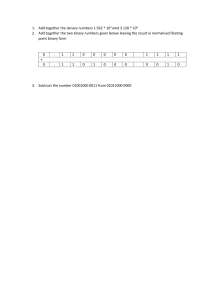
ICT - Unit 5: Binary BY: Phuong Nghi 7b2 Table of Contents Key Vocab Binary Conversion Text into Binary Images into Binary Binary Addition Encryption and Decryption Sound into Binary Key vocab Binary code: a system by which numbers, letters, and other information are represented using only two numbers which are 1 (On) and 0 (Off) because the computer is powered by electricity which can only be off or on. Bit: the smallest unit of data that a computer can process and store (8 bits= byte) Encoding and Decoding: translation (converting) 1. Encoding: letters => binary 2. Decoding: binary => letters Key vocab Overflow: when the data type used to store data was not large enough to hold the data. overflow Pixels: the smallest unit of a digital image or graphic that can be displayed. Binary Conversion Binary: 2 numbers (1 and 0) Denary: decimals 1. Draw the binary conversion table, always write 1 on the right 2. 15 as an example - start from 128 then keep going to the left to see if any number that 15 can subtract without making a negative 3. As we can see that 15 can minus 8 which is 7 as a leftover then 7 minus 4 which gives 3, then 3 continue to minus 2 will give 1 and 1 minus 1 is 0. Binary Conversion Binary: 2 numbers (1 and 0) Denary: decimals 4. If the number can minus the bits then we put a 1 under the number, if not then a 0. 5. So the binary code for 15 is 00001111 or you can simplify it into 1111 (remove the Infront 0s) 6. To check if is it correct then we put the binary code into the conversion table. Add all numbers that has a 1 under it will give you the answer. In this case, 8+4+2+1=15! 7. To convert from binary to denary you just need to put the binary code into a conversion table and do the same as I mentioned Binary Addition 4 important rules: 1. 0+1=1 2. 0+0=0 3. 1+1=0 overflow 1 4. 1+1+1=1 overflow 1 Always start to calculate from the right to the left Remember that like in decimal addition, the last carry just makes the number bigger and is added on to the left of the number. Encryption and Decryption Encryption and Decryption: security (Algorithm + key) Encryption: normal => secure Decryption: secure => normal The algorithm is the method that you use to hide your data. The key is the code that you use in the algorithm to keep your message secret. Example Algorithm: Step 1: Copy the encrypted message into the first row. Step 2: Copy the key into the second row, and keep repeating it until the end. Step 3: For each bit in the third row, if the two bits above it are the same (both white or both black), color it black. Otherwise, leave it white. Text => Binary We use ASCII or Unicode Example: Letter T - 01110100 1. Add those number with a 1 under: 64+32+16+4= 116 2. Find 116 on the ASCII table to check the answer Image => Binary Pixels RGB - Red, Green, Blue (255,255,255) => Why 255? Each pixel in an Red+Green+Blue = White Because image is made up of 1+2+4+8+16+32+64+128 binary numbers =255 (Maximum color) Waves! The higher the bitrate the more data there is in each frame => the better the quality of sound Sound => Binary