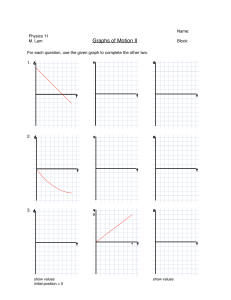
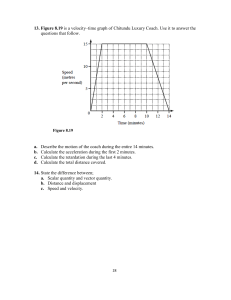
MOTION Objectives At the end of the topic, the students can able to perform the following : a.) Explain clearly the concept of motion and its effect on the body; b.) Differentiate independently speed and velocity, acceleration in a given motion; c.) Demonstrate confidently in selecting appropriate motion formula for a given situation. Overview Motion is a continuous change of position with respect to a specific frame of reference. Specific frame of reference is the fixed position relative to the object moving to justify motion. To understand how object moves, we must describe motion in terms of time, displacement, speed and velocity and this is called Kinematics. In other words, the study of motion gives everyone a thorough description of how an object will move. This can be seen in time motion study, production output, speed limit as an example. Describing motion To understand motion, first we need to know the different terms and units associated with motion. a) Force is a push or pull that cause an object to change its velocity. b) Distance and displacement ( S ) Distance – is a scalar quantity which refers to the total length travelled. Displacement – is a vector quantity which is the change in position. The unit of distance are the same as the displacement: m , km, mi c) Speed and Velocity ( V ) Velocity is a vector quantity that specifies how fast (magnitude) and in what direction an object moves. speed specifies only how fast (magnitude) the object moves – not its direction. The unit velocity are the same as the speed: m/s, km/h, mi/h d) Average Speed, (V) is defined as the distance traveled divided by the time required to travel the distance. Formula : V = Distance travelled /elapsed time V = displacement/elapsed time V = S / t V = S / t e) Instantaneous velocity – is the reading on speedometer. It is the speed of the vehicle that very moment. f) Acceleration ( a ) of the body is the rate at which its velocity is changing. Unit: m/s2 , ft/s2 Example. From point R, a car drives 8 km north & then turns westward and reach the destination at pt. C after driving 2.5 km. It took 0.25 hours to reach destination. Find a) speed b) velocity 2.5km Solution. N C 8km W R From the illustration above; the distance is = 8 km + 2.5 km = 10.5 km. displacement2 = 82 + 2.52 = 8.38 km For the speed and velocity’ a. speed = distance/time = 10.5 km / o.25 hrs. = 42 km/hr. b. Velocity = displacement / time = 8.38 km / 0.25 hrs. = 33.52 km/hr. Rectilinear Motion motion of the body in a straight line like student walking, car in motion. Types of Rectilinear motion 1. Uniform Motion o body covers equal distance at equal interval of time. o Velocity is constant and acceleration is zero. Formula : V=S/T 2. Uniform accelerated motion Velocity changes at co0nstant rate. Acceleration is constant. Basic formulas: 1. Vf = Vo + at 2. Vf 2 = Vo 2 + 2aS 3. S = Vot + ½ at2 Where : Vo – initial velocity, m/s Vf = final velocity, m/s S – distance/ displacement,m t = time a = acceleration , m/s2 and the Note : a. Body starts from rest : Vo = 0 b. Body brought to rest : Vf = 0 acceleration = + a deceleration = – a Example 1.. Find the acceleration of a car that goes from 20 to 30 m/s in 1.2 s . At the same time determine how long will it take the car to go from 30 to 36 m/s. Solution. Given: Vo = 20 m/s Vf = 30 m/s t = 1.5 sec a) Find the acceleration, from formula # 1 a = Vf – Vo = t 30 m/s – 20 m/s 1.5 s a = 8.33 m/s2 b) Find the time, from formula # 1 Solution : Given : Vo = 30 m/s Vf = 36 sm/s t = Vf – Vo a t = 36 m/s – 30 m/s 8.33m/s2 t = 0.72 s Example 2. A car starts at rest and acquires a velocity of 70 m/s in 20 sec. Find : a) its acceleration b ) the distance travel in 8 sec. Solution. Given: Vo = O Vf = 70 m/s t = 20 s a ) Find acceleration, a = Vff – Vo t a= (70 - 0) m/s 20 s a = 3.5 m/s2 b) Find the distance travelled in 8 seconds at2 2 = 0 + 3.5 m/s2 ( 8 s )2 2 S = 112 m S = Vot + Free Falls Motion A freely falling body is a body moving under the influence of gravity alone. It is the most common type of uniformly accelerated motion. A body dropped from a height starts at zero initial velocity. Since it is acted upon by gravity, its velocity increases by “g”. A body thrown up into the air is given an initial velocity. It then travels against the gravity, so its speed slows down until it reaches a maximum height where its velocity is zero. It will then goes down, increasing its velocity at the rate of “g”. Gravitational acceleration is positive for downward motion, while it is negative for an upward motion. Formula : 1. Vf = Vo + gt 2. Vf 2 = Vo2 + 2gS 3. S = Vot + ½ gt2 Where : Vo = initial velocity, m/s ; Vf = final velocity, m/s S =distance/ displacement, m ; t = time g = gravitational acceleration; = 9.8 m/s , 980 cm/s , 32 ft/s a = acceleration , m/s2 Note : a. Body starts from rest : Vo = 0 b. Body brought to rest : Vf = 0 c. Acceleration = + a g( downward) = + g( upward ) = ― Deceleration = ― a Example 1. A stone was dropped from the bridge strikes the water 2.5 seconds later. a) What is its final velocity in meters per second? b) How high is the bridge? Solution. a) Find the final velocity using formula # 1 given that initial velocity is zero ( rest ) V = gt V = 9.8 m/s2 x 2.5 s V = 24.5 m/s b) Find the height of the bridge, using formula # 3 and initial velocity is zero ( rest ) h = gt2 2 h = 9.8 m/s2 ( 2.5s )2 h = 30.6 m Example 2. An arrow was shot vertically upward from the ground. It fell down 5 seconds later. Find its a) initial velocity b) maximum height reach. maximum height Solution. Given: Vf = 0; T = 5 sec. a) Find its initial velocity using formula # 1 and – g is negative ( upward ) Vo = Vf – gt Vo = 0 – ( – 9.8 m/s2) (2.5s) Vo = 24.5 m/s b) Find its maximum height, using formula # 3 and initial velocity is zero ( rest ) S = Vot + gt2 2 S = 24.5 m/s (2.5s) + ( – 9.8 m/s2 )(2.5s)2 2 S = 61.25 meters - 30.65 meters S = 30.60 meters Name ________________________________________ Prog/yr/sec ___________________________________ Score________________ Date:________________ Activity No.3.1 Rectilinear Motion 1. An air conditioned bus travels 65 Km from monument circle to Pampanga in 1.25 hrs. (a.) What is the average speed? _____________________ (b.) How far will it go in 3 hours at this average speed? ____________________ (c.) How long will it take to reach Baguio city which is 282 km at this average speed?_________________ 2. A passenger jeep is traveling at 40 m / s when the breaks are applied. It comes to a stop after 10 seconds Find a) acceleration __________________ b) distance travel after the breaks are applied. _________________ 3. A car has an acceleration of 8 m/s2. a) How much time is needed for it to reach a velocity of 24 m/s if it starts from rest? _______ b ) How far does it go during this period? __________ 4. While moving at 40 m/s , an object accelerates uniformly by 6 m/s 2 in 9 seconds. a) What is the velocity after this time interval ? ________ b) How far does it go during this period ? ______ 5. A moving car decelerates uniformly by 8 m/s2 and comes to stop after 6 seconds. What is the distance travelled during deceleration ? _____________ 6. The train engineer of the new PNR train applied the brake while moving at 45 m/s. It produce a breaking acceleration of 1.25 m/s2 .How much distance would be needed to fully stop the train. Name ________________________________________ Prog/yr/sec ___________________________________ Score________________ Date:________________ Activity No.3.2 Free Falling Body 1. A ball is dropped from a window 50 m above the ground. a) How long does it take the ball to reach the ground? b) What is its final velocity? 2. A pebble was dropped from the window of a building, 80 meters above the ground. a) How many seconds will it take the pebble to reach the ground? b) How fast is it after 2.0 seconds? c) When will its velocity be 25 m/s? 3. A stone is tossed upward at the moment a ball is dropped from a height of 25 meters. The stone’s initial velocity is 25 m/s. At what height will the two meet? In how many seconds. 4. A ball is thrown downward with an initial velocity of 20 ft/s. a) How fast is it moving 2s later? b) How far does it fall in these time ?