1. Issues arising from machine learning Privacy and data protection Lack of privacy Misuse of personal data Security problems Reliability Lack of quality data Lack of accuracy of data Problems of integrity Transparency Lack of accountability and liability Lack of transparency Bias and discrimination Lack of accuracy of predictive recommendations Lack of accuracy of non-individual recommendations Safety Harm to physical integrity 2. Living in a digital world Economic issues Disappearance of jobs Concentration of economic power Cost to innovation Justice and fairness Contested ownership of data Lack of access to public services Violation of fundamental human rights of end users Violation of fundamental human rights in supply chain Negative impact on vulnerable groups Unfairness Freedom Lack of access to and freedom of information Loss of human decision-making Loss of freedom and individual autonomy Broader societal issues Unequal power relations Power asymmetries Negative impact on democracy Problems of control and use of data and systems Lack of informed consent Lack of trust Potential for military use Negative impact on health Reduction of human contact Negative impact on environment Uncertainty issues Unintended, unforeseeable adverse impacts Prioritisation of the “wrong” problems Potential for criminal and malicious use