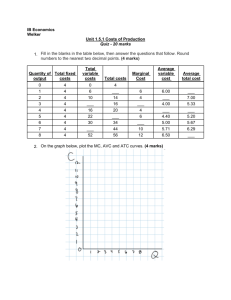
ASSESSMENT 1 – MAJOR ASSIGNMENT 1 – 15% Instructions Due in Week 8 (Friday 22nd March 2024 at 6pm) Total Marks is equal to 200 Marks Total Weight of Assignment 1 is 15% of the final mark and grade Do and answer all questions as instructed. Write and submit your answers only Submission of Assignment 1 will be accepted through the approved online modals (Moodle and Email) and hard copy through the assignment box prior to and on the due date PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (100 Marks) (Select the correct answer for each question. Answer all questions. Each question is worth 2 marks) 1. Suppose you decide to attend summer school and that this is considered a rational choice. When making this choice, A) you must ignore the problem of scarcity. B) you considered the marginal cost and marginal benefit of your choice. C) you have used the ceteris paribus assumption. D) you have made a positive statement. E) you must have considered the social interest. 2. Kevin is re-finishing an antique grandfather clock that he purchased at a flea market for $300. He expects to be able to sell the clock for $450. At the last minute, Kevin discovers that he needs to repair the gears at a cost of $175 to make the clock worth $450 to potential buyers. It turns out that he could also sell the clock now, without completing the additional repairs, for $250. What should Kevin do? A) He should sell the clock now for $250. B) He should keep the clock but not make the repairs since the original $300 is a sunk cost. C) He should complete the additional repairs and sell the clock for $450. D) He should keep the clock after making the repairs since it is not rational to spend a total of $475 on an item that can only be sold for $450. E) Kevin is indifferent between selling the clock as is or selling it after completing the repairs. 3. Which of the following scenarios describes an action that is NOT rational from an economic point of view? A) After drinking one martini (shaken, not stirred), James buys and drinks a second martini even though the marginal benefit of the second martini is lower than the marginal benefit of the first. B) Eric buys a replacement ticket to the basketball game after he realizes that he accidentally left his original ticket at home. C) Emily chooses to attend a social event on Tuesday night instead of studying even though she has an important exam on Wednesday morning. D) US Airways sells a last minute ticket to Don for $50 even though its average cost per passenger is $250. E) None of the above 4. Which of the following statements is correct? A) An increase in productivity moves the economy from inside the production possibilities frontier to the frontier itself. B) An increase in productivity shifts the economy from producing at a point on the production possibilities frontier to a point outside the production possibilities frontier. C) An increase in unemployment shifts the economy further inside its production possibilities frontier. D) An increase in unemployment shifts the economy from a point outside the production possibilities frontier back to the production possibilities frontier. E) A reduction in unemployment shifts the entire production possibilities frontier outward. 5. Gregory is considering attending a concert with a ticket price of $40. He estimates that the cost of driving to the concert and parking there will add an additional $20. In order to attend the concert, Gregory will have to take time off from his part-time job. He estimates that he will lose 5 hours at work, at a wage of $8 per hour. In terms of dollars, Gregory's opportunity cost of attending the concert equals A) $80. B) $100. C) $40. D) $60. E) $20. 6. Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia, and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF3? A) India B) Germany C) Estonia D) France and Germany equally E) France 7. Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia, and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, which country is most likely to expand its PPF to PPF1? A) France and Germany equally B) India C) Estonia D) France E) Germany 8. The figure above shows the production possibilities frontiers for the United Kingdom and France. What is the opportunity cost of one bushel of wheat in France? A) 1/4 of a pound of fish B) 4 pounds of fish C) 1 pound of fish D) 100 pounds of fish E) 2 pounds of fish 9. The figure above shows the production possibilities frontiers for the United Kingdom and France. What is the opportunity cost of one bushel of wheat for the United Kingdom? A) 1/4 of a pound of fish B) 1/2 of a pound of fish C) 1 pound of fish D) 200 pounds of fish E) 2 pounds of fish 10. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium when people's incomes decrease. If pizza is a normal good, then which point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 11. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium when the cheese used to produce pizza falls in price. What point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 12. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium when the wages paid pizza workers increases. What point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 13. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium when some of the pizza firms go out of business. What point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 14. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium when people learn that eating pizza helps prevent heart disease. What point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 15. The above figure shows the market for pizza. The market is in equilibrium. Pizza and tacos are substitutes for consumers. The price of tacos falls. What point represents the most likely new price and quantity? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 16. Suppose the price of a DVD rose from $15 to $17 and the quantity demanded decreased from 1,000 per month to 900 per month. Using the midpoint formula, the ________ percent change in price lead to a ________ percent change in the quantity demanded. A) 12.5; 10.5 B) 13.3; 10.0 C) 11.8; 11.1 D) 8.0; 9.5 E) None of the above answers is correct. 17. If the price of a six-pack of Pepsi falls from $4 to $3 and the quantity purchased increases 80 percent, then demand is A) inelastic. B) elastic. C) unit elastic. D) perfectly inelastic. E) perfectly elastic. 18. Suppose the demand for ring cake sold from one roadside stand in Honiara is perfectly elastic. As a result, a 7 percent increase in the price charged by the owner of this stand leads to A) zero ring cake sold by this stand. B) no change in the quantity demanded at this stand. C) a 7 percent decrease in the quantity demanded at this stand. D) a 7 percent decrease in demand at this stand. E) a virtually infinite increase in the quantity demanded at this stand. The figure above shows the demand curve for Starbucks latte. 19. In the figure above, the demand is elastic in the range of prices between A) $3.50 and $4.50 per cup. B) $2.50 and $3.50 per cup. C) $1.00 and $2.00 per cup. D) $2.00 and $4.00 per cup. E) $1.75 and $2.75 per cup. 20. In the figure above, the demand is unit elastic A) at the point where the price is $3.00 per cup. B) at the point where the price is $2.00 per cup. C) at the point where the price is $4.00 per cup. D) at the point where the price is $2.50 per cup. E) at all points along the demand curve. 21. 10) Katie has $15. She likes M&M candies and Hershey's white chocolate bars. M&M candies are $1.50 a pack and (the large) Hershey bars are $3.00 each. Katie can choose to buy A) 4 Hershey bars and 2 packs of M&Ms. B) 2 Hershey bars and 6 packs of M&Ms. C) 5 Hershey bars and 10 packs of M&Ms. D) Answers A and B are correct. E) Answers A, B, and C are correct. 22. 17) Sarah earns $500 per week selling baskets made out of tree vines. With this money she buys sushi and rose bushes. Each piece of sushi costs $1 and each rose bush costs $10. If Sarah spends $170 per week on sushi, the maximum quantity of rose bushes can she buy each week is ________ bushes. A) 33 B) 330 C) 3 D) 17 E) None of the above answers is correct. The figure above shows three budget lines. 23. Based on the figure above, which of the following would lead the consumer's budget line to shift from BL0 to BL1? A) a rise in the price of water B) a fall in the price of water C) a rise in the price of water and the price of gum D) a decrease in the consumer's budget E) an increase in the consumer's budget 24. Based on the figure above, which of the following would lead the consumer's budget line to shift from BL0 to BL2? A) a rise in the price of water B) a fall in the price of water C) a rise in the price of water and the price of gum D) a decrease in the consumer's budget E) an increase in the consumer's budget 25. Based on the figure above, on which budget line is the relative price of gum the highest? A) budget line BL2 B) budget line BL0 C) budget line BL1 D) The relative price is the same along all three budget lines. E) To answer the question, more information is needed about the consumer's income. 26. Billy has a $20 budget to spend on yogurt and cereal. Yogurt cost $2 each and cereal costs $4 each. Suppose that the quantity of yogurt is on the vertical axis and the quantity of cereal is on the horizontal axis. If the price of yogurt increases, which of the following is TRUE? i. The budget line rotates outward. ii. Yogurt's marginal utility per dollar decreases. iii. The relative price of yogurt increases. A) i and ii B) i and iii C) ii and iii D) i, ii, and iii E) only i 27. Chase has a budget of $14 which he must allocate between steak and cranberry juice. The table gives his marginal utility and the marginal utility per dollar for both of those goods. The price of steak is $10 per serving and the price of cranberry juice is $2 per serving. To maximize his utility, Chase should buy A) 2 servings of steak and 2 servings of cranberry juice. B) 2 servings of steak and 4 servings of cranberry juice. C) 1 serving of steak because this has the highest marginal utility. D) 1 serving of steak and 2 servings of cranberry juice. E) 4 servings of steak and 4 servings of cranberry juice. Quantity of pizza 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total utility from Quantity of Diet Total utility from pizza Pepsi Diet Pepsi 0 0 0 24 1 14 44 2 26 60 3 36 72 4 44 76 5 50 79 6 54 80 7 56 28. Suppose that you consume only pizza and Diet Pepsi. The table above gives your utility from consuming these two goods. What is the marginal utility you get from the fourth slice of pizza? A) 36 B) 18 C) 12 D) 4 E) 72 29. Suppose that you consume only pizza, which costs $4 per slice, and Diet Pepsi, which costs $2 each. The table above gives your utility from consuming these two goods. If your income is $14, which of the following consumption combinations will you choose? A) 3 slices of pizza and 1 Diet Pepsi B) 2 slices of pizza and 3 Diet Pepsis C) 1 slice of pizza and 5 Diet Pepsis D) 0 slices of pizza and 7 Diet Pepsis E) None of the above answers is correct. 30. Suppose that you consume only pizza, which costs $4 per slice, and Diet Pepsi, which costs $2 each. The table above gives your utility from consuming these two goods. If your income is $20, which of the following consumption combinations will you choose? A) 5 slices of pizza and no Diet Pepsi B) 4 slices of pizza and 2 Diet Pepsis C) 3 slices of pizza and 4 Diet Pepsis D) 2 slice of pizza and 6 Diet Pepsis E) None of the above answers is correct. 31. ________ in consumer surplus occurs when the price of a good ________. A) An increase; decreases and consumers can buy more of the good at the lower price B) A decrease; decreases and consumers buy less of the good at the cheaper price C) An increase; decreases and consumer efficiency declines D) A decrease; increases and the paradox of value is no longer valid E) An increase; increases but the relative price does not change 32. Diamonds have ________ consumer surplus because ________. A) a smaller; fewer diamonds are sold at higher prices B) a smaller; there is a lower marginal utility for diamonds C) a large; diamonds are a rare and valuable stone D) zero; diamonds have a high price and provide low total utility E) zero; diamonds are not necessary for life 33. The table above shows the total product schedule for Rick's Lawn Service, a yard care company. The total product schedule shows A) increasing marginal returns when the 6th worker is hired. B) decreasing marginal returns when the 1st worker is hired. C) first increasing and then decreasing marginal returns. D) output first increases then increases. E) only decreasing marginal returns. 34. The table above shows the total product schedule for Rick's Lawn Service, a yard care company. Increasing marginal returns A) end when the fourth worker is hired. B) occur at all levels of employment. C) occur as long as output increases. D) end when the second worker is hired. E) never occur. 35. The table above shows the total product schedule for Rick's Lawn Service, a yard care company. Decreasing marginal returns start to occur after the ________ worker is hired. A) first B) fourth C) fifth D) sixth E) third 36. The table above shows the total product schedule for Rick's Lawn Service, a yard care company. When the 4th worker is hired, the ________ product of labor equals ________ lawns mowed. A) average; 60 B) average; 3.75 C) marginal; 3.75 D) marginal; 0 E) marginal; 15 37. The table above shows the total product schedule for Rick's Lawn Service, a yard care company. When the ________ worker is hired, the average product of labor ________ the marginal product of labor. A) 4th; exceeds B) 5th; exceeds C) 6th; exceeds D) 7th; is less than E) 7th; equals 38. The figure shows the cost curves for Phil's Phone Repair, a cell phone repair firm. When output is ________ repaired phones, average total cost is ________. A) below 12; increasing B) more than 12; increasing C) between 10 and 12; less than marginal cost D) greater than 5; constant E) less than 5; increasing 39. The figure shows the cost curves for Phil's Phone Repair, a cell phone repair firm. The figure shows marginal cost ________ which explains why ________. A) is decreasing up until 5 units; average total cost decreases B) is less than average total cost up until 12 units; average total cost decreases C) is greater than average total cost; average variable cost decreases D) is greater than average total cost when more than 12 phones are repaired; average total cost increases E) both B and D are correct 40. The figure shows the cost curves for Phil's Phone Repair, a cell phone repair firm. If Phil increases his workers' wages, ________ curve(s) will shift ________. A) the MC, ATC and AVC; upward B) only the MC; upward C) only the AVC; upward D) the AVC and ATC; downward as production falls E) the MC, AVC and ATC; downward as production falls 41. The figure shows the cost curves for Phil's Phone Repair, a cell phone repair firm. Using this information, we know that the AVERAGE PRODUCT of repairing phones reaches A) a minimum when 10 phones are repaired each hour. B) equals the average of cost of repairing phones. C) a maximum when 10 phones are repaired each hour. D) a minimum when between 5 and 10 phones are repaired. E) a maximum when more that 12 phones are repaired. 42. The graph shows long run costs for a firm. The firm experiences economies of scale A) up until 1,000 units are produced. B) once production exceeds 9,000 units. C) once production exceeds 5,000 units. D) only after 1,000 units are produced. E) when average costs are minimized at 5,000 units. 43. The graph shows long run costs for a firm. If the firm produces ________ units, it will experience ________. A) less than 1,000; diseconomies of scale; average costs decrease B) 5,000; diseconomies of scale because average variable costs decrease C) more than 9,000; diseconomies of scale because managing larger firms results in higher costs D) more than 9,000; economies of scale because fixed costs are spread over large quantities E) less than 9,000; a diminishing marginal product of labor The above figure shows some a firm's cost curves and its marginal revenue curve. 44. Based on the figure above, what is the price of a can? A) $0 B) $3.00 per can C) $5.15 per can D) None of the above prices is correct. E) More information is needed to determine the price of a can. 45. Based on the figure above, if the firm produces 7 cans per day, the firm ________ maximizing its profit and is ________. A) is; incurring an economic loss B) is; making zero economic profit C) is; making an economic profit D) is not; incurring an economic loss E) is not; making zero economic profit 46. Suppose the price of a can was $5.14. In this case, to maximize its profit the firm illustrated in the figure above would A) increase its production and would make an economic profit. B) not change its production and would make zero economic profit. C) not change its production and would make an economic profit. D) increase its production and would incur an economic loss. E) not change its production and would incur an economic loss. 47. The price for the shutdown point is A) $5.14. B) between $3.01 and $5.13. C) $3.00. D) between $0 and $2.99. E) greater than $5.15. 48. The firm in the figure above has a total cost equal to A) $5.14 × 7. B) $3.00 × 7. C) ($5.14 - $3.00) × 7. D) ($3.00 - $5.14) × 7. E) None of the above answers is correct because more information is needed. 49. The firm in the figure above has a total revenue equal to A) $5.14 × 7. B) $3.00 × 7. C) ($5.14 - $3.00) × 7. D) ($3.00 - $5.14) × 7. E) None of the above answers is correct because more information is needed. 50. The firm in the figure above is ________ that is equal to ________. A) making an economic profit; $5.14 × 7 B) making an economic profit; $3.00 × 7 C) incurring an economic loss; $5.14 × 7 D) incurring an economic loss; ($5.14 - $3.00) × 7 E) making an economic profit; ($5.14 - $3.00) × 7 PART B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (100 Marks) 1. The figure above shows Prakash's and Gail's production possibilities frontiers for writing books and magazine articles. (8 marks) a. What is Prakash's opportunity cost of a book? What is Gail's opportunity cost? Who has the comparative advantage in writing books? (3 marks) b. Who has the comparative advantage in writing magazine articles? (3 marks) c. According to their comparative advantages, who should write books and who should write magazine articles? (2 marks 2. The above table gives the demand and supply schedules for cat food. (8 marks) a. If the price is $3.00 per pound of cat food, will there be a shortage, a surplus, or is this price the equilibrium price? If there is a shortage, how much is the shortage? If there is a surplus, how much is the surplus? (2 marks) b. If the price is $1.00 per pound of cat food, will there be a shortage, a surplus, or is this price the equilibrium price? If there is a shortage, how much is the shortage? If there is a surplus, how much is the surplus? (2 marks) c. The above table gives the demand and supply schedules for cat food. What is the equilibrium price and quantity? (2 marks) d. The above table gives the demand and supply schedules for cat food. If the supply increases by 20 tons at every price, what is the new equilibrium price and quantity? (2 marks) 3. The table above gives the demand schedule for museum visits. (10 marks) a. You, as the resident economist, have been given the task of maximizing the museum's total revenue. What admission price should you charge? (2 marks) b. What is the elasticity of demand at the midpoint between $6 and $4? (4 marks) c. Moving along the demand schedule from $10 to $8 to $6 and ultimately to $4, how does the price elasticity of demand change in size? (4 marks) 4. Recently the governor of Vermont proposed that cigarette taxes in Vermont should be increased substantially, from 44 cents a pack to 66 cents a pack. He estimates that Vermont can raise $20 million in revenue from this tax hike. He also pointed out that the neighboring state of New Hampshire was considering an increase in cigarette taxes. (6 marks) a. How can it be that an increase in cigarette taxes will increase tax revenue, because, after all, a higher tax will increase cigarette prices and thereby decrease the quantity demanded? (3 marks) b. If New Hampshire chooses not to increase cigarette taxes, is it likely that Vermont can still raise $20 million in tax revenue? Why or why not? Explain (3 marks) 5. Professor Rush decided to quit teaching economics and opens a shoe store out at the mall. He gave up an annual income of $50,000 to open the store. A year after opening the shoe store, the total revenue for the year was $200,000. Rush's expenses were $30,000 for labor, rent was $18,000, and utilities were $1,200. He also had to purchase new shoes from manufacturers, at a cost of $60,000, which was financed by cashing in his savings of $60,000 that had been in a bank earning 8 percent per year. The normal profit from operating a shoe store in the mall is $20,000. Determine Professor Rush's explicit costs, implicit costs, and economic profit. (10 marks) 6. Ajax Manufacturing has a fixed scale of plant with the levels of total product given in the table below for different levels of labor. Calculating the average product and marginal product for each level of total product. (10 marks) 7. The table below has the total product schedule for an imaginary good called a widget. Each unit of labor costs $25 and the total cost of capital is $100. (20 marks) a. Use this information to complete the table. In the table, TFC is the total fixed cost, TVC is the total variable cost, TC is the total cost, AFC is the average fixed cost, AVC is the average variable cost, ATC is the average total cost, and MC is the marginal cost. (10 marks) b. Suppose that labor becomes twice as expensive (so that one unit of labor now costs $50) but nothing else changes. Complete the above table with the new cost schedules. If you plotted the cost curves, how would the increased wage rate affect the cost curves? (10 marks) 8. Jones Production started business with a small scale plant. Fortunately for Smith, the owner of Jones Production, the business grew rapidly. The table below gives the total costs and the associated output for each year. (8 marks) a. Complete the table by finding the average cost for each scale. (3 marks) b. Over what range of total product (output) did Jones Production experience economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale? (5 marks) 9. The table below shows the total cost schedule for a perfectly competitive firm. The market price is $250 per unit. Complete the table. (10 marks) 10. Acme is a perfectly competitive firm. It has the cost schedules given in the table below and has a fixed cost of $12.00. The price of Acme's product is $14.20. What is Acme's most profitable amount of output? What is Acme's total economic profit or loss? (10 marks) The End