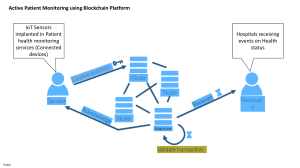
Summary:- Blockchain came into existence in 2008 with the whitepaper published by Satoshi Nakamoto. Even though Satoshi was his pseudonym, no one knows who he really was or where he came from. Since then, the world has gone from being associated with Bitcoin to being a disruptive force in various industries. In this summary, we will look at how blockchain came into existence, its journey to mainstream adoption, its advantages and disadvantages, a speculative view of its future, thoughts on its broader implications, and finally, a deep understanding of its importance in our digital age. Origins of Blockchain:- The origins of blockchain can be traced back to the concept of decentralisation. The very word “decentralization” was a ground-shaking concept in itself. It shattered the centuries-old superstitions about money and the idea of money. Decentralization took the power away from the government and the central banks and put it back into the hands of the people, just as it did before the Federal Reserve Act of 1929. Decentralization was described as a trustless system by Satoshi Nakamoto in his seminal whitepaper, The Making of a Secure, Transparent, and Unchangeable Ledger—the fundamental building blocks of the blockchain’s structure. Nakamoto’s design addressed the weaknesses of centralized systems by providing a novel way to establish trust within a distributed network. Journey to Mainstream Adoption:- Blockchain's journey from a cryptographic curiosity to a mainstream phenomenon has been characterized by a rough and steep path; it did not receive widespread acceptance the day it was released; instead, it was initially regarded as a toy played by internet geeks with no material value in the real world. There are examples of people selling Bitcoins for pennies, believing they are worthless and not worth the effort. In 2011, one man sold 11000 Bitcoins for two pizzas, a phenomenon that is still referred to as the world's most expensive pizza ever. At first, it was limited to the cryptocurrency space, but as more industries realized how revolutionary the technology could be, the adoption of it grew.Financial institutions embrace blockchain for secure and quick transactions, supply chains use it for improved traceability, and governments investigate its potential for ensuring data integrity in a variety of sectors. The most significant event that triggered the shift toward mainstream adoption was the emphasis on blockchain's versatility, which means that it was initially poorly understood by the mainstream, but with the passage of time, more and more people, particularly financial institutions, began to accumulate knowledge, resulting in mass adoption by the general public, resulting in a flood of cryptocurrencies, positioning it as a catalyst for innovation and efficiency in diverse domains. Pros of Blockchain:- Blockchain provides numerous and significant benefits. The establishment of a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger that is more secure than ever in internet history is at the top of the list. Think of an instance a where a hacker needs to compromise a single computer. That which might be a simple task, but if he had to compromise ten million computers, that be an enormous task that take an eternity to complete. This is exactly what happens with blockchain technology; it adds layers to your network in a way that makes it nearly impossible for the entire architecture to be compromised, reducing the risks associated with fraud. One of the most important aspects of our daily lives is transparency. It is very difficult to bring transparency into our daily lives, which is why the issuance of money has always been a matter of nation/state because individuals can't be trusted in their own vicinity, so there's always a gap of trust between individuals, but when blockchain technologycame into being, it added a leyer of transparency between individuals because every transaction was being recorded by every individual in the system, making it impossible to fringe the data, a corollary of the blockchain technology Smart contract integration automates and streamlines processes, reducing reliance on intermediaries and, as a result, operational costs. The immutability of blockchain ensures the permanence of recorded transactions, bolstering the overall system's integrity. Because of these built-in advantages, blockchain is seen as a game-changer with broad ramifications for sectors looking to improve operational security, efficiency, and trust. Cons of Blockchain:- Despite its numerous positive outcomes, blockchain continues to face numerous challenges that impede its widespread adoption. Even now, scalability and public understanding are still major concerns because certain networks cannot manage the infinite amount of transactions, which could result in bottlenecks and system failures. The huge system required to mine is another major reason why adoption has not spread widely among people: energy consumption. According to current estimates, mining just Bitcoin requires 150 tetrawatts of electricity annually, which is more than Argentina's entire electricity consumption for a country of 45 million people. raises concerns about sustainability and the environment, especially in proof-of-work-based blockchains like Bitcoin. sparking debates about the ecological impact of blockchain technology. Concerns regarding blockchain's incorporation into conventional systems are also exacerbated by its linkage to illegal activity and the regulatory uncertainties surrounding its application. For blockchain technology to continue developing and being accepted, these obstacles must be overcome. Future of Blockchain:- The trajectory of blockchain's future is shaped by ongoing efforts to address its limitations and capitalize on its strengths. Although there is some turbulence due to ongoing tensions between crypto exchanges and the SEC, Sam Altman's famous FTX crash also sent shockwaves around the world, and the US is more hesitant to use Blockchain technology in a controlled manner. With scalability and energy efficiency emerging as key development areas, blockchain is set to see increased adoption across a range of industries. A more connected and effective digital environment could be achieved through the idea of interoperability, which enables various blockchains to interact with one another without any problems. The evolution of consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake, offers potential solutions to energy concerns while also increasing the appeal of blockchain. Furthermore, the emergence of new applications and use cases, ranging from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), demonstrates the dynamic nature of blockchain technology, which is poised to reshape industries and digital interactions. Implications of Blockchain:- Blockchain's implications extend beyond its immediate applications, casting a transformative shadow across industries and societal structures. The potential disruption of traditional business models, particularly those that rely on intermediaries, causes a rethinking of established norms. Blockchain promises to revolutionize the financial, real estate, and legal services sectors by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for middlemen. Governments must strike a balance between the need for innovation and security and accountability concerns, as well as modify regulatory frameworks to account for the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. The way that technology progresses and laws are implemented will determine how widely blockchain technology is adopted and incorporated into existing systems. Conclusion:- Finally, the evolution of blockchain from its conception in Satoshi Nakamoto's whitepaper to its current status as a disruptive technology demonstrates its transformative potential. Blockchain continues to redefine trust, transparency, and efficiency in digital transactions even as it faces challenges such as scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory uncertainty. Blockchain has a bright future, provided these issues are resolved and regulatory environments are managed. Blockchain technology will have a significant impact on a variety of industries as it develops, changing business models, upending conventional wisdom, and changing what trust is in an increasingly digitalized world. The journey that blockchain underwent from its inception to widespread adoption is evidence of its adaptability and resilience, solidifying its status as a cornerstone of 21st-century technological innovation.