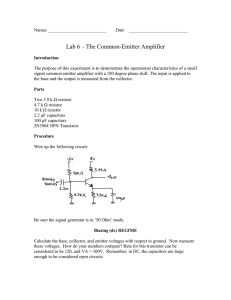
3/1/2024 E-Leaning 2.1.2. Common Source (CS) amplifier EX1: Consider the common-source (CS) amplifier in the figure besides, where RI = 1.00 K, R1 = 180.00 K, R2 = 82.00 K, RS = 33.00 K, R3 = 68.00 K, RD = 22.00 K, VSS = 10 V. MOSFET có Kp = 0.3 mA/V2, Vtp = 1 V, T = 0.5x109 rad/s, Cgd = 5 pF. a/ Determine the Q-point of this circuit. b/ Draw the small-signal highfrequency equivalent circuits for this amplifier. c/ Find the transfer function Av(s) = vo/vI at high frequency and plot Bode 19/11/2015 402060 – Chapter 2. The high-Frequency Response in Transistor Amplifiers 38 E-Leaning 2.1.3. Common Emitter (CE) amplifier EX2: Transistor operates at high frequency, given = 100, r = 1000Ω, C = 5pF, ωT = 109 rad/s. a/ Draw the high-frequency small-signal equivalent circuit. b/ Find the voltage transfer function at high frequency c/ Plot Bode for low (fL) and high (fH) cut-off frequency for circuit. 19/11/2015 VCC Rc 1k Ri Cb →∞ Cc Vout 10µF Q RL 1k 1k Vi 0 R2 100k 10µF Re 0 Ce 1k VBB 0 0 402060 – Chapter 2. The high-Frequency Response in Transistor Amplifiers 39 1 3/1/2024 E-Learning 2.1.3. Common Emitter (CE) amplifier EX3: Consider the figure besides, where RI = 1.00 K, RB = 68 K, RE = 47.00 K, R3 = 33.00 K, VCC = 12 V, VEE = 12 V. BJT has = 75, T = 0.5x109 rad/s, C = 25 pF. a/ Determine the Q-point of this circuit. b/ Draw the small-signal equivalent circuit at high frequency. c/ Determine the voltage transfer function Gv(s) = vo/vI at high frequency. 19/11/2015 402060 – Chapter 2. The high-Frequency Response in Transistor Amplifiers 40 2